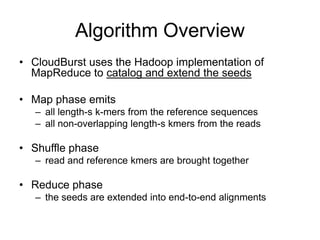
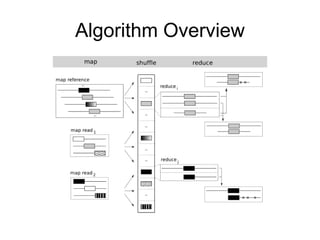
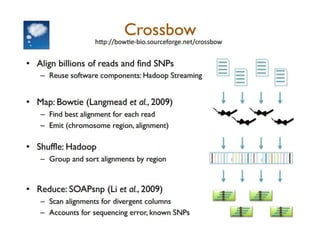
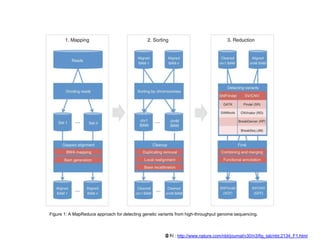
CloudBurst is a parallel read mapping algorithm optimized for mapping next-generation sequencing (NGS) data to reference genomes using MapReduce. It models the short read mapper RMAP and can report all alignments or the best alignment for each read with any number of mismatches. CloudBurst uses Hadoop's MapReduce to parallelize the computation across multiple nodes, reducing the running time from hours to minutes for typical jobs involving millions of reads.