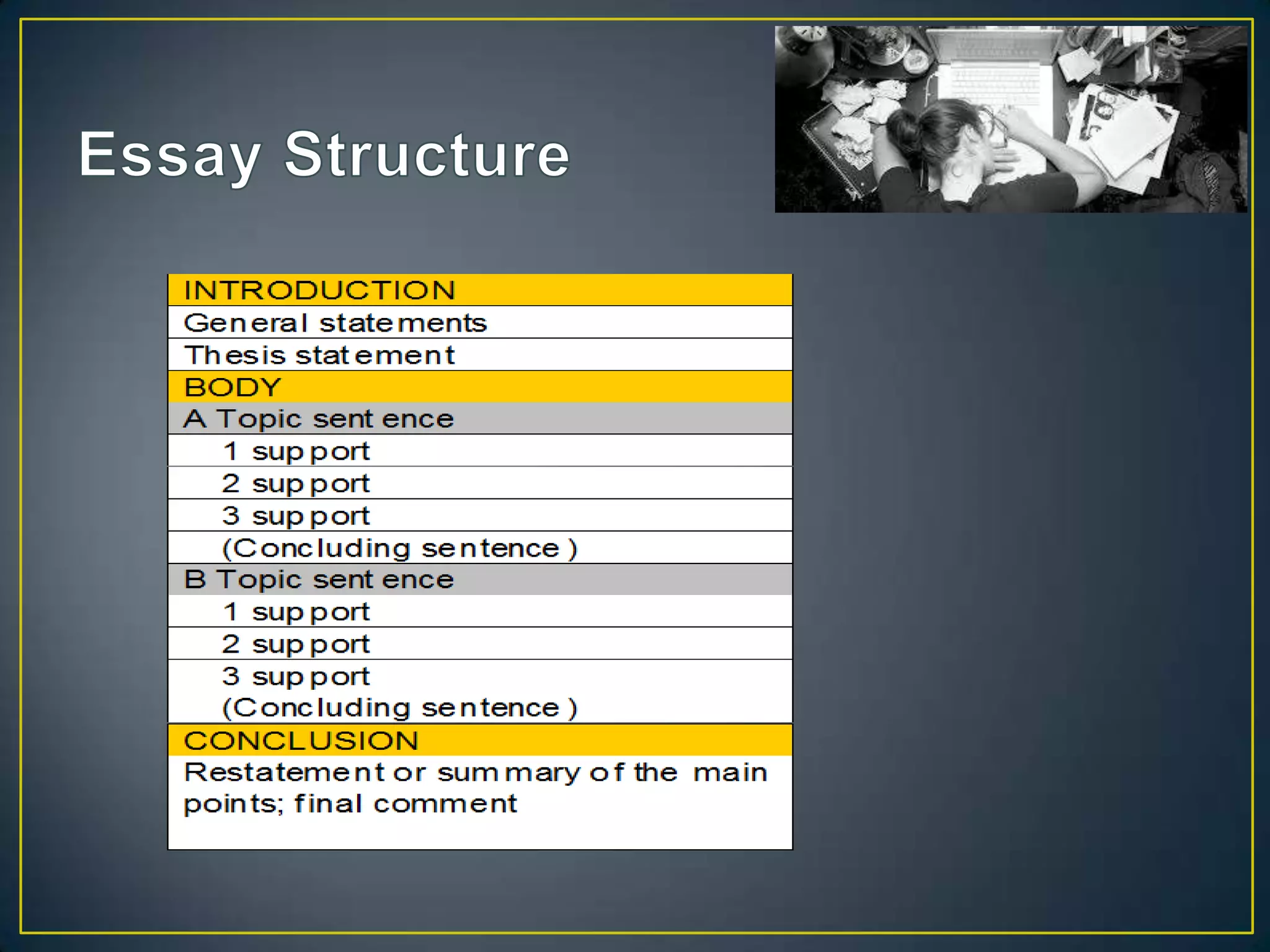
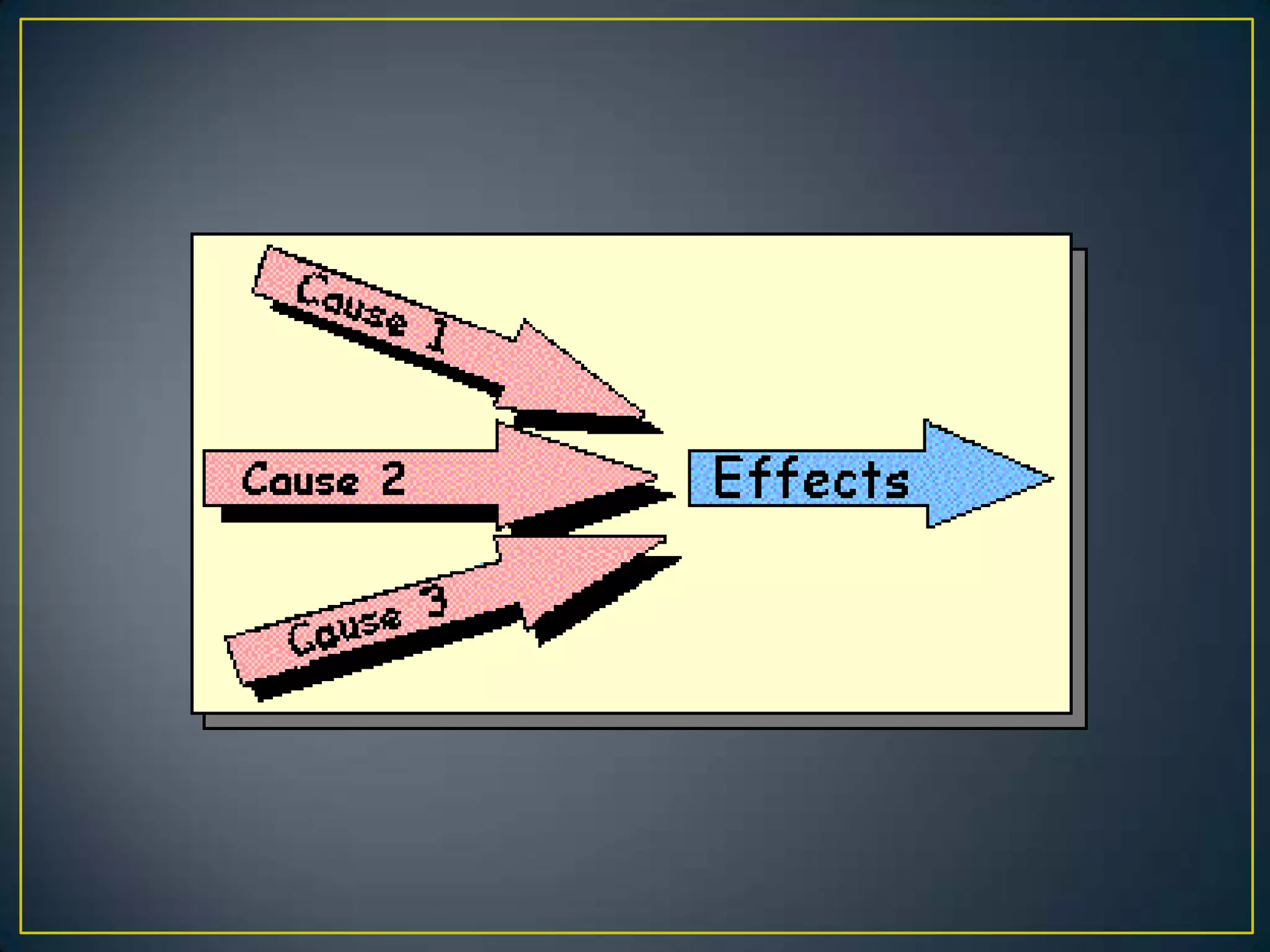
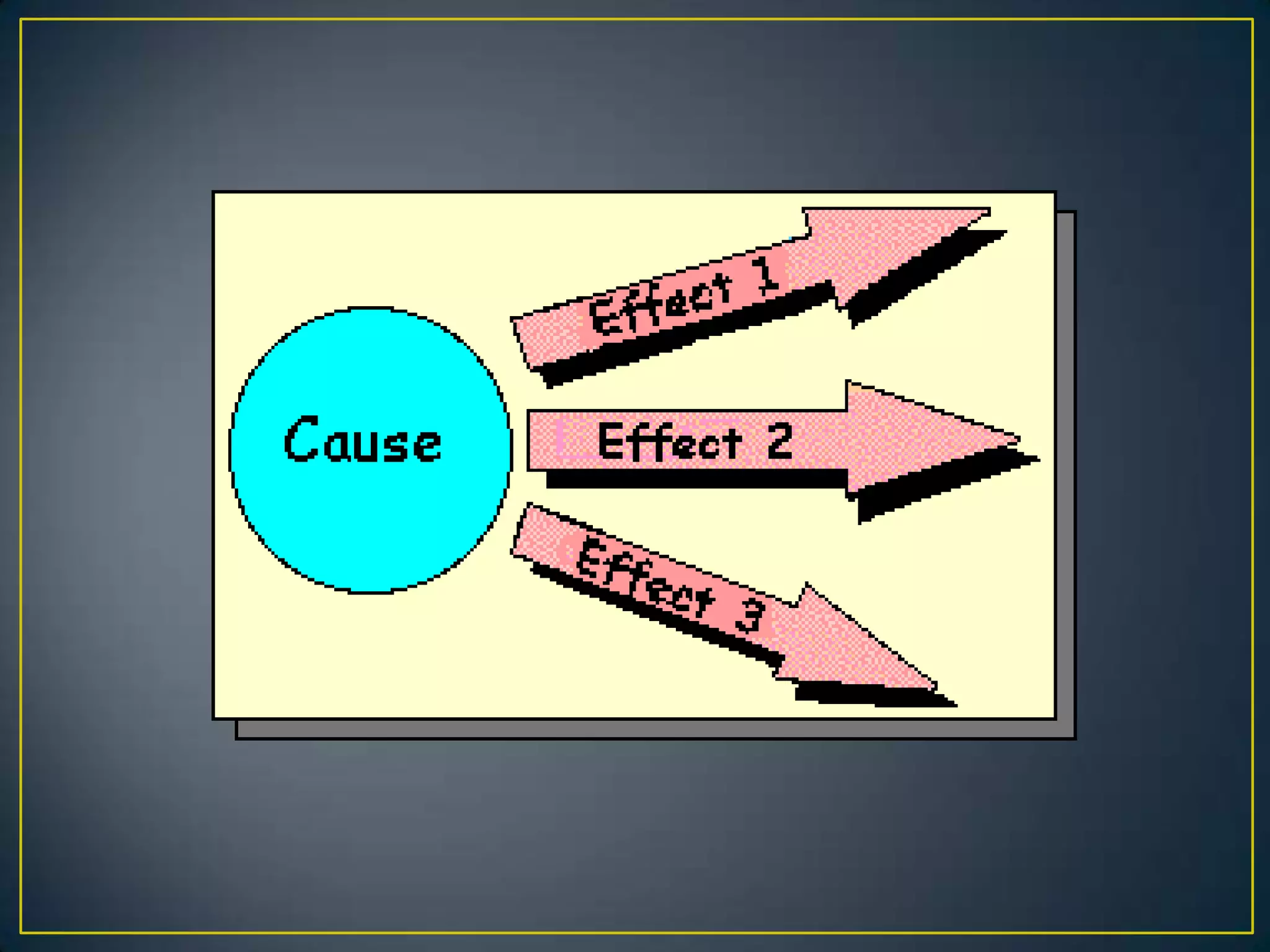
This document provides guidance on essay writing structure and types of essays. It explains that an essay has three main parts: an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction presents the topic and thesis. The body paragraphs develop the topic and support the thesis with evidence. The conclusion restates the thesis and main ideas. It also describes common essay types like descriptive, narrative, cause and effect, compare and contrast, process, expository, and persuasive essays. Each type has a distinct purpose and organizational structure.