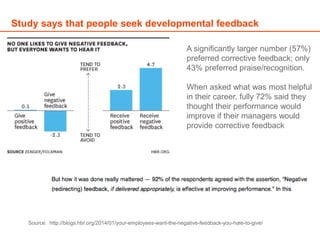
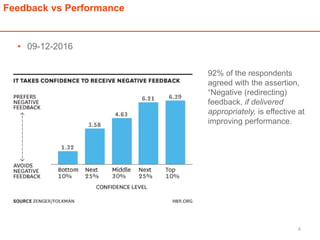
The document discusses the importance of feedback for team improvement, revealing that a significant majority of individuals prefer corrective feedback over praise for development. It outlines effective methods for delivering constructive feedback, including focusing on issues rather than personal attributes, demonstrating empathy, and facilitating discussions to achieve performance goals. It emphasizes the costs of not providing negative feedback and highlights common mistakes to avoid when giving feedback.