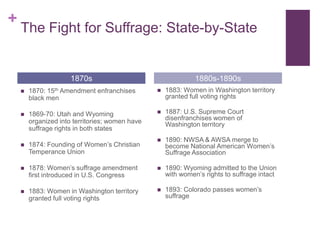
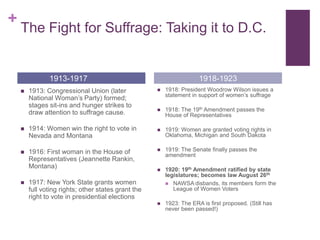
The document summarizes the history of the women's suffrage movement in the United States from the late 18th century to the ratification of the 19th Amendment in 1920. It discusses early organizing efforts in the 1800s, the state-by-state fight for voting rights, and the final push to pass an amendment at the federal level during World War 1. It also notes how changing gender roles, the rise of consumerism, and women's expanding public roles contributed to the shifting social views that helped secure suffrage.