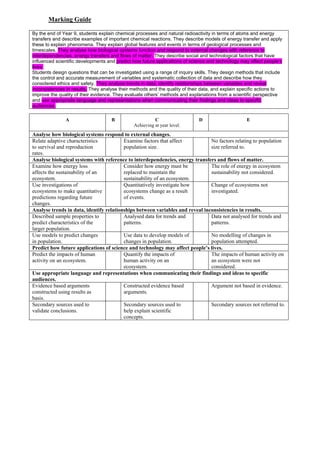
The document provides instructions for a Year 9 science assignment on the Mud Creek ecosystem case study. Students are asked to answer one of two questions about changes to the ecosystem by urbanization and a proposed development. They must state their opinion, support it using data from class activities, and write in an essay format. Tables provide focus questions to guide their answers and analysis of the ecosystem.