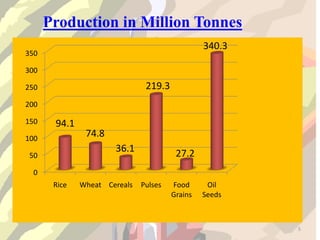
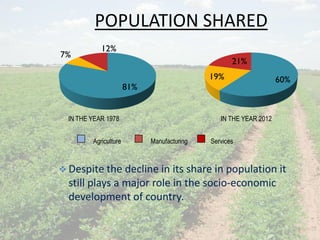
This document discusses boosting agricultural productivity in India. It notes that agriculture is still a major part of the Indian economy, providing food for over 1 billion people and contributing 1/6 of export earnings. However, there are also weaknesses like fragmented land ownership, illiteracy among farmers, and a lack of technological inputs. The document argues that increasing farmer literacy, improving infrastructure connectivity, and sustainable resource use could help boost agricultural productivity in India. The government should also play a larger facilitator role to support better production.