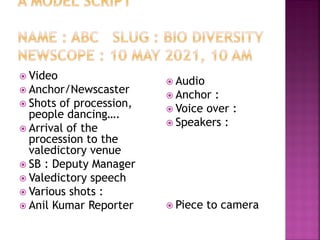
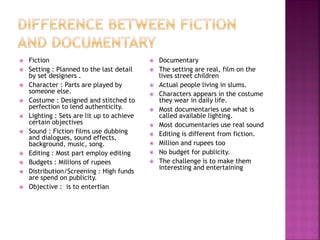
The document provides guidance on writing scripts for television news. It discusses various script elements like the slug, anchor leads, voiceovers, sound bites, stand ups, and sign offs. It emphasizes writing in a concise and conversational style using short sentences and attribution. Proper formatting of timecodes and attribution is also covered. Overall, the document offers a comprehensive overview of the components and best practices for writing television news scripts.