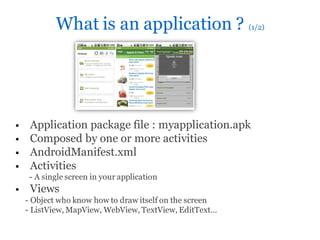
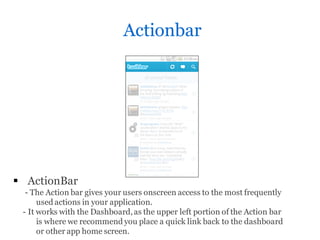
The document discusses best practices for developing Android applications, including an overview of Android and its components, tools for Android development in Java using the Android SDK, guidelines for designing user interfaces, and recommendations for common UI patterns like dashboards and action bars. It provides resources for documentation, help, icon templates, and prototyping tools to help developers code well-designed Android apps.