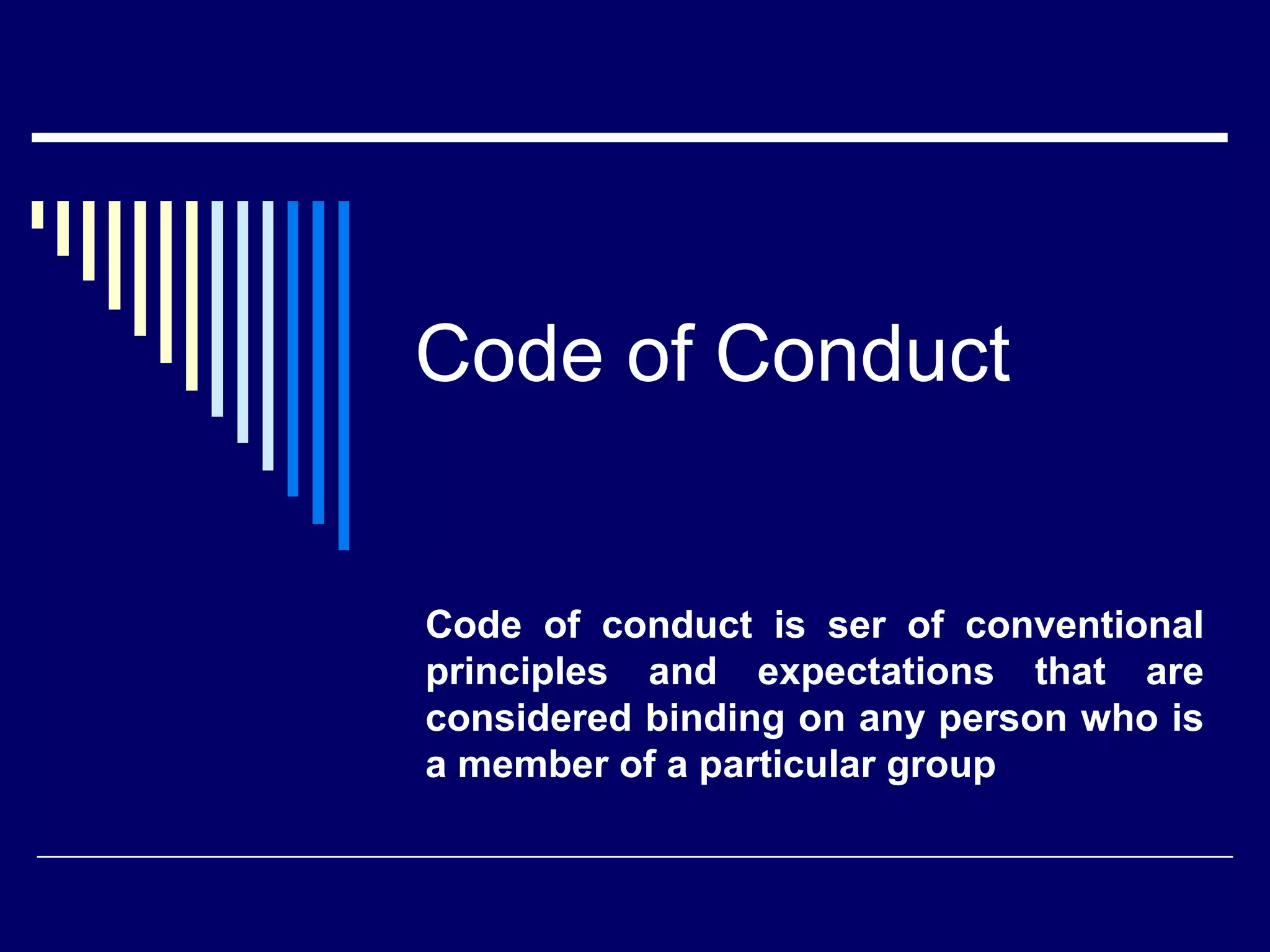
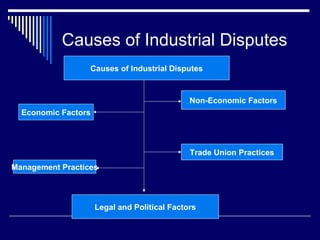
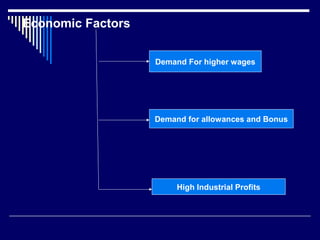
The document discusses codes of conduct, their key features, and factors that guide codes of conduct. It also discusses industrial conflicts, their nature, causes, and economic, non-economic, management, trade union, and legal/political factors that can cause industrial disputes. The code of conduct establishes principles and expectations for group members. It aims to prevent disputes through voluntary self-discipline and cooperation between workers and management. Economic factors that can cause industrial disputes include demands for higher wages and profits, while non-economic factors include working conditions and political issues.