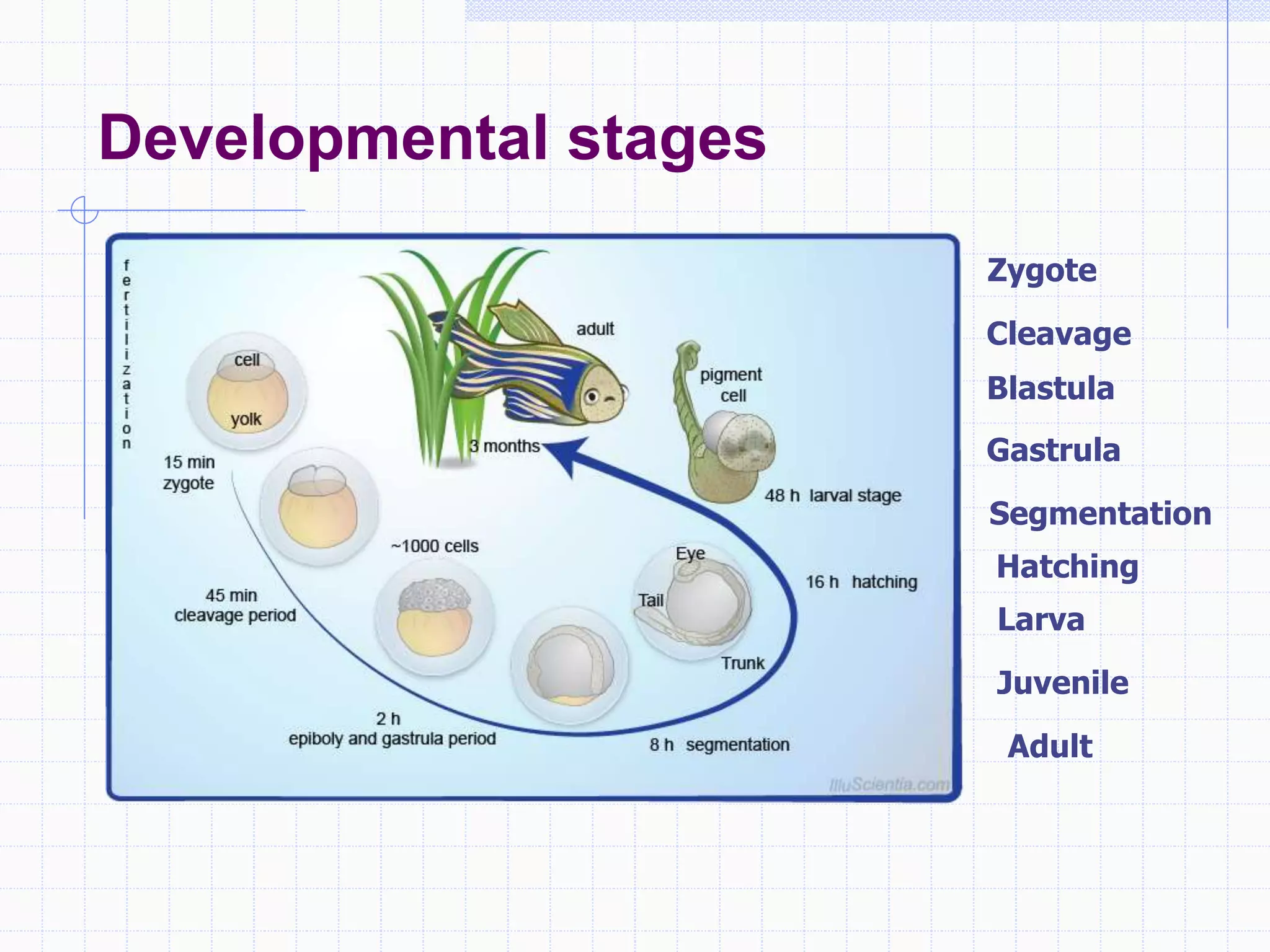
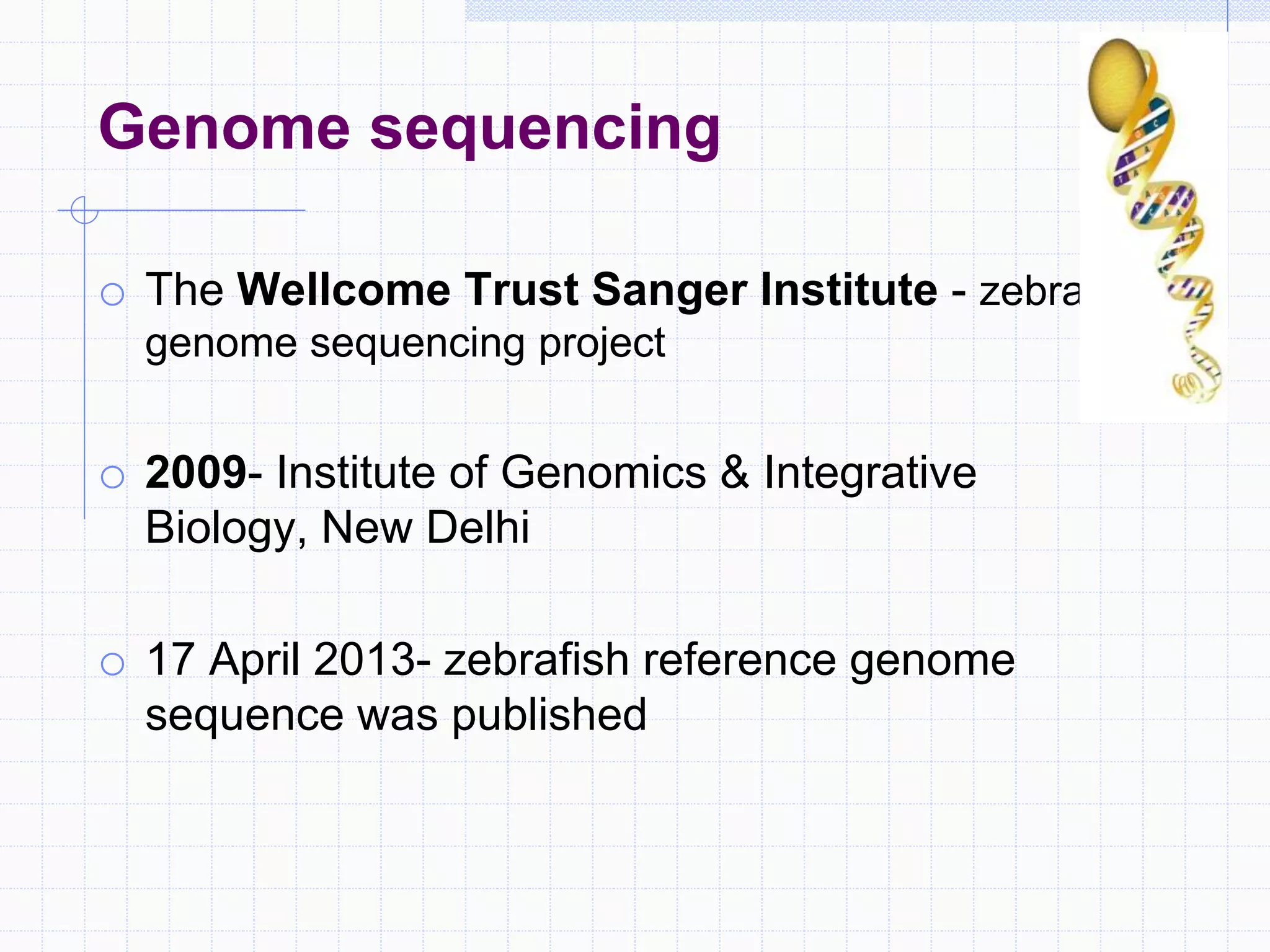
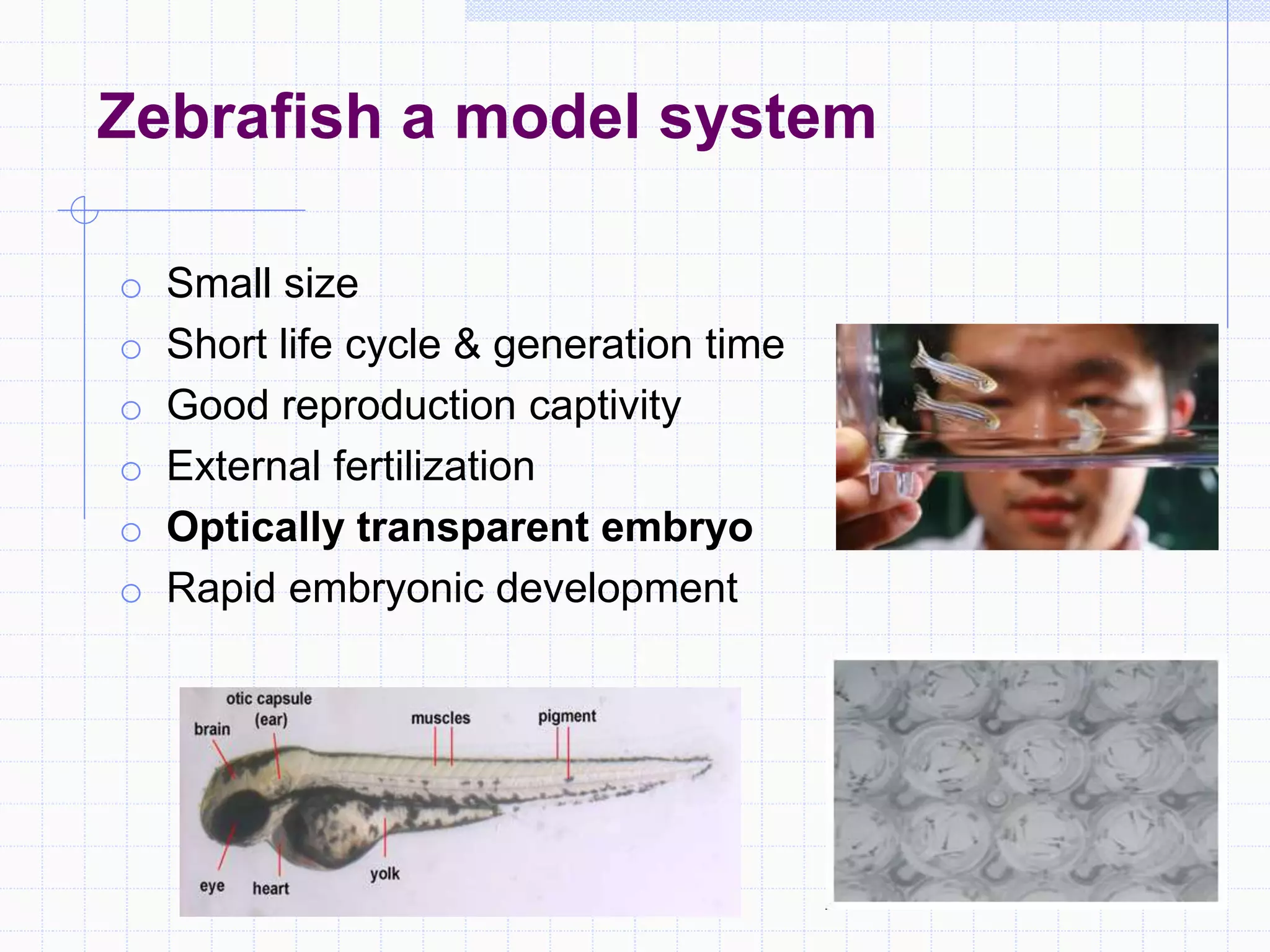
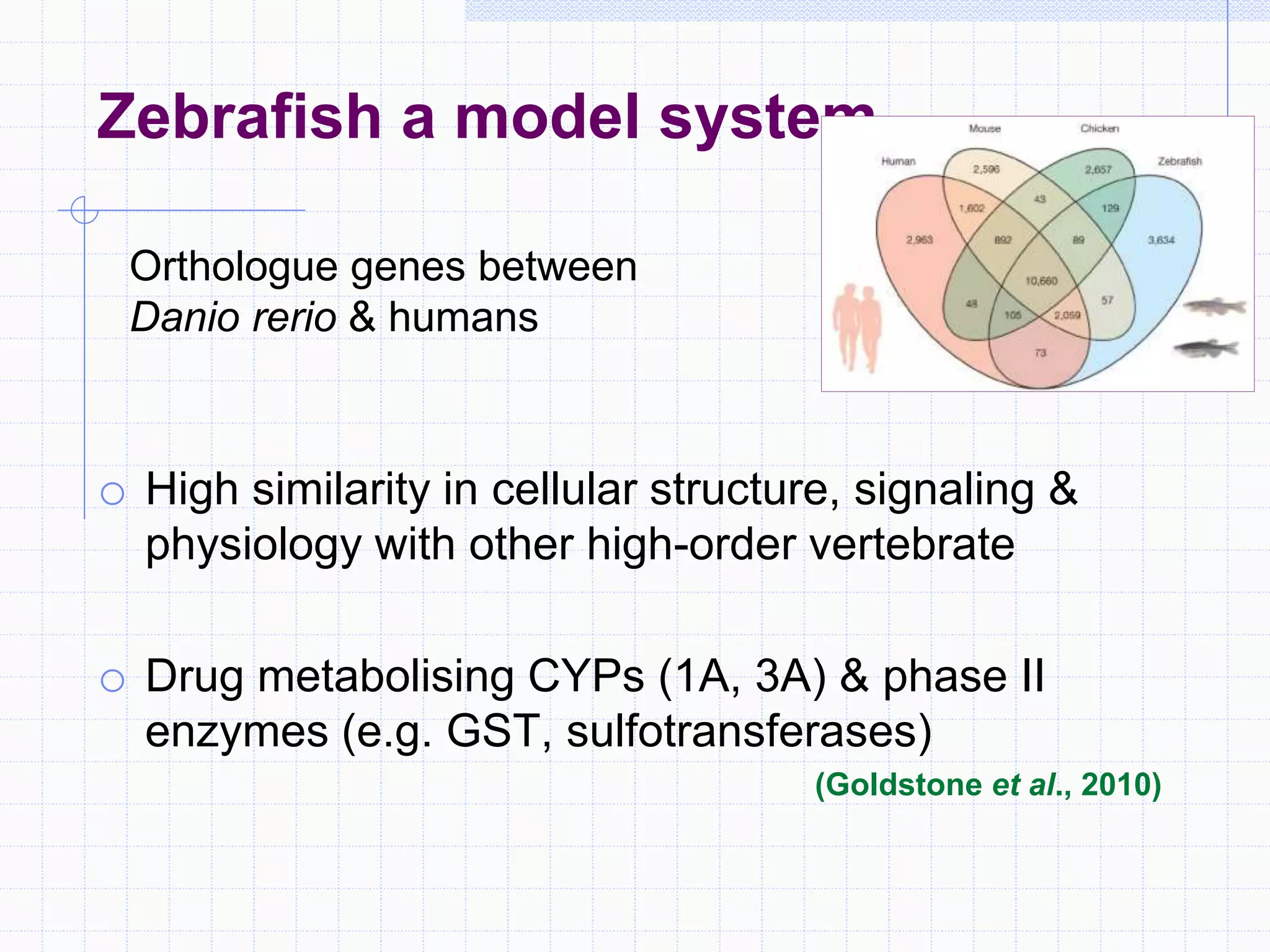
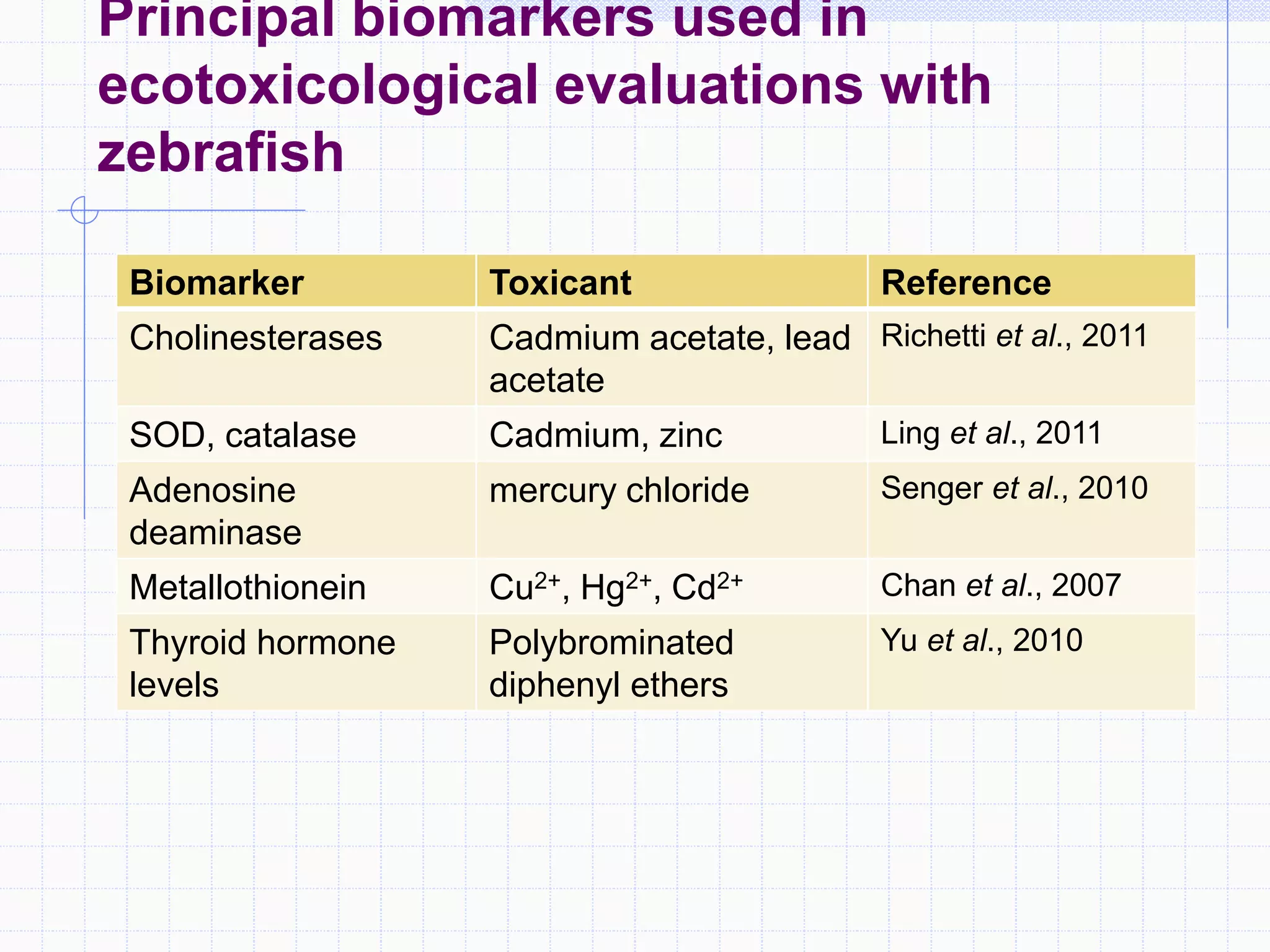
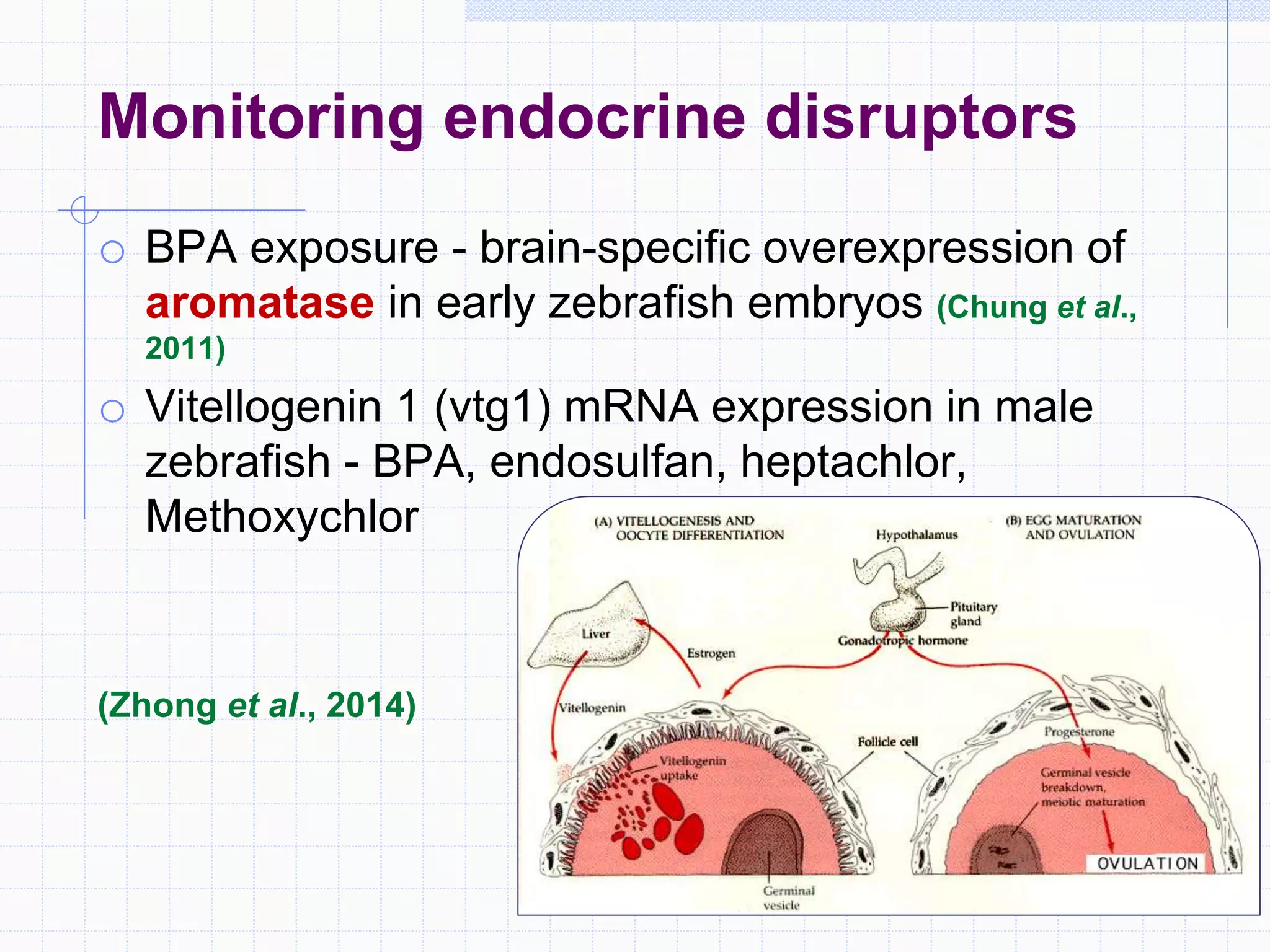
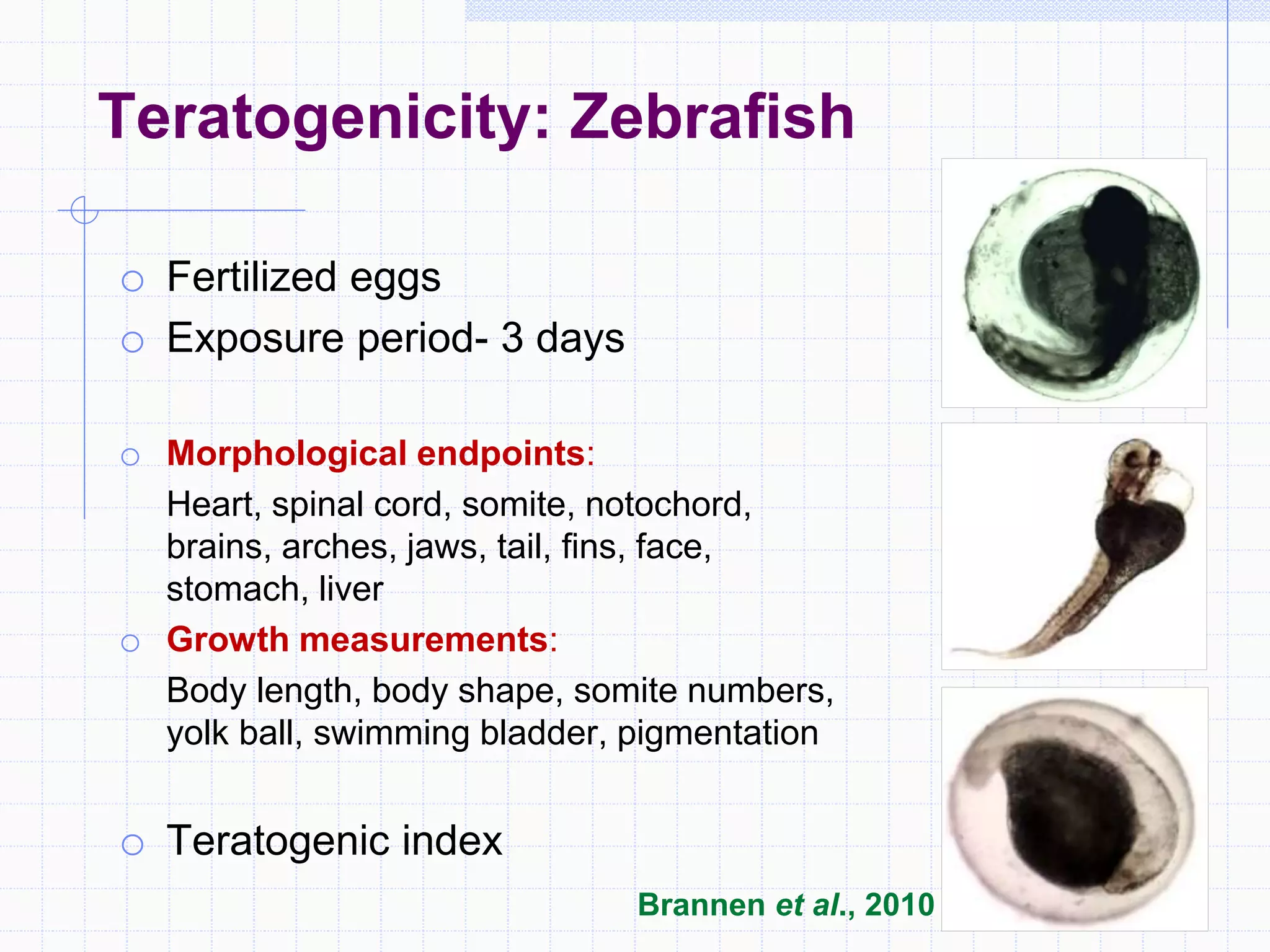
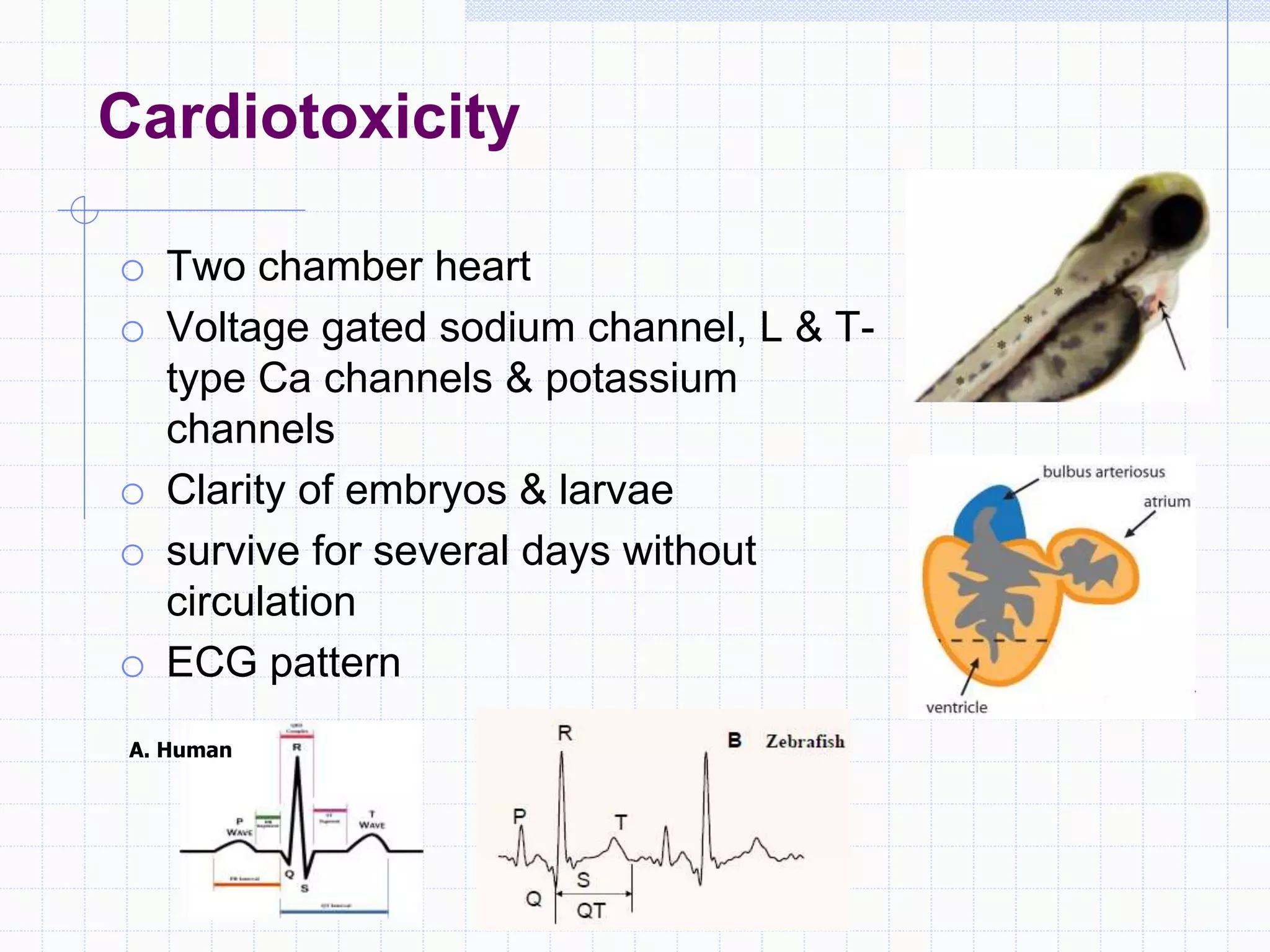
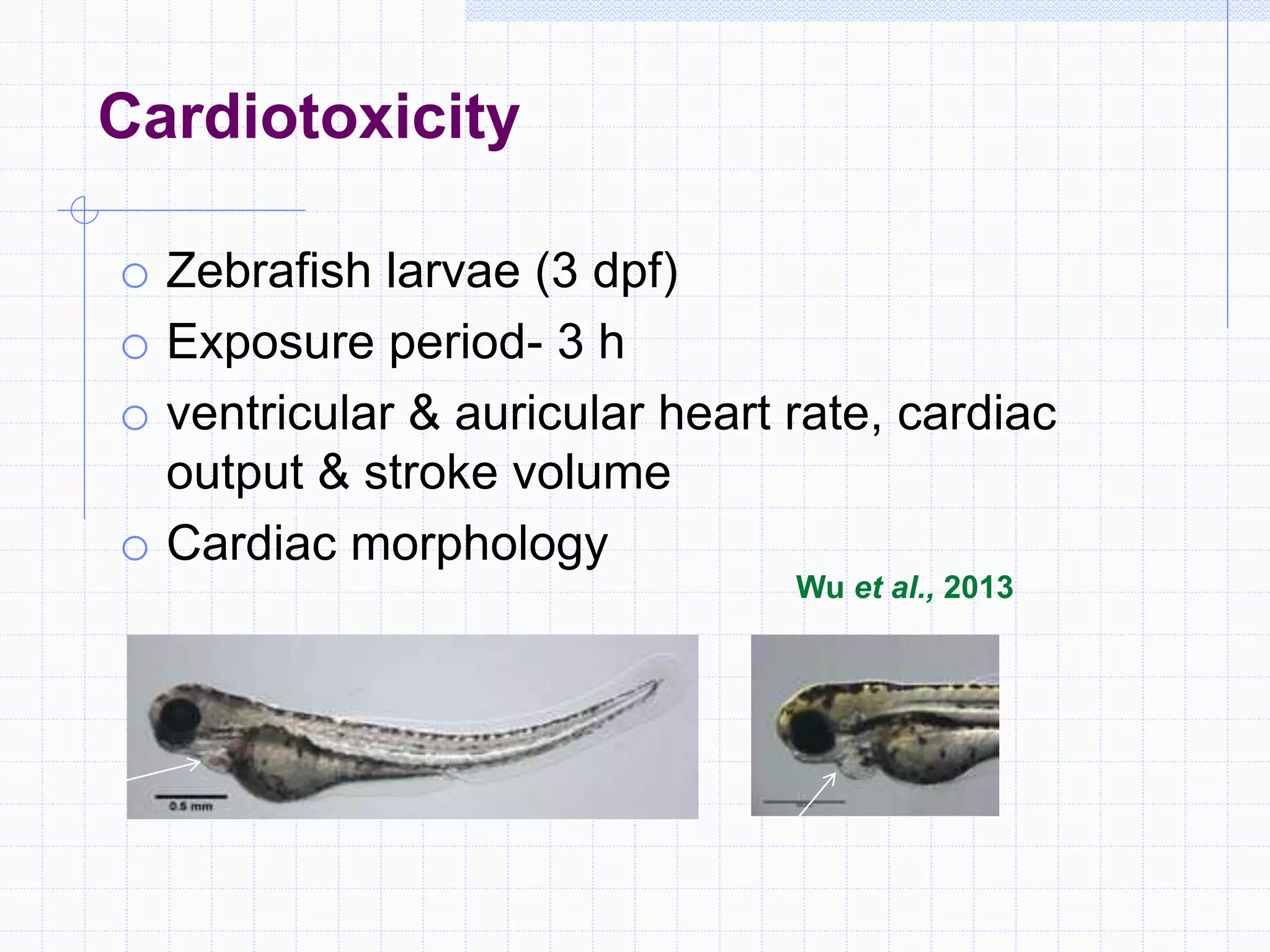
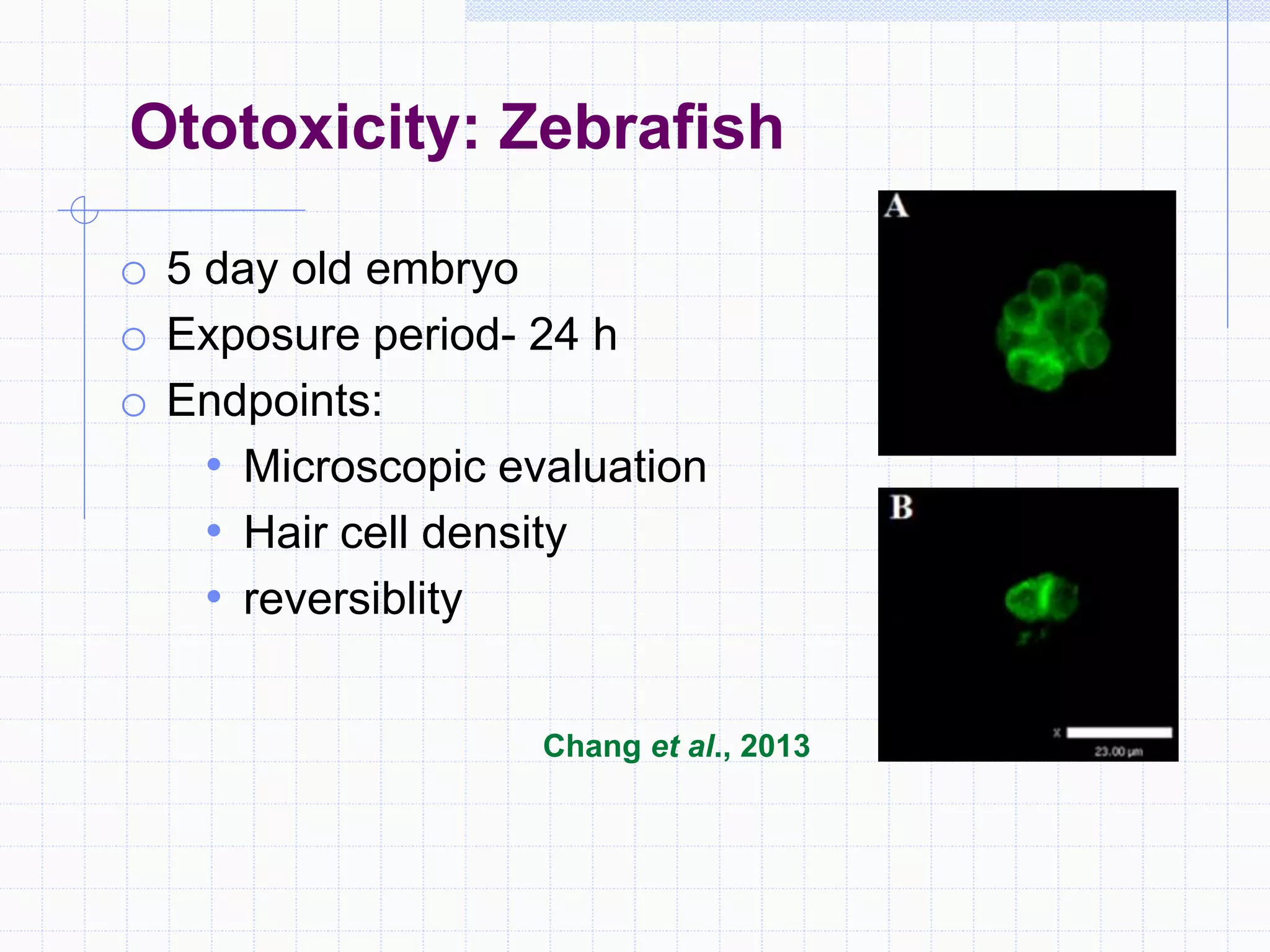
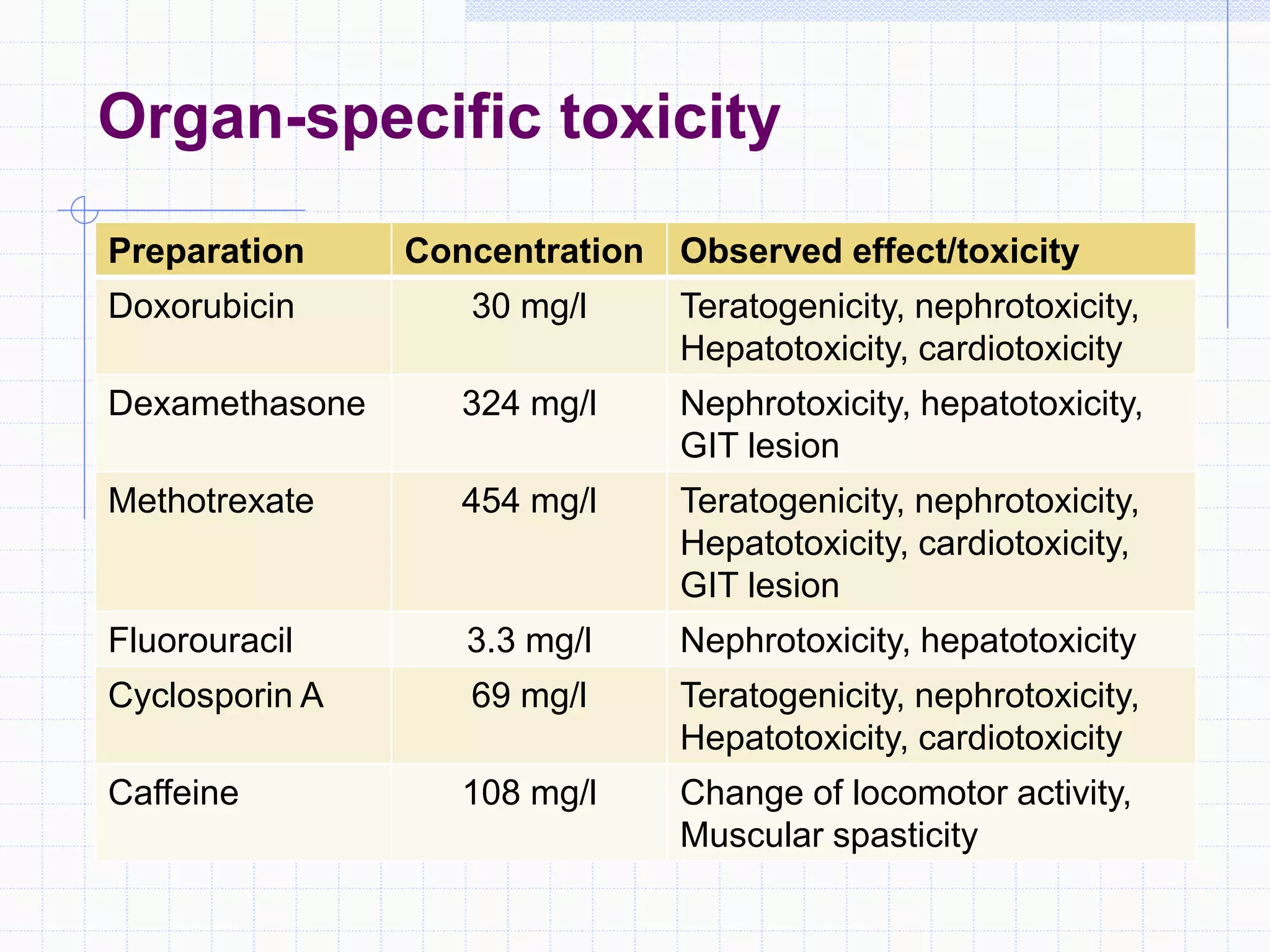
Zebrafish are a popular model organism used in research due to their low cost, short lifecycle, optical transparency during development, and genetic similarity to humans. They can be used to study various types of toxicity including developmental toxicity, cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and organ-specific toxicity. While zebrafish have limitations compared to mammalian models, assays using zebrafish embryos and larvae can provide early stage screening of compounds to evaluate teratogenicity and predict toxicity in mammals.