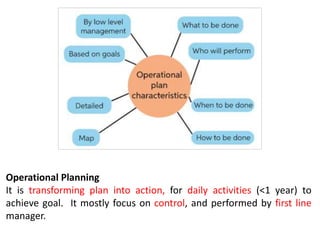
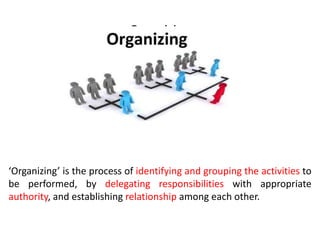
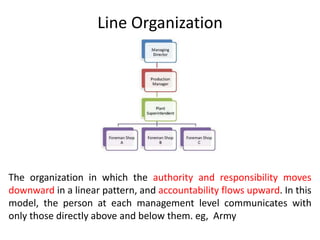
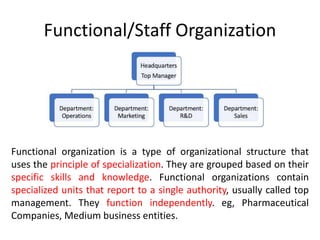
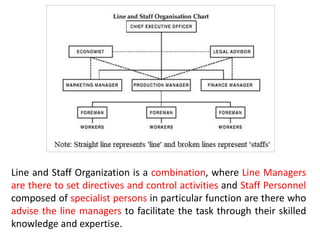
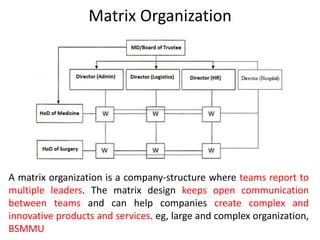
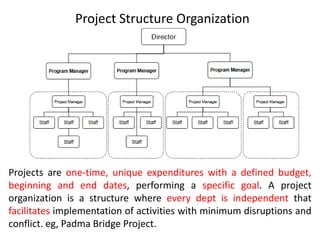
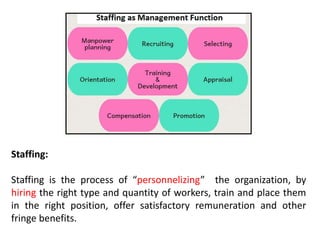
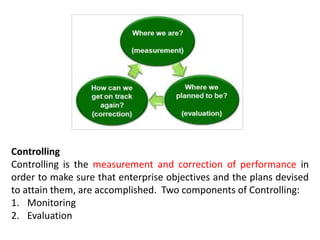
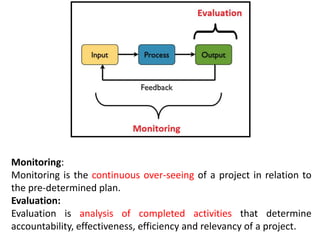
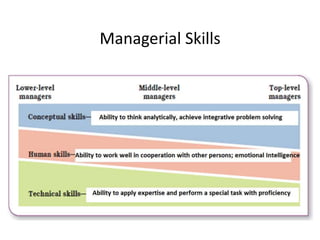
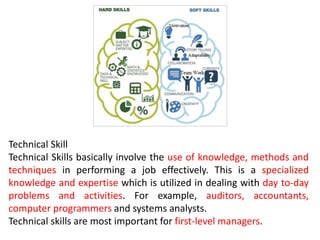
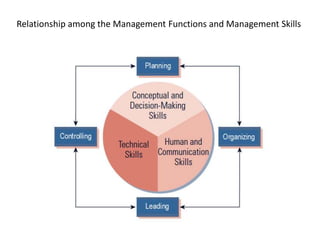
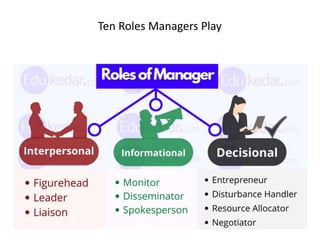
This document discusses key management concepts including functions, skills, roles, and planning. It provides details on:
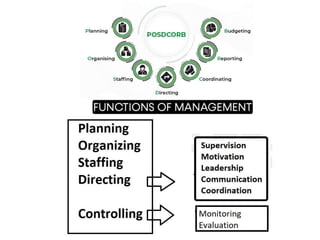
1) The five main management functions are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Planning involves deciding future actions, organizing is grouping tasks and