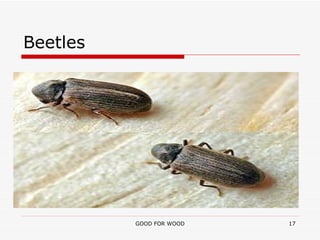
Wood is a precious natural resource that requires preservation to protect it from environmental factors like moisture and insects that can damage it over time. There are various types of wood preservatives that can be used, including solvent-borne and water-borne preservatives with different active ingredients like copper, chromium, and arsenic. It is important to choose preservatives based on their effectiveness, toxicity, and other characteristics to properly preserve wood and extend its usable lifespan.