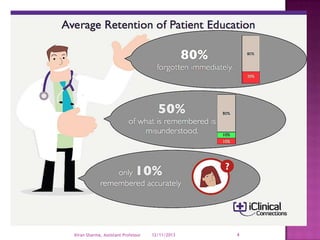
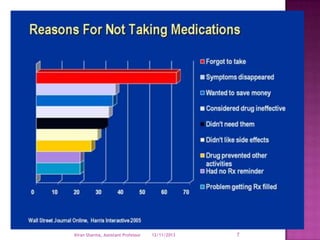
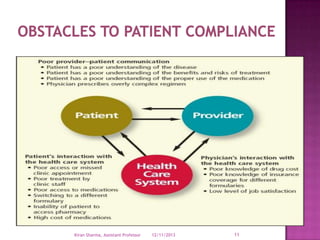
Patient compliance describes how closely a patient follows medical advice, particularly with respect to medication, but also other treatments like device use or therapy. It is important for conditions requiring ongoing treatment, replacement therapies like insulin, or controlling diseases of public health concern. Rates of compliance are assessed through various objective and subjective methods like pill counts, health outcomes, and patient interviews. Improving compliance requires addressing barriers like cost and complex regimens through subsidization, generic drugs, and education by pharmacists and other providers.