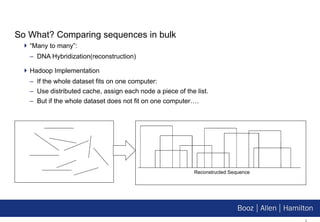
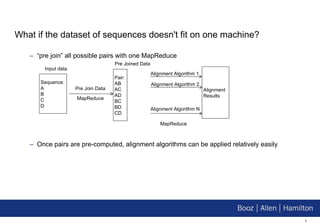
1. Hadoop provides a scalable platform for storing and processing large datasets in a distributed manner at low cost, enabling computational applications that were previously impossible.
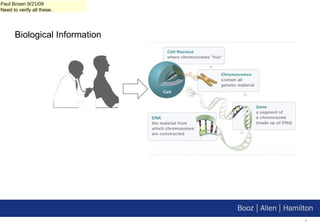
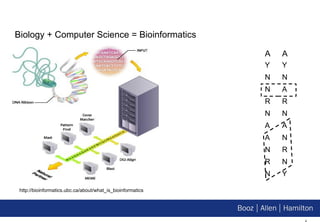
2. This talk explores how Hadoop can have a transformative impact on bioinformatics by enabling the comparison and analysis of very large DNA and protein sequences.
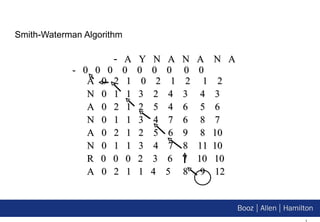
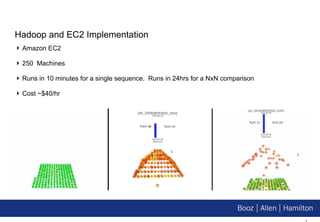
3. The document demonstrates implementations of common bioinformatics algorithms like sequence alignment on Hadoop, showing it can scale to analyze much larger datasets than on a single computer.
![Hadoop World 2009 New York Oct 2, 2009 Sequence Alignment and Hadoop . Booz Allen Hamilton Inc. 134 National Business Parkway Annapolis Junction, MD 20701 Tel (301) 543-4665 [email_address] Paul Brown Associate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hw09-proteinalignment-091025150641-phpapp02/85/Hw09-Protein-Alignment-1-320.jpg)