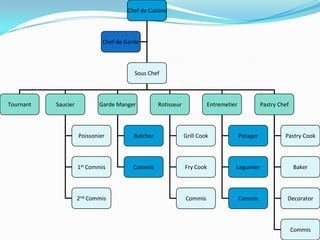
The document describes the brigade system used in professional kitchens to organize staff. It explains that chefs adopted the military's brigade system using a chain of command. Key positions include the chef de cuisine at the top followed by sous chefs, chef de garde, tournant and various station chefs overseeing areas like sauce, meat, fish, etc. Down the chain are commis assistants and cross training allows flexibility. Beyond the kitchen, departments include dining room, purchasing, and catering.