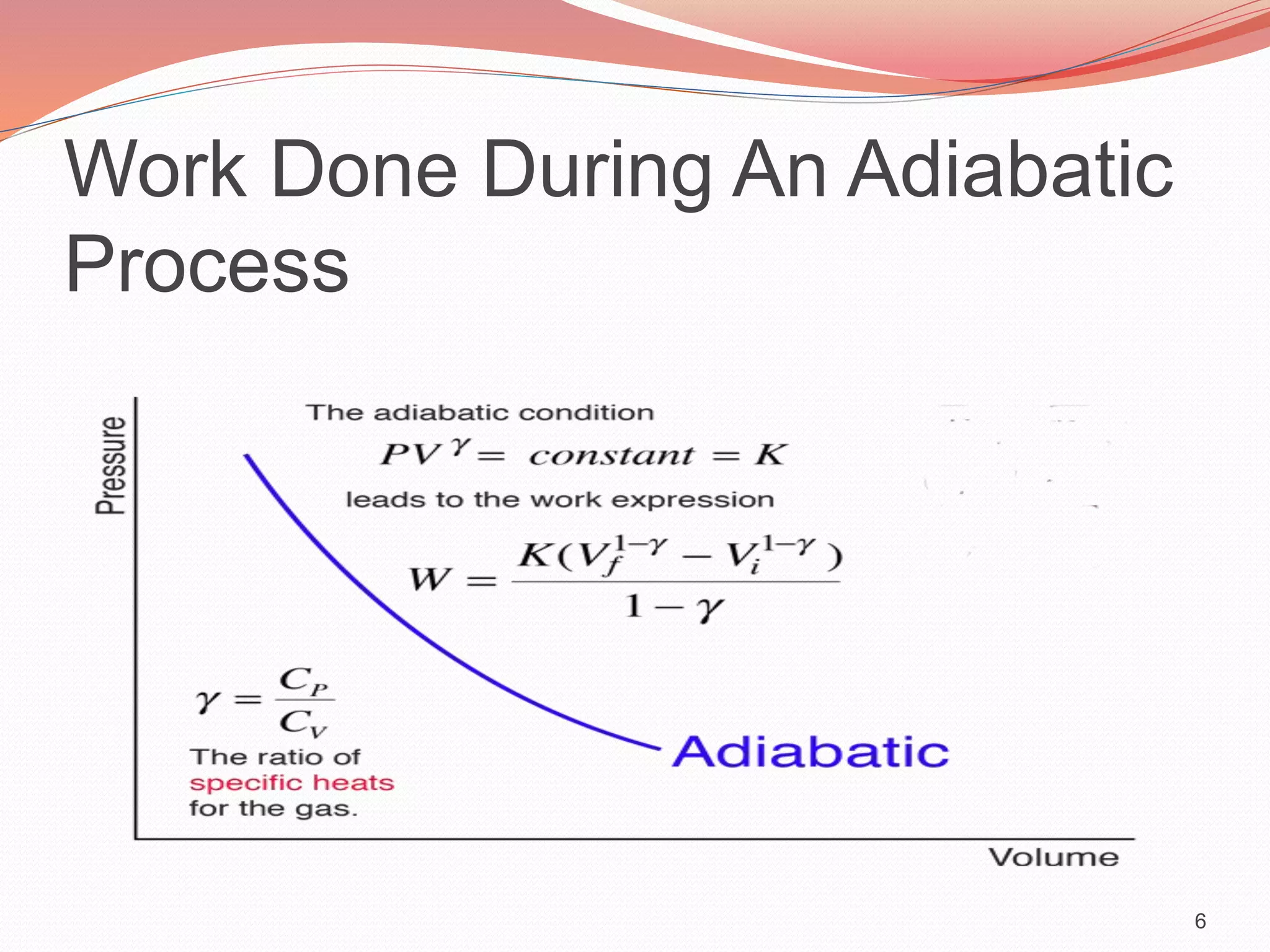
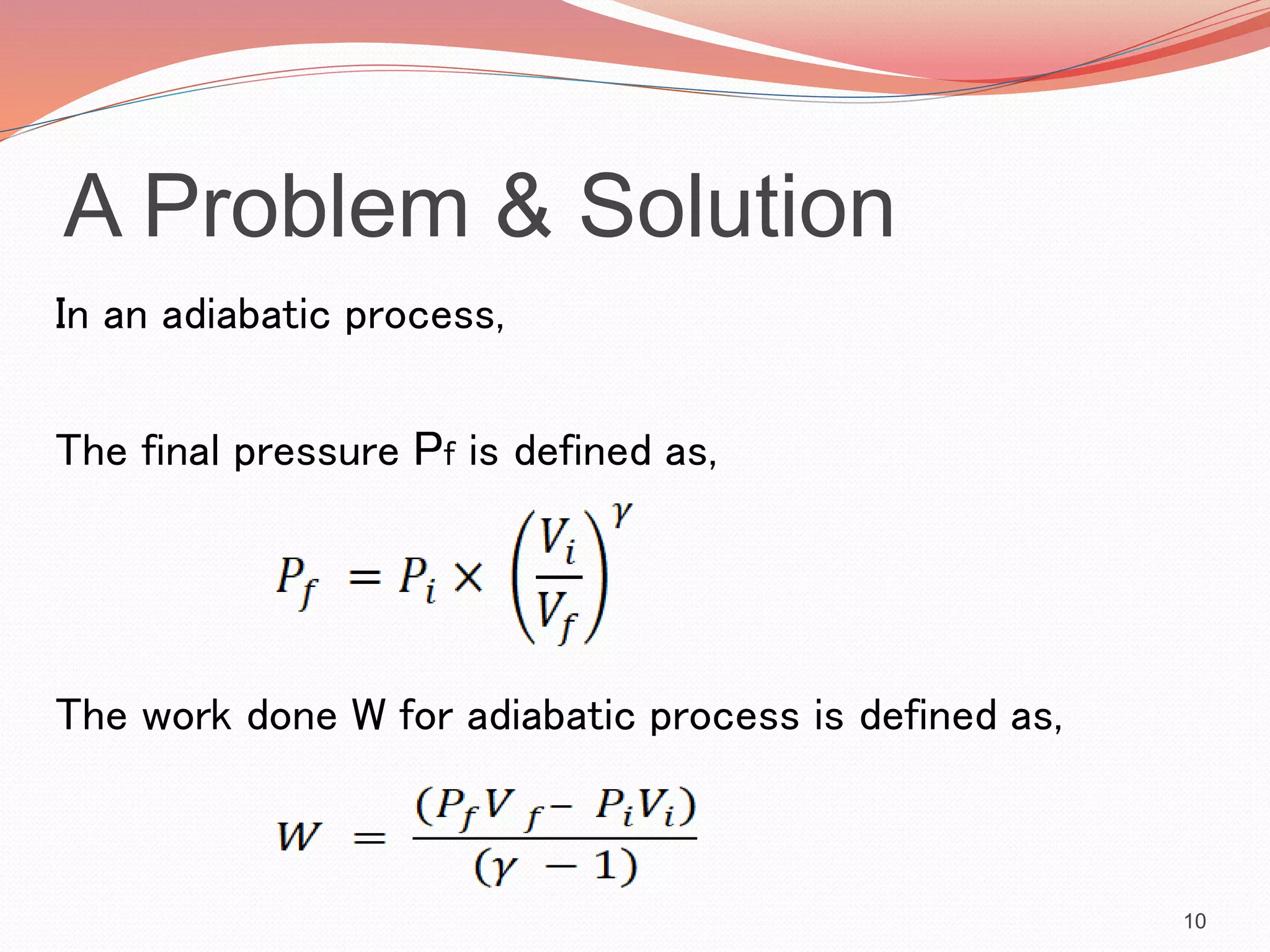
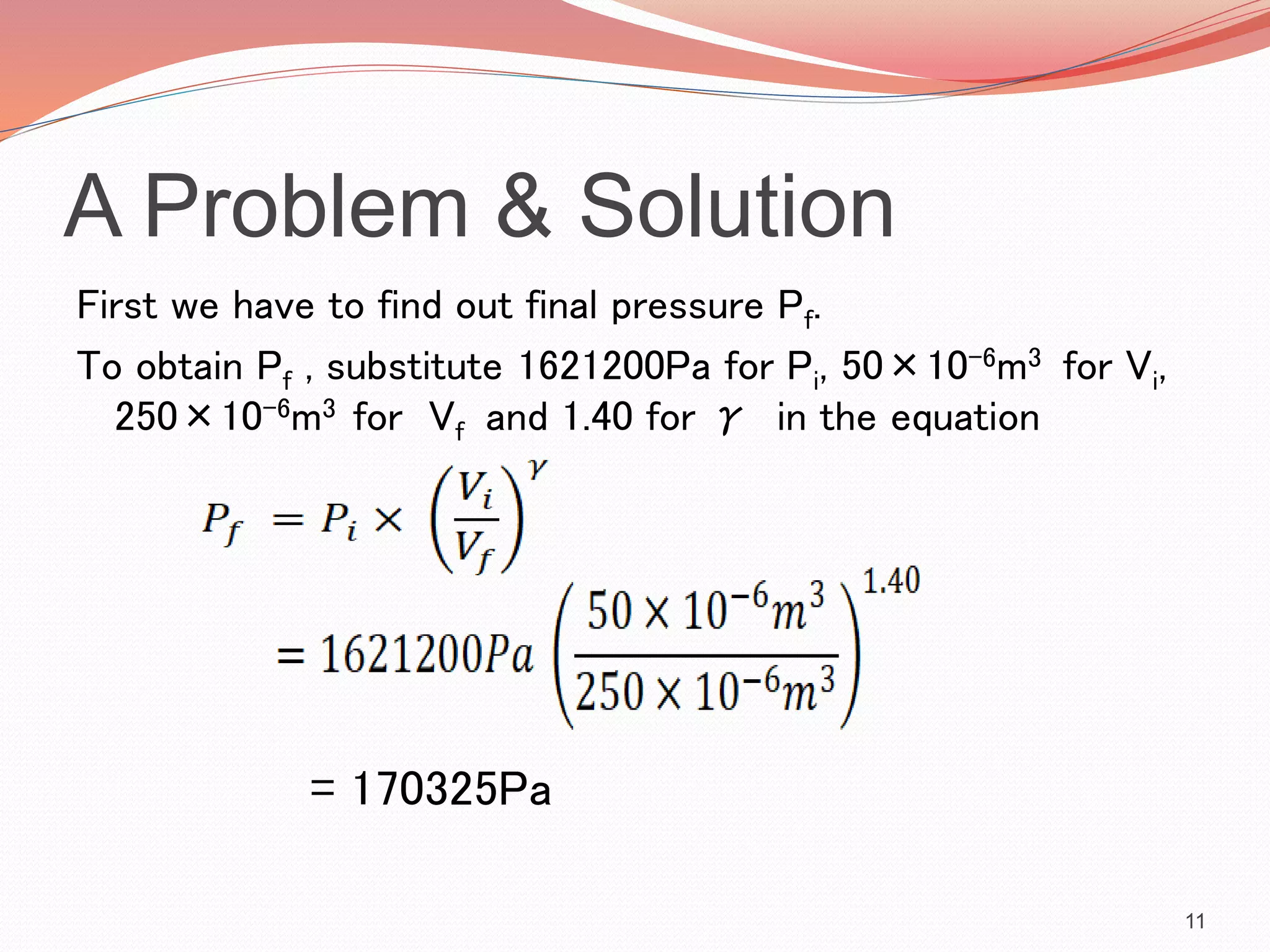
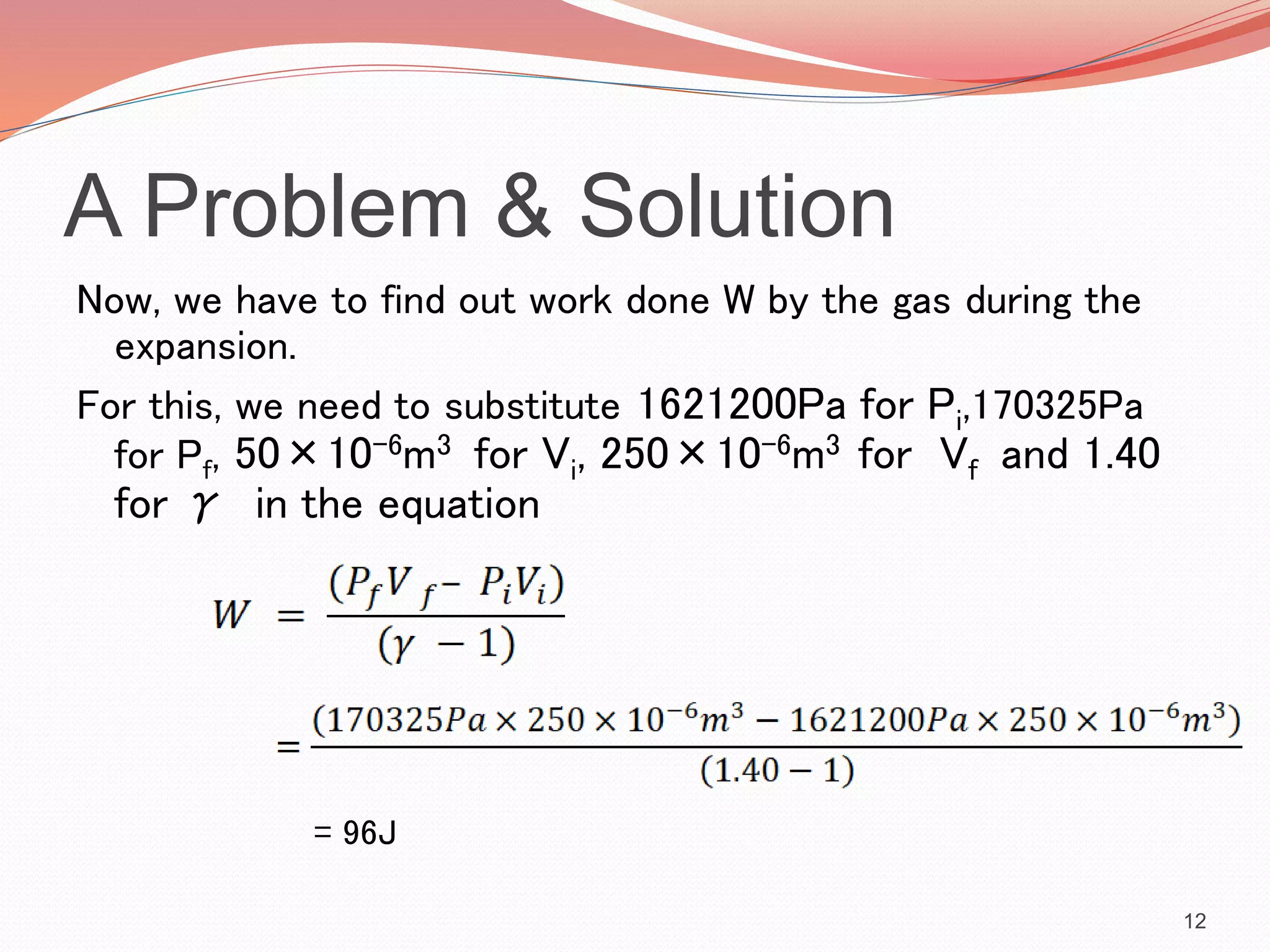
This presentation discusses work done during adiabatic processes. It defines key terms like work, adiabatic processes, adiabatic expansion and compression. As an example, it calculates the average power involved when a motorcycle engine undergoes adiabatic expansion each cycle at 4000 RPM. Using the initial and final volumes and pressures, it determines the work done is 96J per cycle. Given the engine speed, it then calculates the average power over time as 12800W.