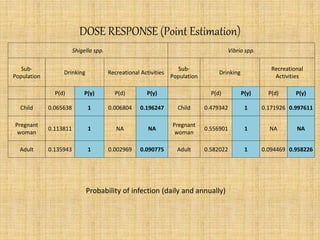
1) The study analyzed the microbial risks from exposure to pathogens in the Yamuna River for villagers in village DD. Quantitative microbial risk assessment was conducted to estimate annual infection risks from Shigella spp. and Vibrio spp. for different exposure scenarios.
2) Monte Carlo simulation was used to model the risks, which showed mean annual infection risks exceeding international guidelines. Drinking river water posed the highest risks. Children and pregnant women were most vulnerable.
3) Risk management recommendations included establishing water treatment, sanitation improvements, and public awareness campaigns about water boiling and filtration to reduce microbial concentrations and infection risks.