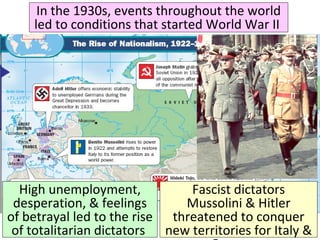
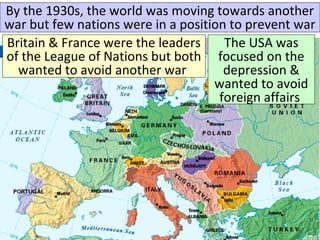
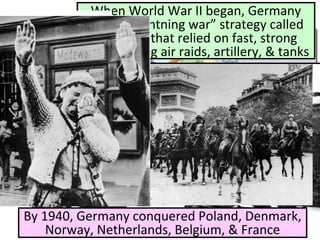
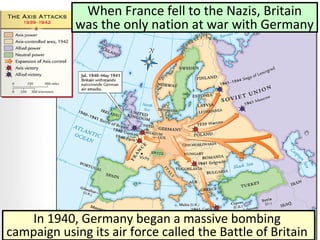
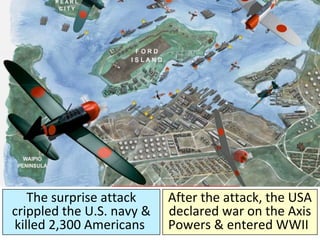
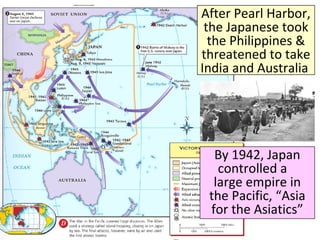
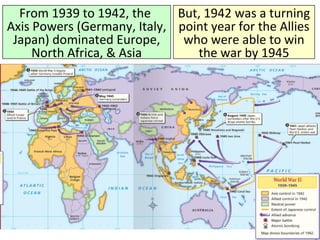
- From 1939-1942, Germany and its Axis allies conquered much of Europe and Asia, while Britain resisted the Nazis. The US initially remained neutral but entered the war after Japan's 1941 attack on Pearl Harbor.
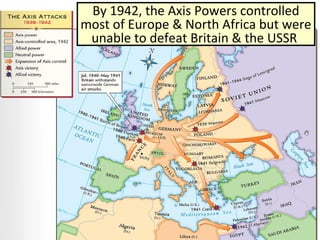
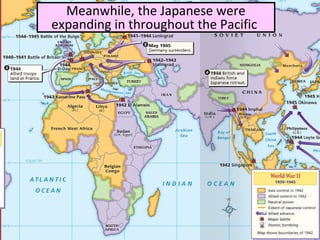
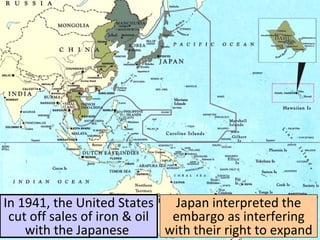
- By 1942, the Axis controlled Europe, North Africa, and Asia, but could not defeat the USSR or Britain. Meanwhile, Japan expanded its empire until the US embargo led to its attack on Pearl Harbor.
- This period saw major Axis victories but proved a turning point as Allied resistance stiffened and the US entered the war, shifting the momentum against Germany and Japan by 1945.