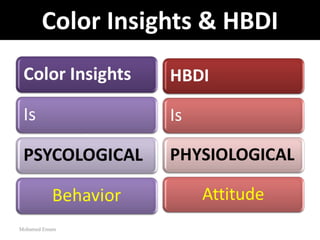
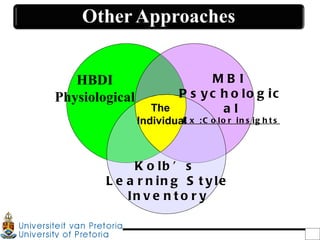
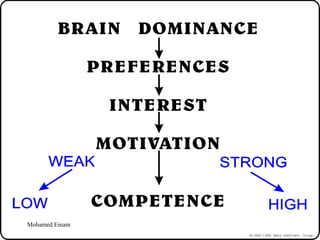
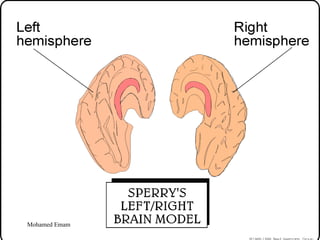
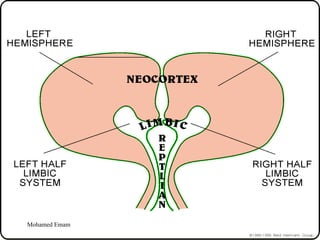
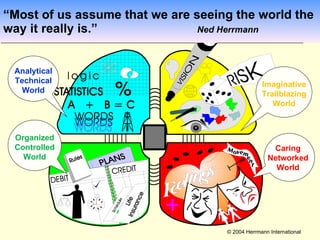
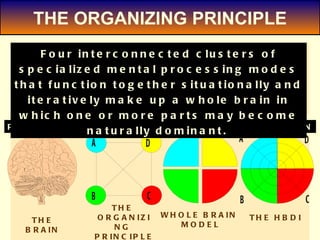
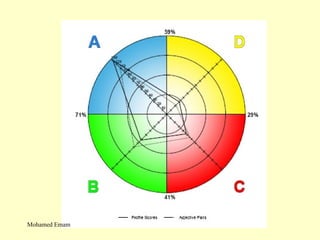
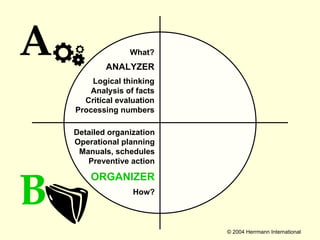
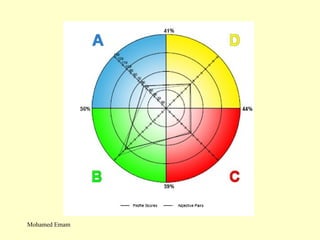
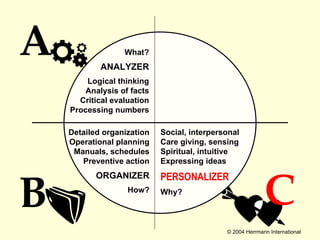
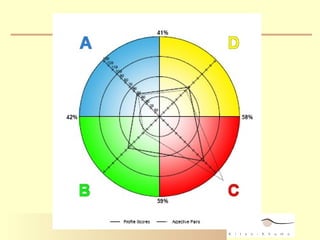
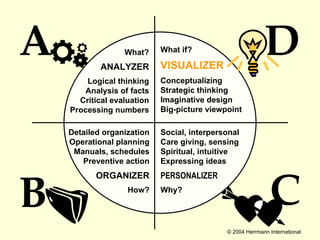
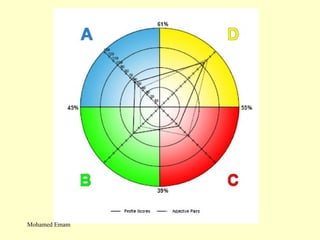
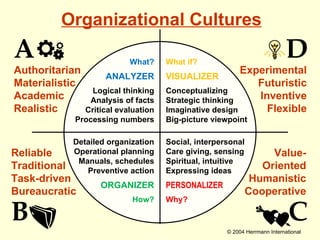
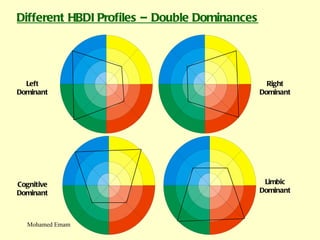
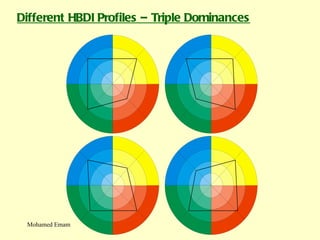
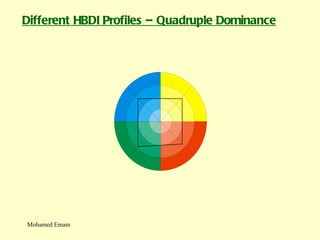
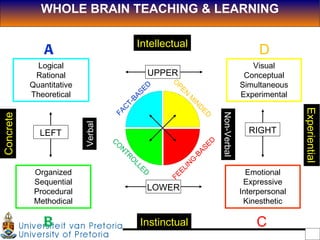
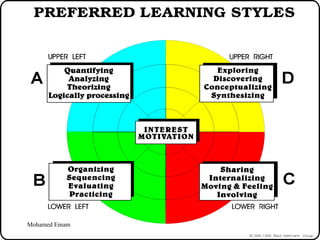
1. The document discusses the Hermann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI), which models four different thinking styles - Analytic, Organized, Personal, and Visual thinking.
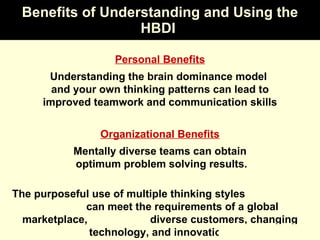
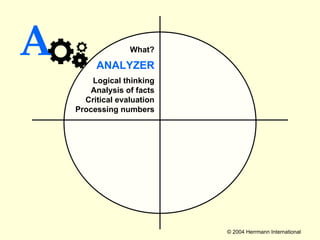
2. Each thinking style has distinct tasks, career preferences, and vocabulary. Understanding individual thinking preferences and leveraging diverse styles can improve teamwork, communication, and problem solving.
3. The HBDI can be used to assess thinking styles and understand how to communicate and work with others more effectively. Whole brain thinking that utilizes multiple styles is most optimal.

![HBDI ; The Hermann Brain Dominance Instrument Thinking Preferences in the Workplace JOHAN OLWAGEN MA (Counselling Psychology); HDE (Post Grad) Director: Kitso-Khumo Business Consulting (Pty) Ltd [email_address] 082-552-9542 ()12) 344-1390 Mohamed Emam Wisdom Is Wealth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hbdi-13280964407681-phpapp02-120201054233-phpapp02/85/Hbdi-2-320.jpg)