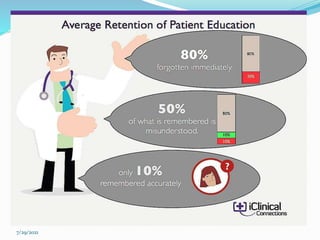
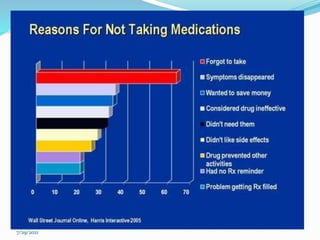
Patient compliance refers to how well a patient follows medical advice, especially regarding medication. Compliance can be full, partial, or non-existent. Adherence is a more active choice by the patient to follow treatment while taking responsibility for their health. Factors affecting compliance include the patient's social and economic situation, their relationship with healthcare providers, characteristics of the disease and treatment, and individual factors like age and memory. Compliance can be measured directly through medical tests or indirectly through prescription refills, outcomes, and patient interviews. Pharmacists can help improve compliance through education, monitoring therapy, and simplifying dosing.