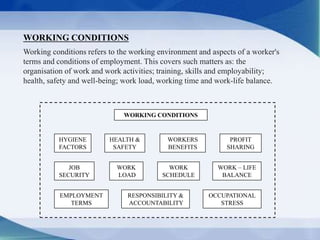
Working conditions refer to the working environment and aspects of a worker's employment terms and conditions. This covers matters like work organization, health and safety, workload, work schedules, and work-life balance. The document discusses several low-cost facilities that can improve working conditions and productivity, such as providing clean drinking water, adequate sanitation facilities, first aid kits, rest areas, and canteens serving nutritious meals. It also suggests transport and childcare facilities to help workers balance their work and personal lives.