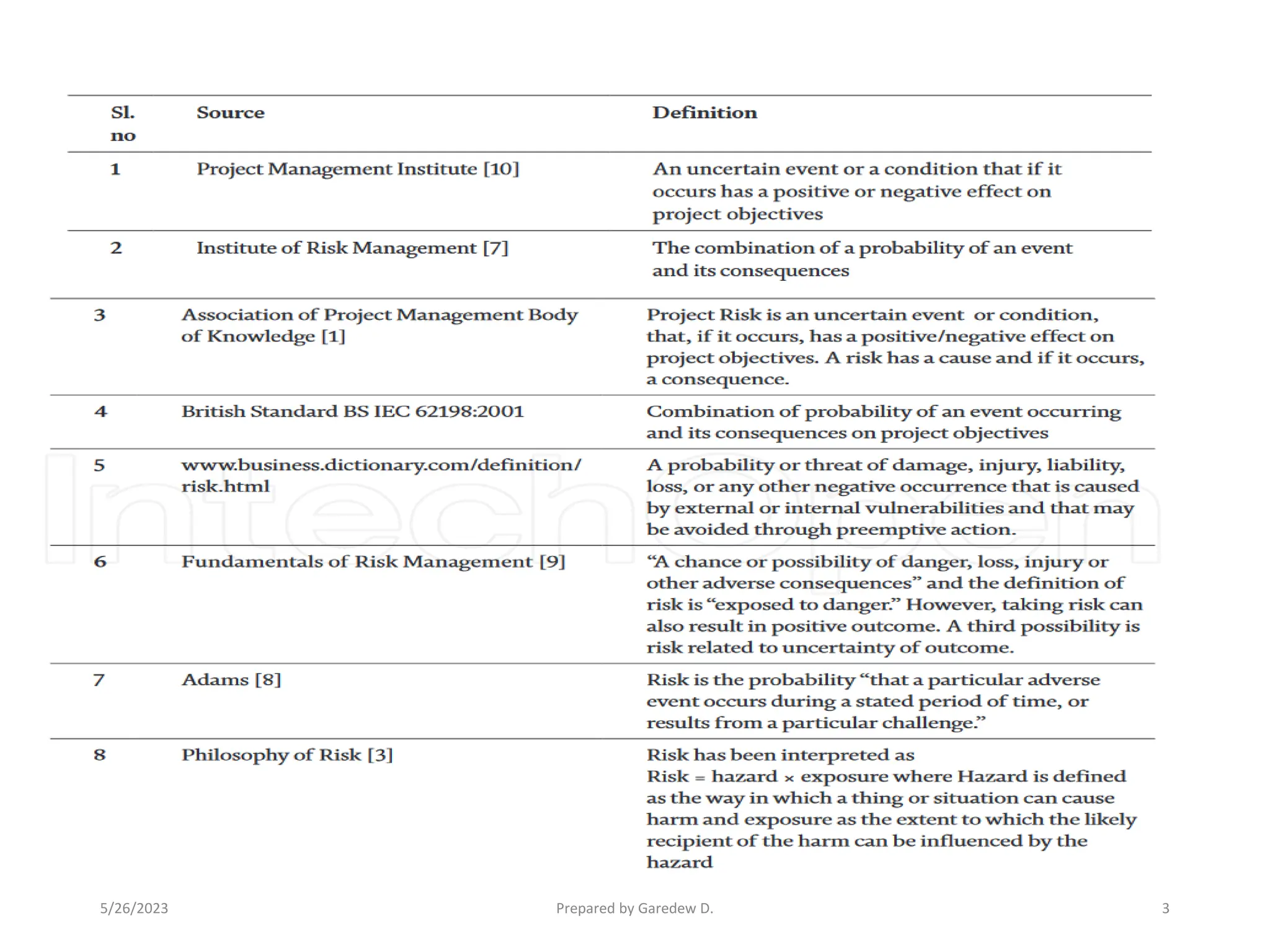
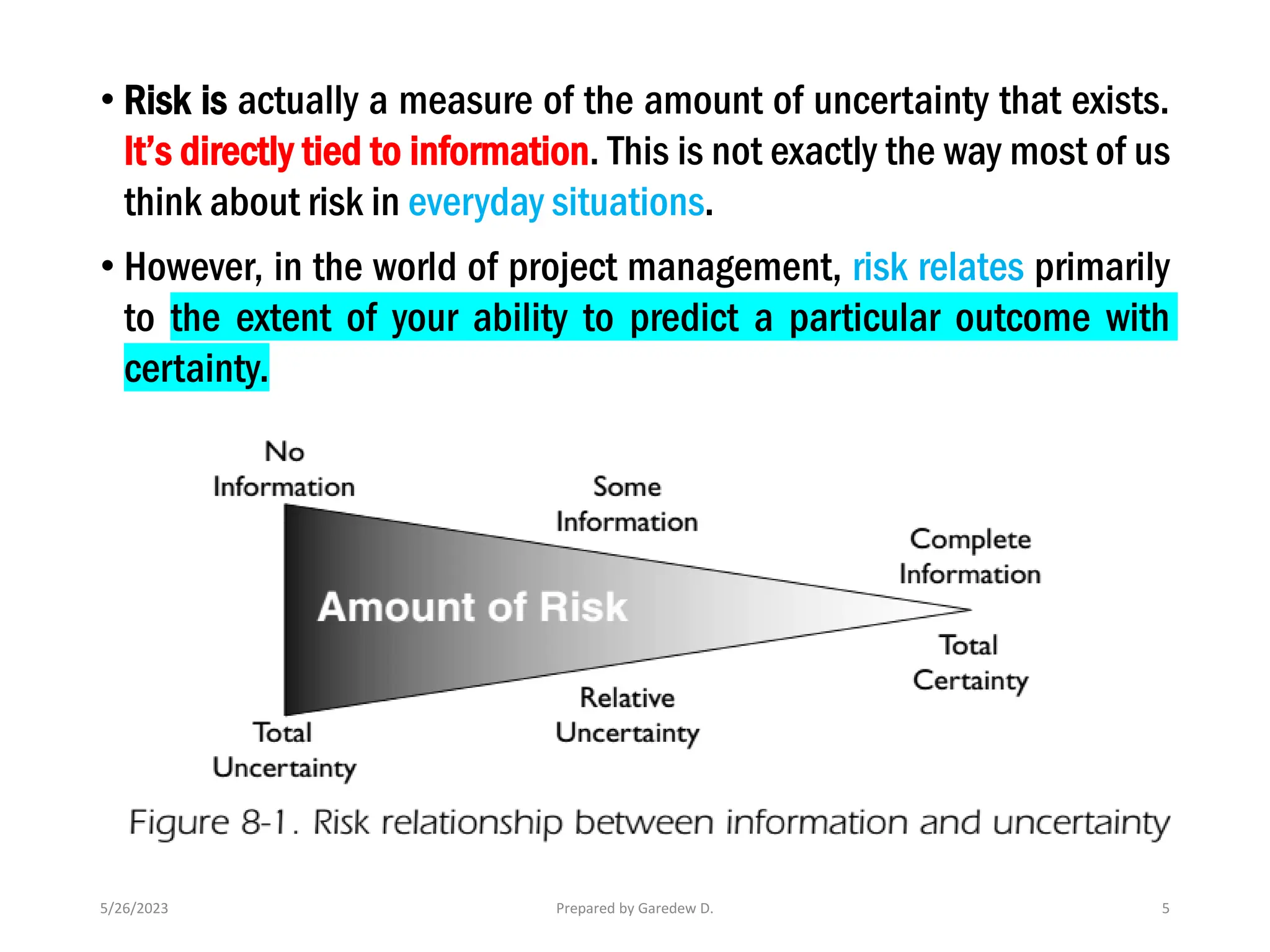
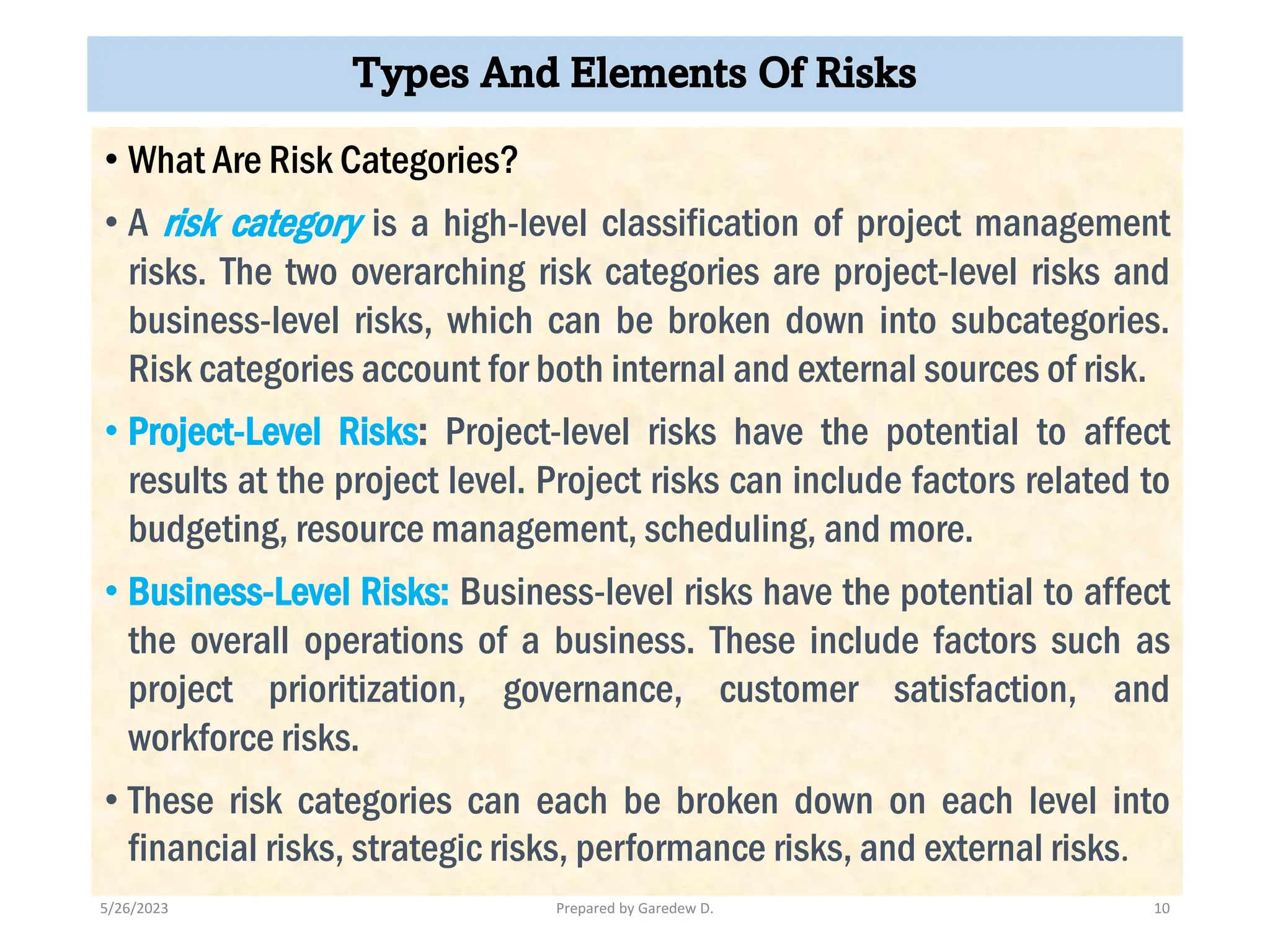
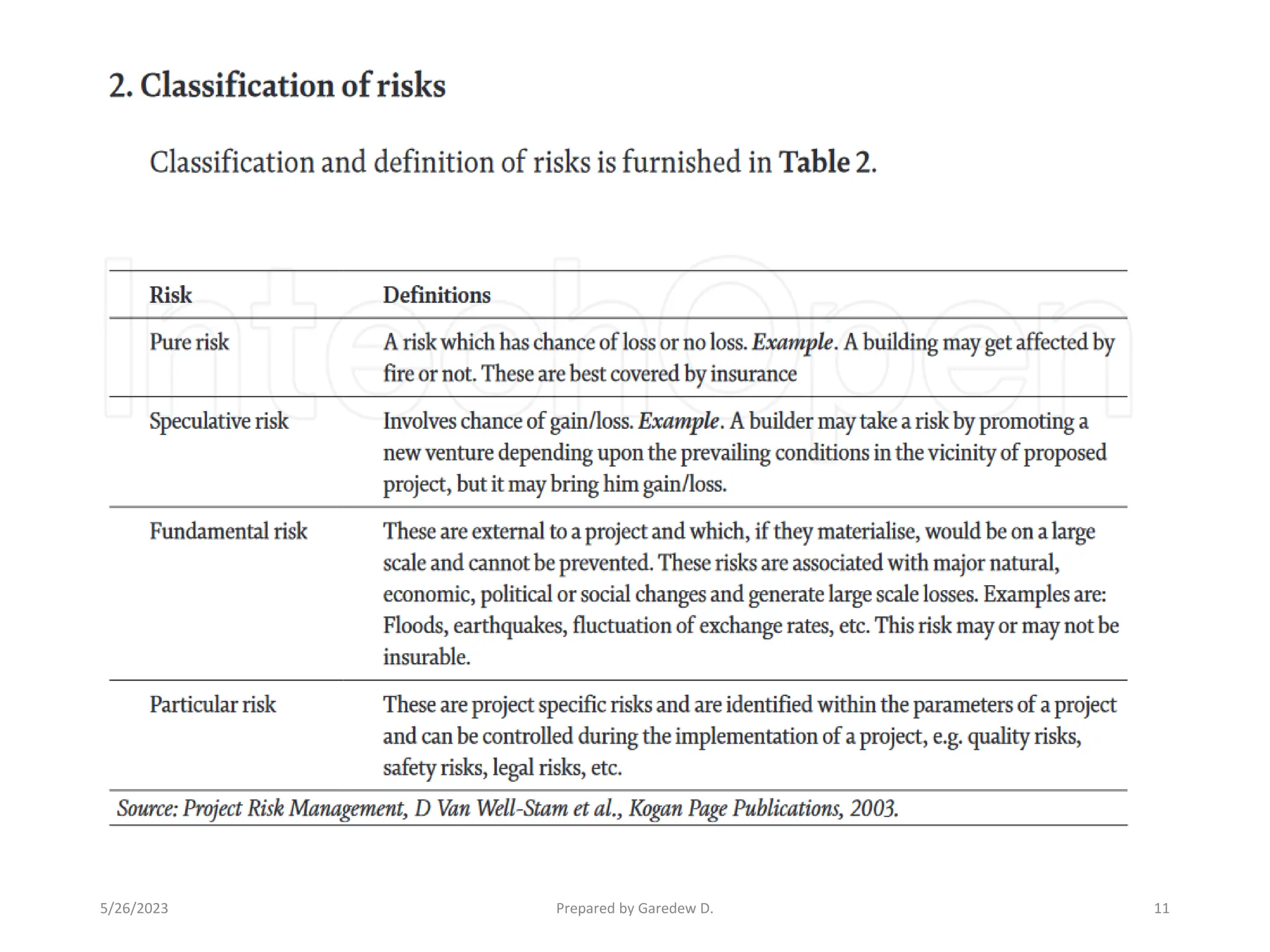
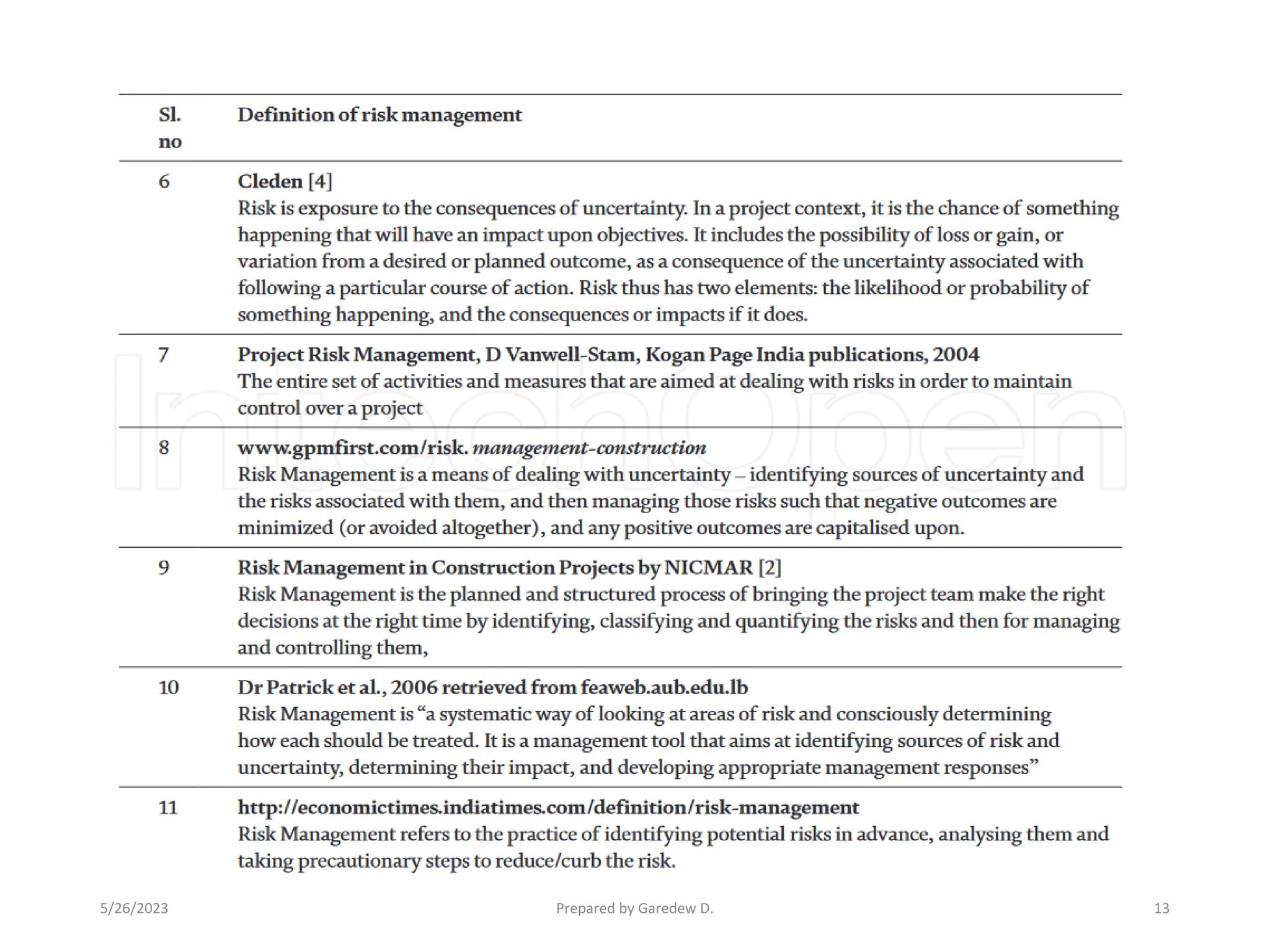
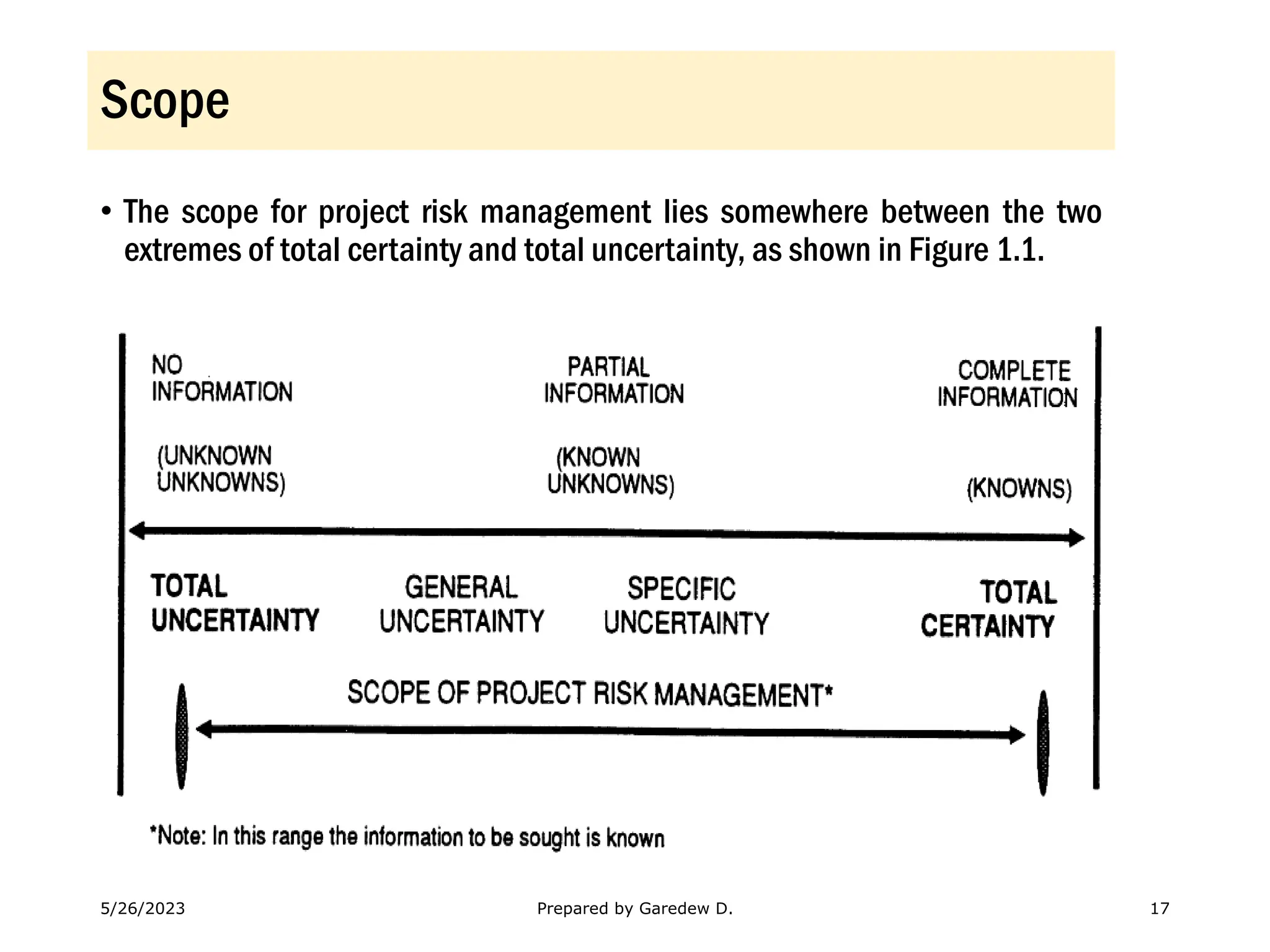
The document outlines the concepts of risk and uncertainty in project management, emphasizing that risk is defined as uncertain events affecting project objectives, which can have positive or negative effects. It highlights the importance of a structured risk management process to identify, quantify, and mitigate risks throughout the project lifecycle to ensure project success. Additionally, it categorizes risks into project-level and business-level risks and addresses the need for continuous risk assessment to maximize opportunities and minimize negative impacts.