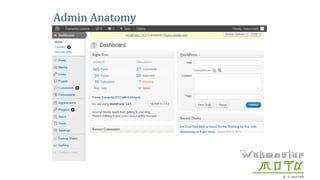
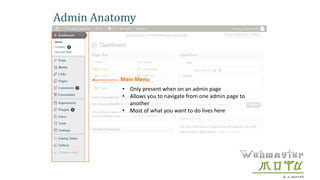
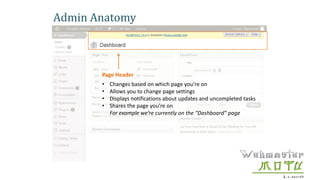
- The document provides an overview of WordPress, including what it is, how it works, and how to modify a WordPress website.
- WordPress is a free content management system that allows users to easily create and manage website content without coding. Over 20% of websites use WordPress.
- The document demonstrates how to perform common WordPress tasks like adding users, writing and formatting posts/pages, uploading images and files, and getting help resources.