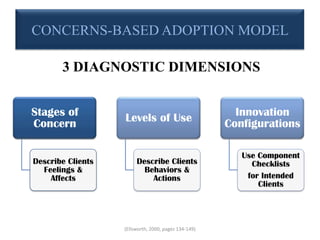
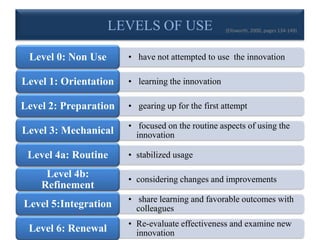
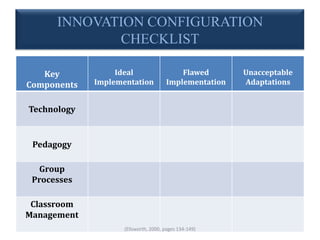
This document discusses the Concerns-Based Adoption Model (CBAM), which focuses on facilitating change at the individual level. The CBAM uses three diagnostic dimensions to measure change: Stages of Concern, Levels of Use, and Innovation Configurations. Stages of Concern describes clients' feelings about change, Levels of Use describes their behaviors and actions, and Innovation Configurations uses component checklists to assess clients' implementation of innovations. The CBAM aims to provide strategies and support to intended adopters through collecting and measuring data over time to prescribe specific interventions for implementing change.