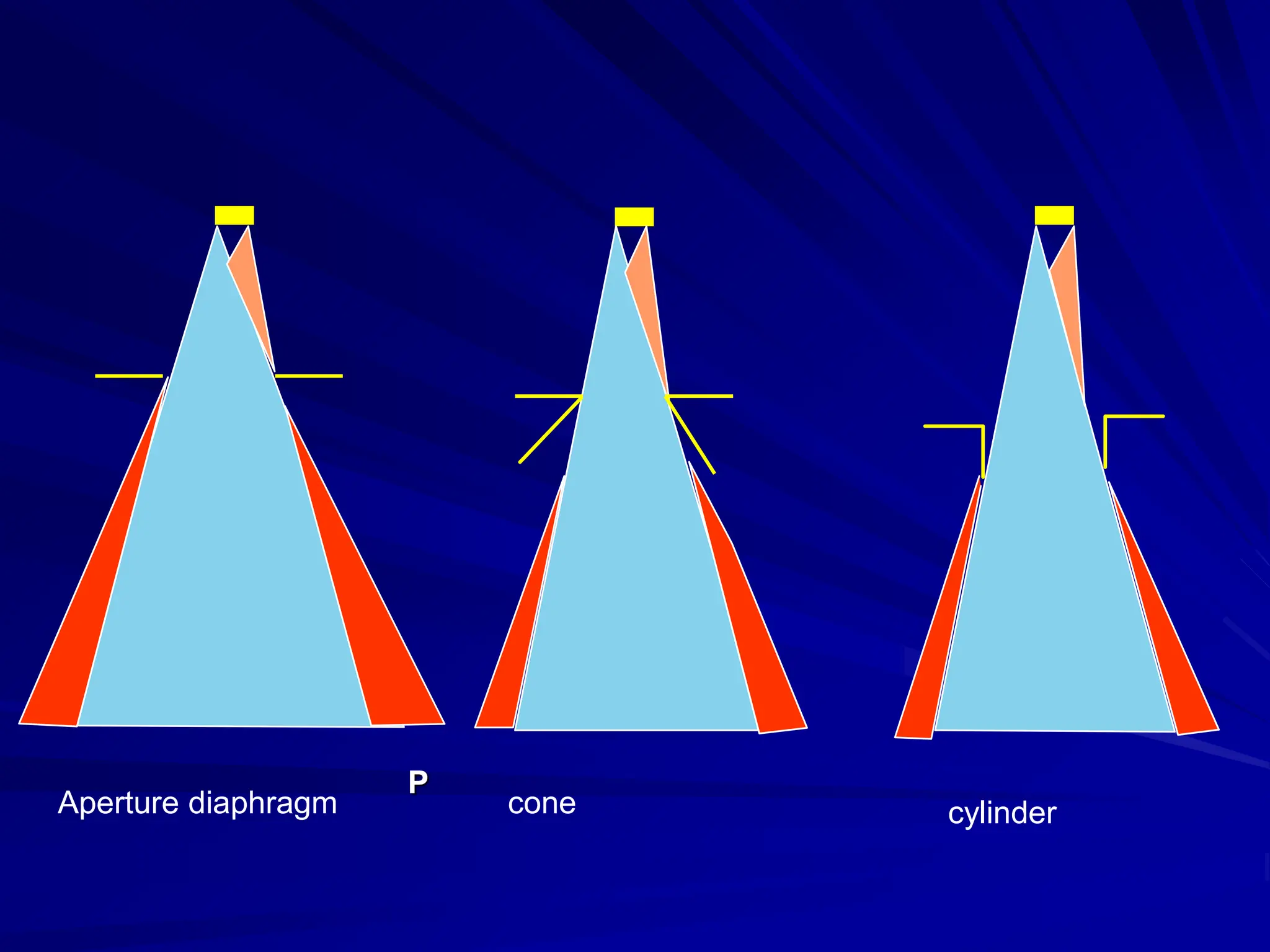
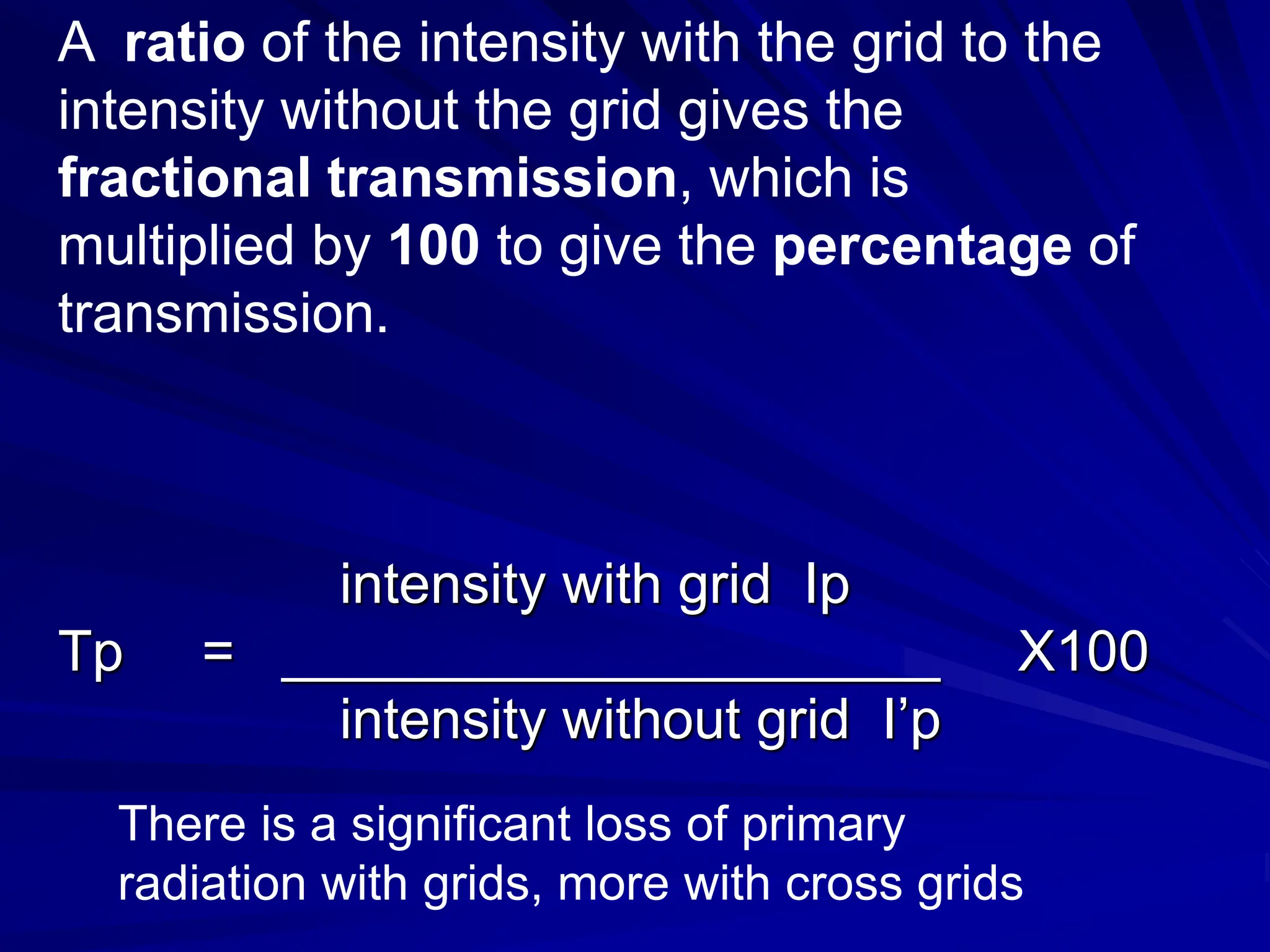
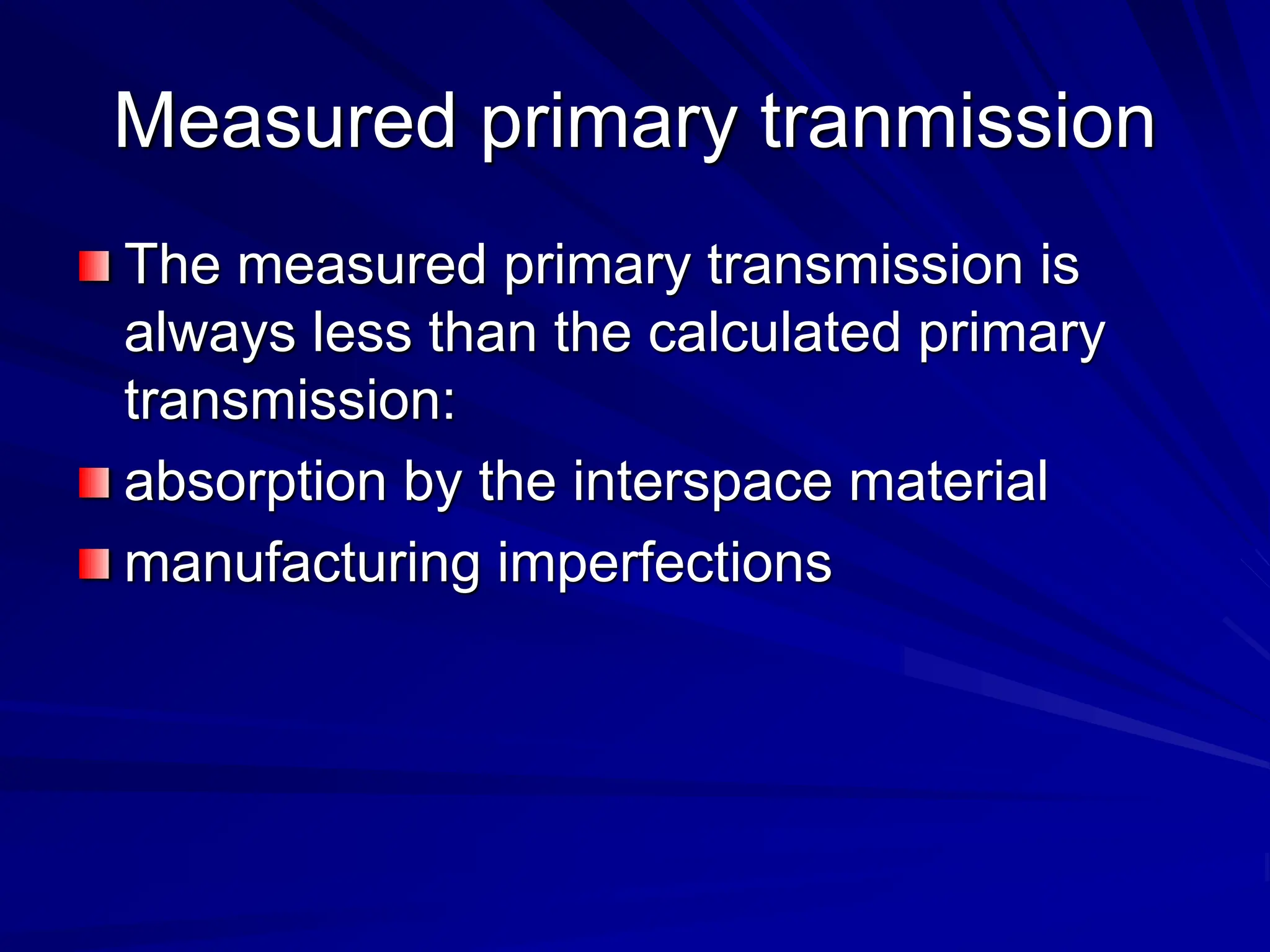
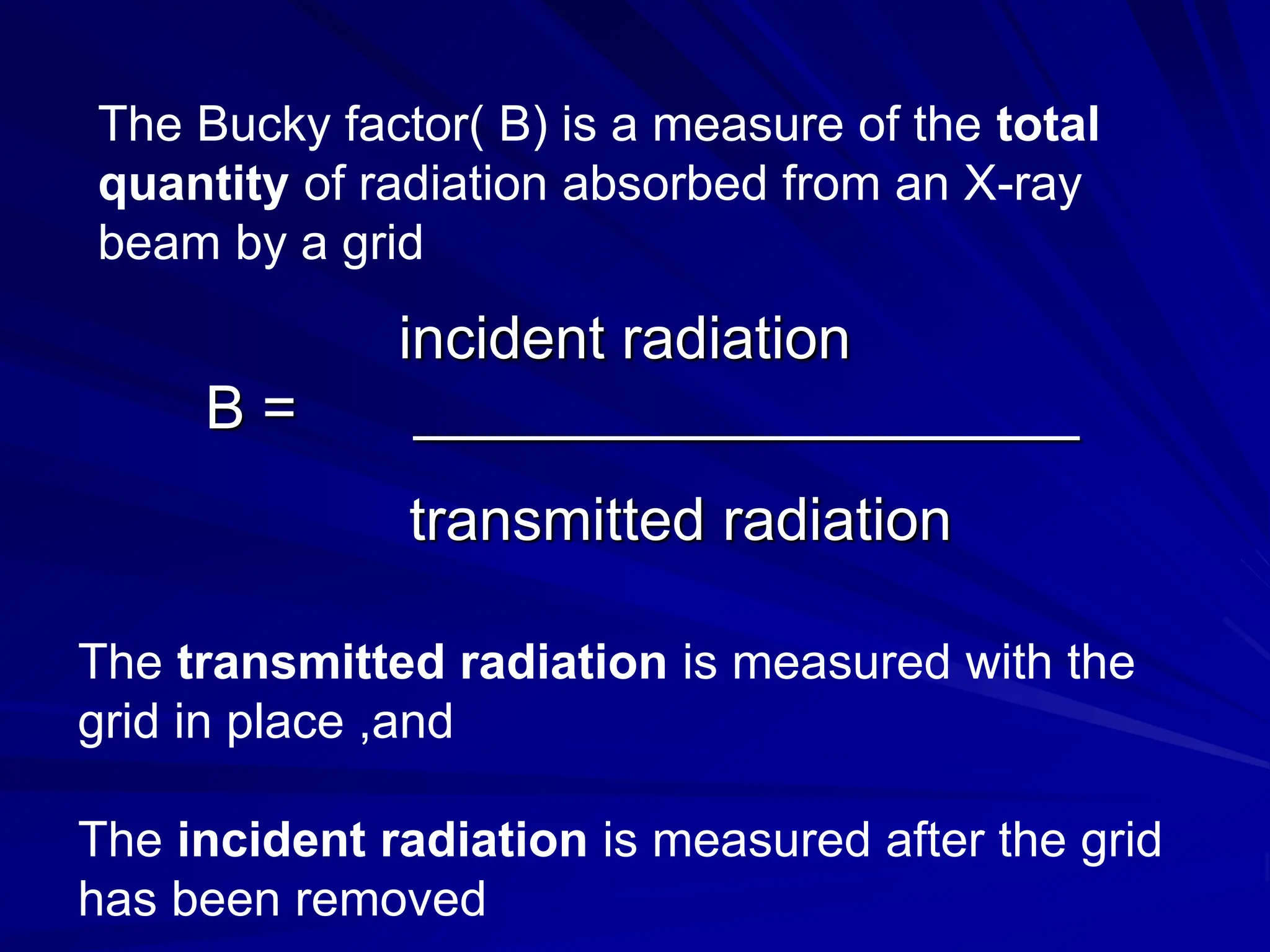
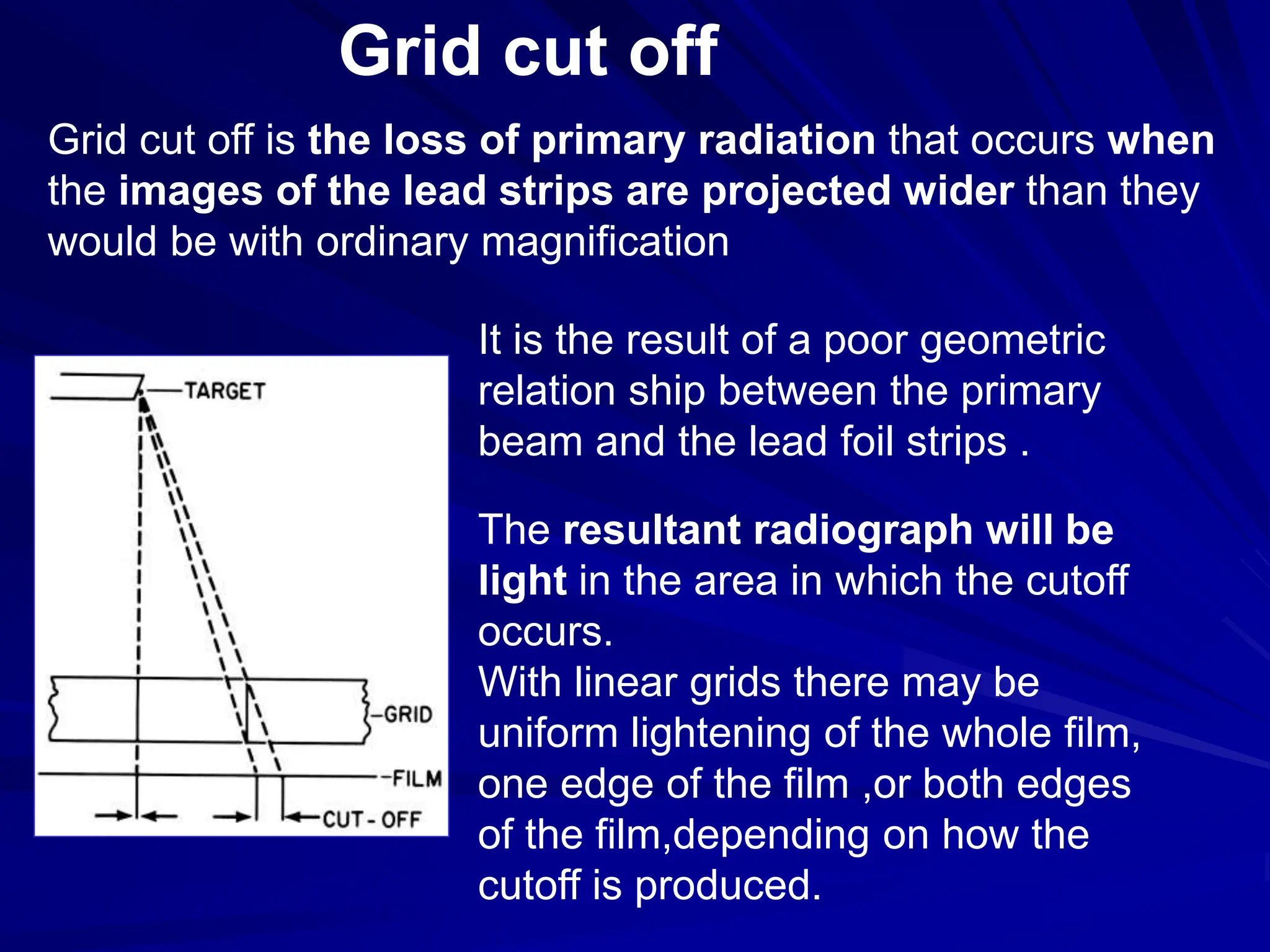
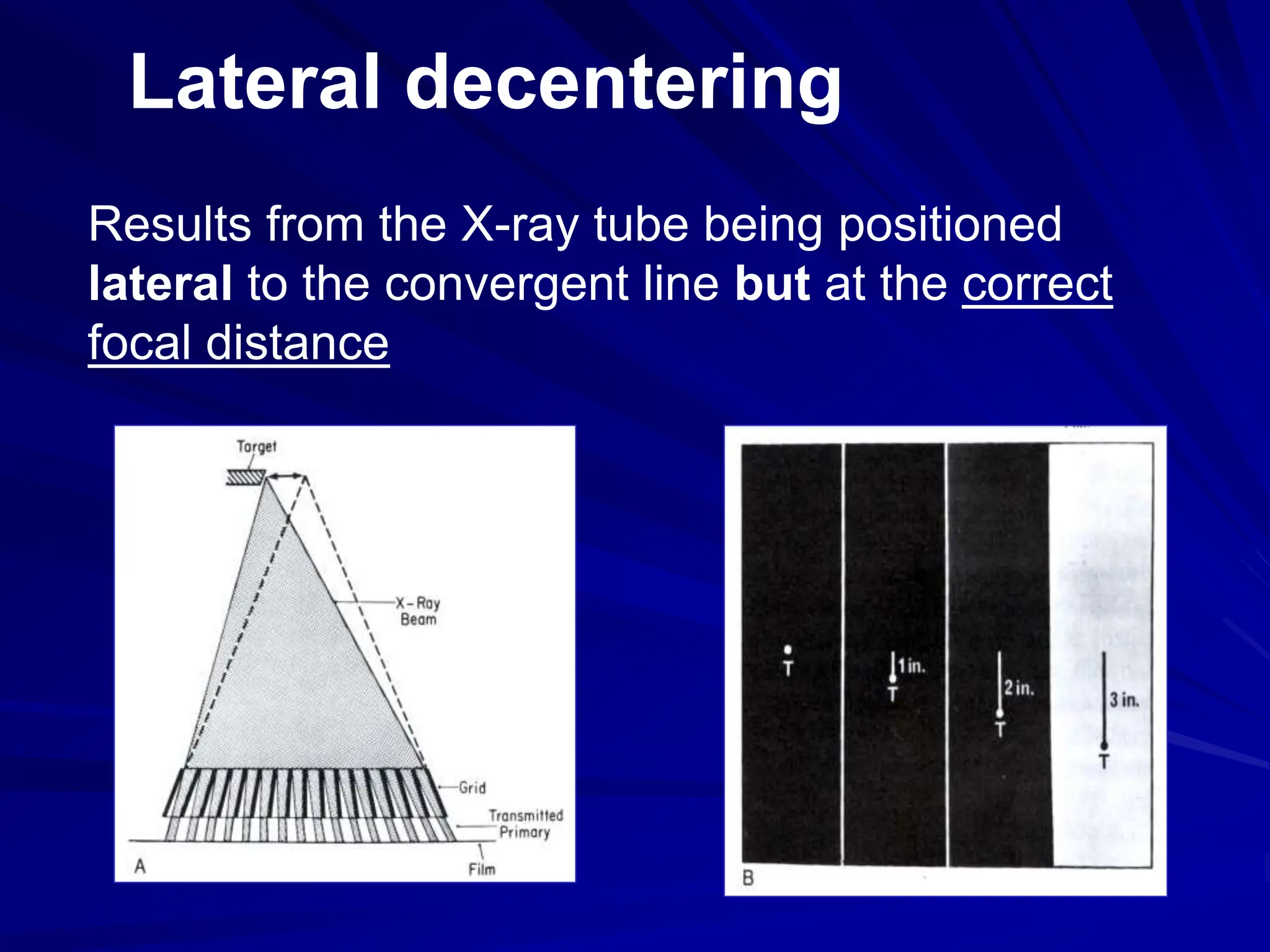
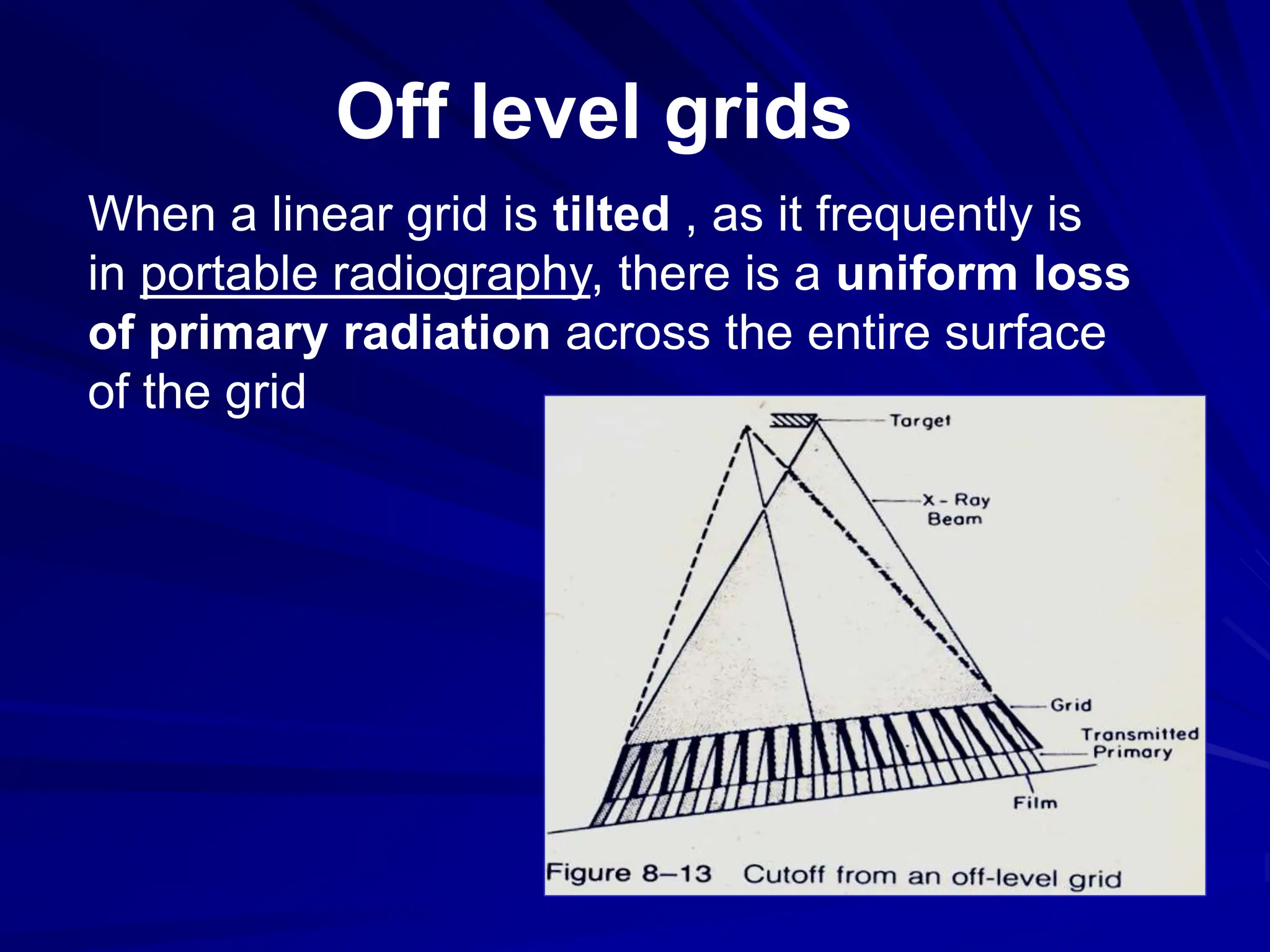
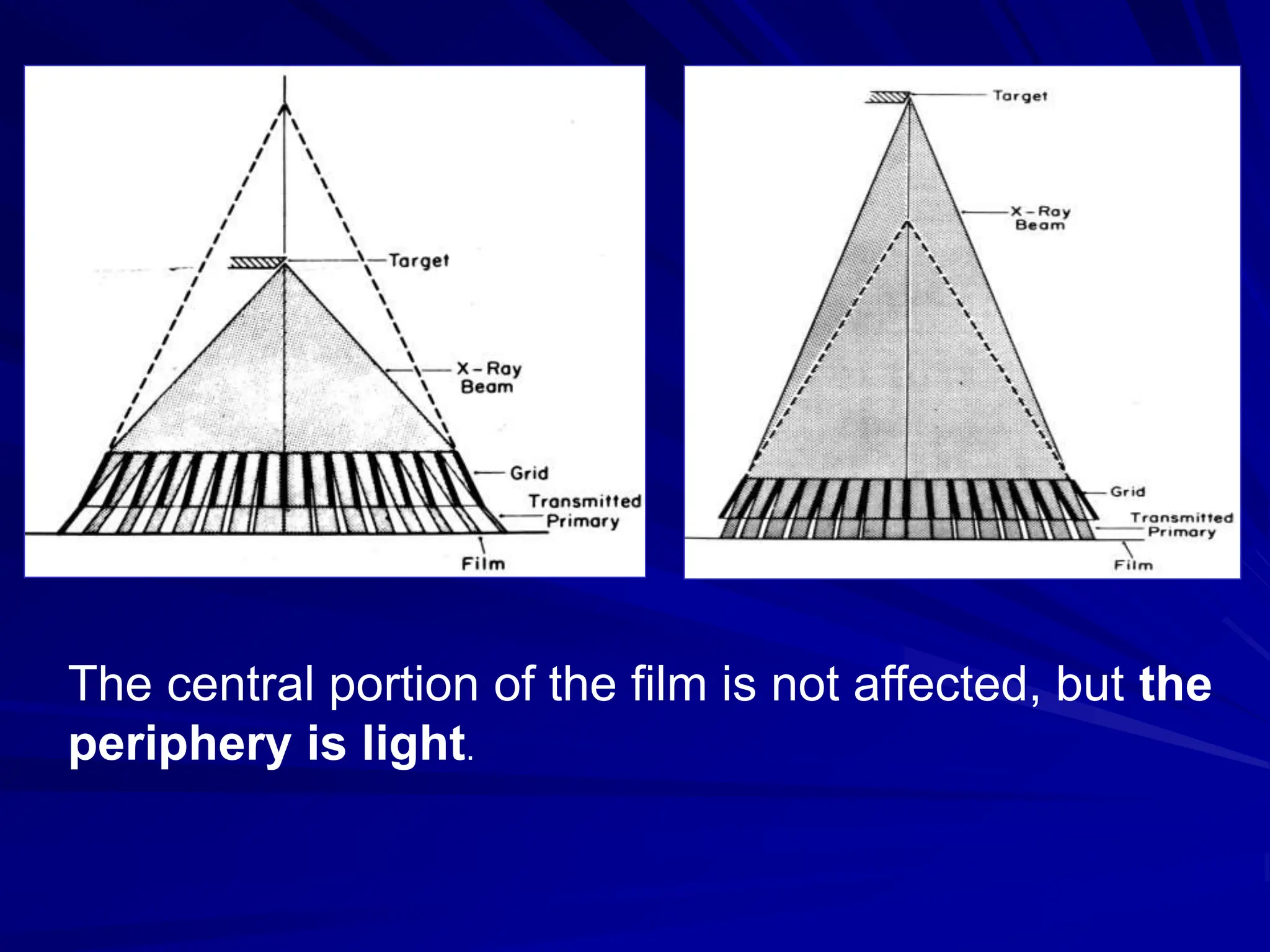
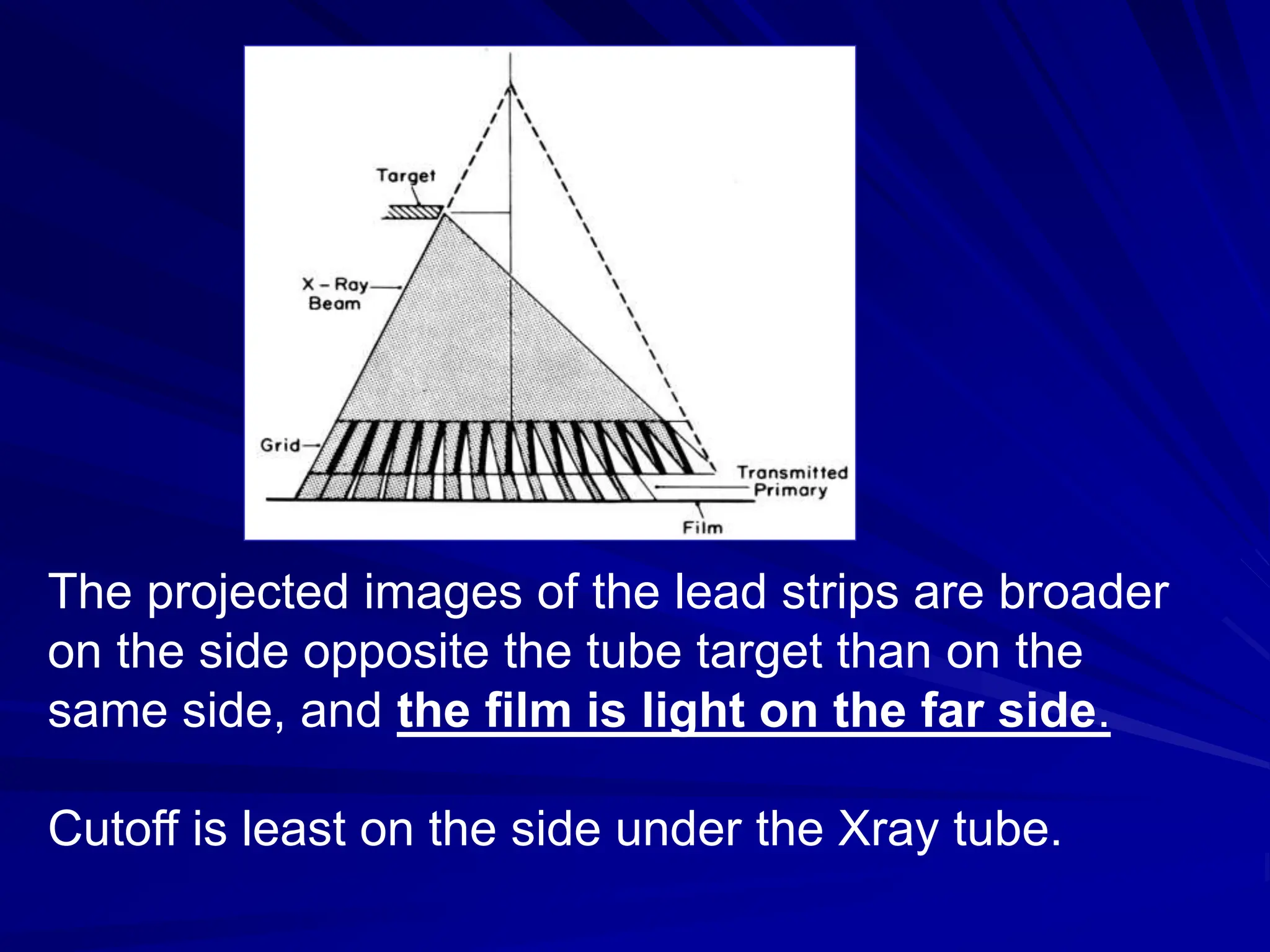
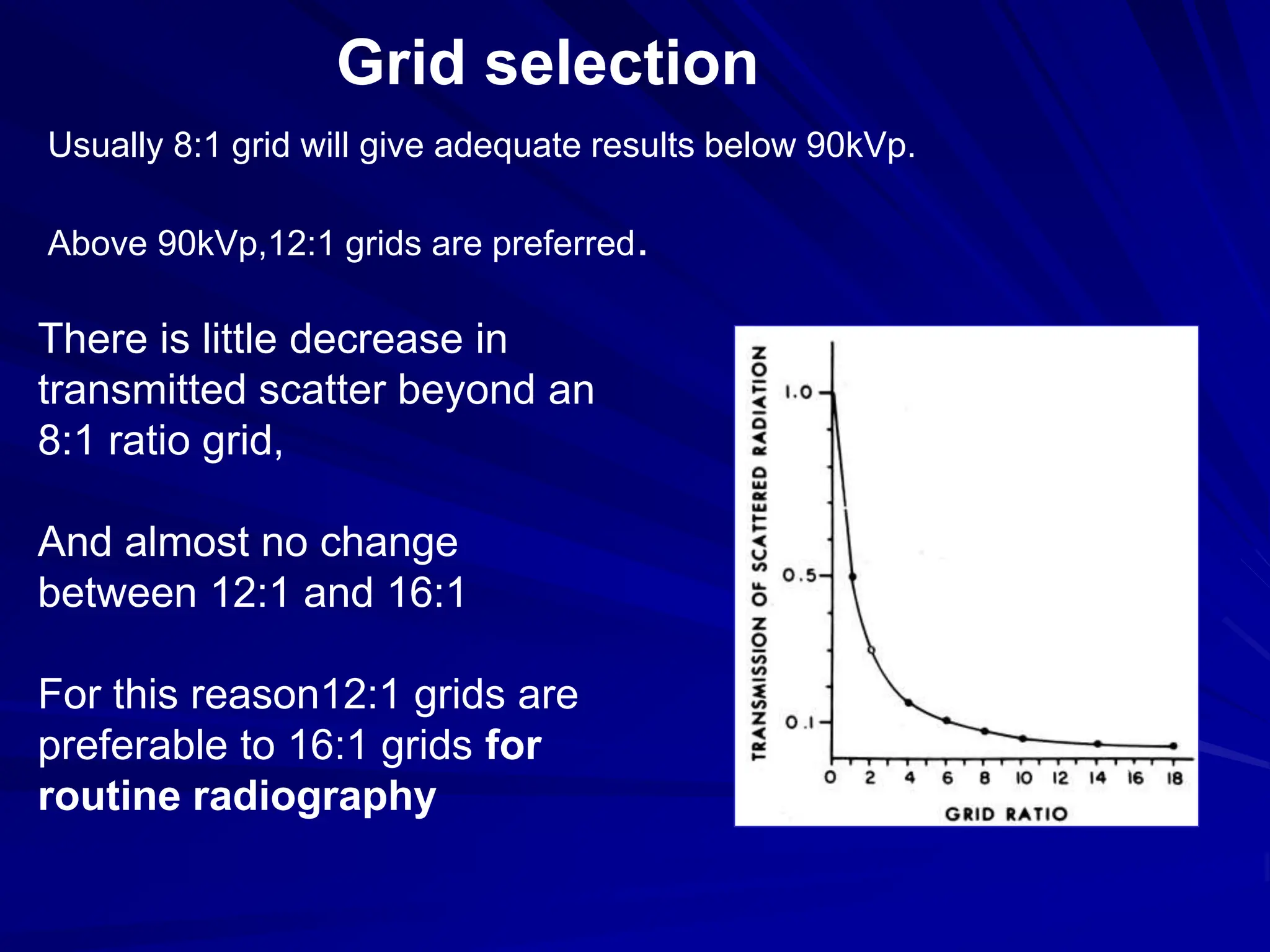
Filters and grids are used to shape and restrict the X-ray beam in diagnostic radiology. Filters absorb low energy photons to increase the ratio of useful to harmful photons. Diagnostic beams are polychromatic. Inherent filtration comes from the tube housing while additional filtration uses materials like aluminum and copper. Filtration reduces patient dose and lowers required exposure factors. Grids help reduce scatter radiation and improve contrast. They are made of lead strips separated by transparent spacers. Higher ratio grids provide better contrast improvement but require greater exposure. Positioning and alignment affect grid performance and can cause cutoff artifacts if not properly used.