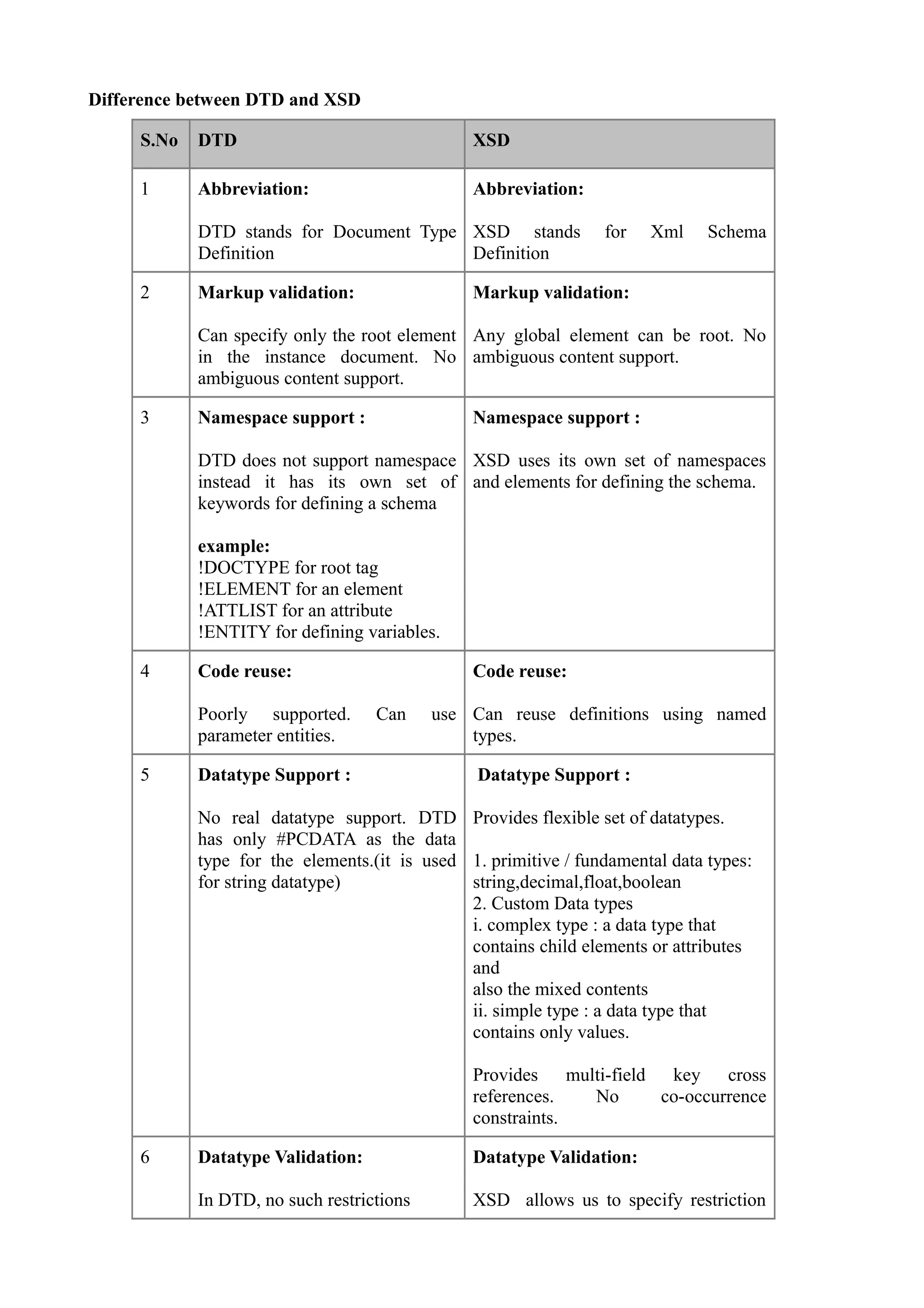
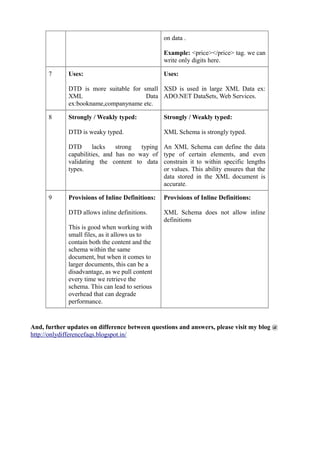
DTD and XSD are both used to define the structure and legal elements of an XML document, but XSD provides more robust validation capabilities. DTD has limitations in that it only supports validation of the root element, lacks namespaces and data types, and is weakly typed. In contrast, XSD supports validation of any element, uses namespaces, provides primitive and custom data types with restrictions, and is strongly typed. While DTD is suitable for small XML data, XSD is better suited for large XML documents like those used in web services and datasets due to its stronger validation features.