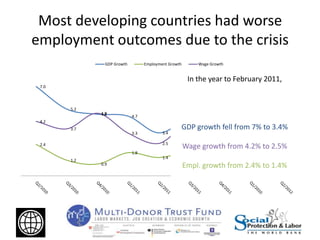
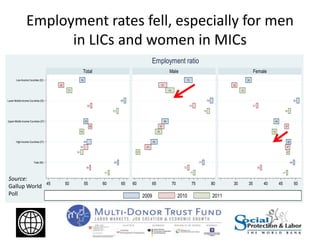
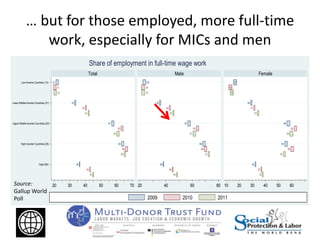
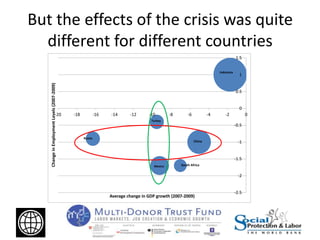
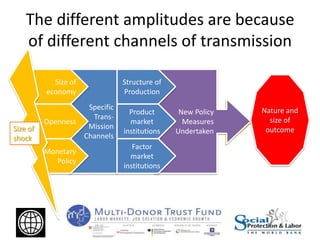
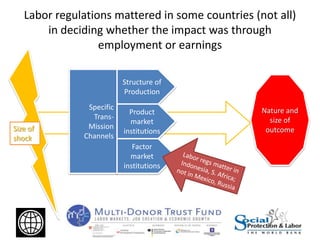
The Great Recession had mostly negative impacts on employment outcomes and wage growth in developing countries. While GDP growth fell significantly between 2007-2009 in most countries, the effects varied based on factors like economic structure, openness, labor policies, and size of fiscal stimulus programs. Countries with larger, more open economies that relied heavily on exports saw bigger drops in employment levels compared to declines in GDP. Macroeconomic policies were more effective than labor market interventions in mitigating the crisis impacts. The document recommends using economic booms to strengthen social safety nets that can expand during downturns to protect the vulnerable.