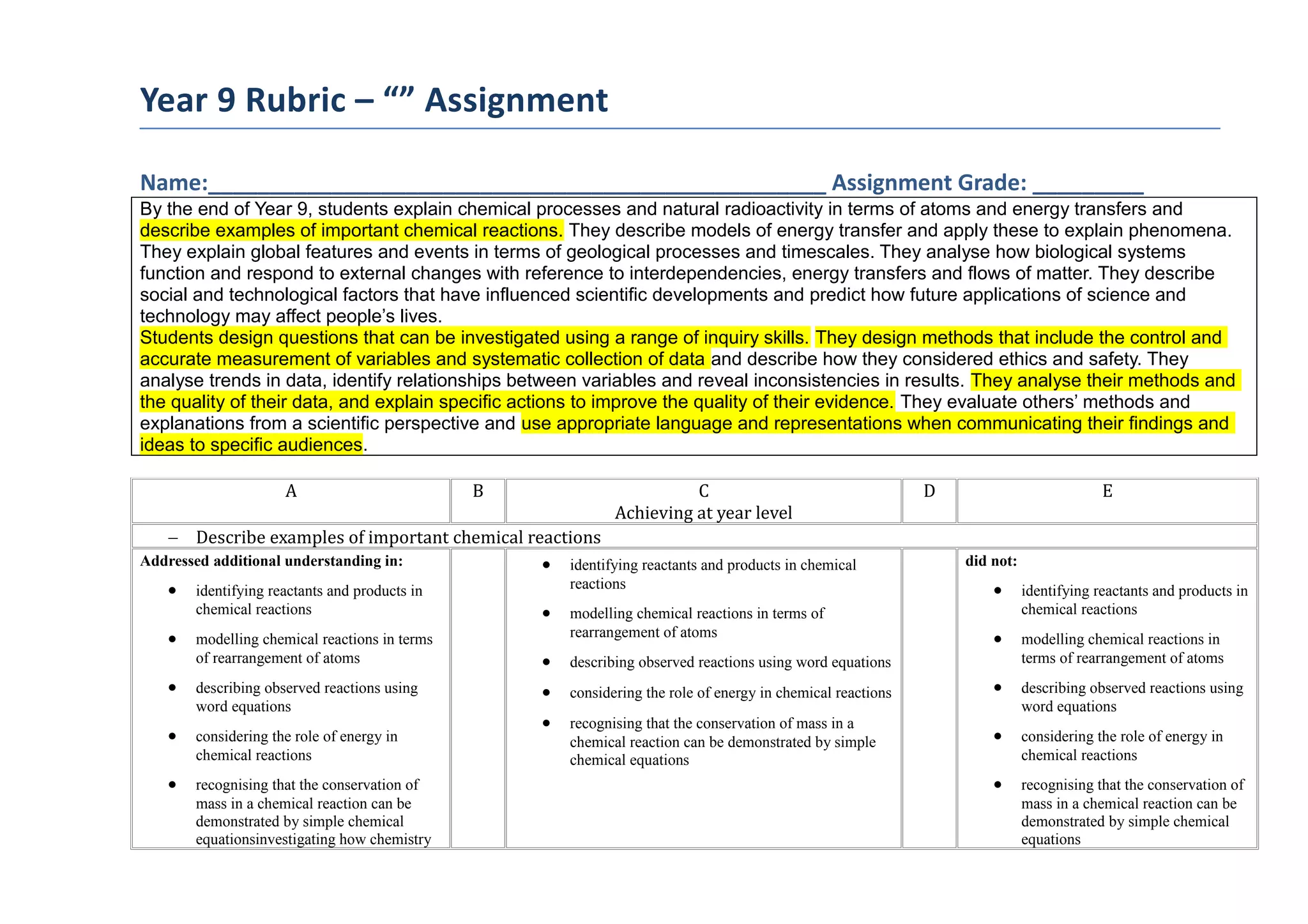
This document is a rubric for assessing a Year 9 student's assignment. It outlines the key areas that students should demonstrate by the end of Year 9, including explaining chemical processes and natural radioactivity in terms of atoms and energy transfers. Students should be able to design investigation questions, control variables, collect data, and analyze their methods and results. The rubric also provides examples of what a student has achieved and not achieved in describing important chemical reactions.