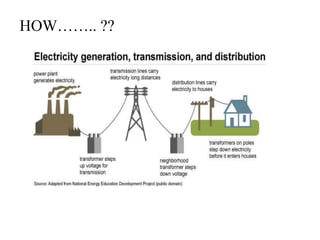
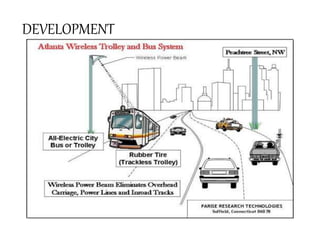
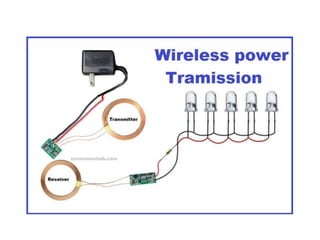
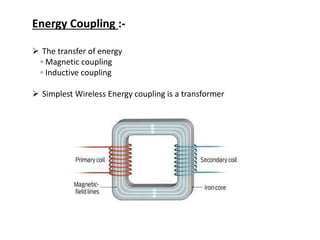
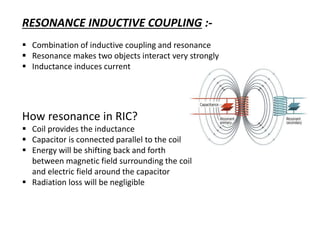
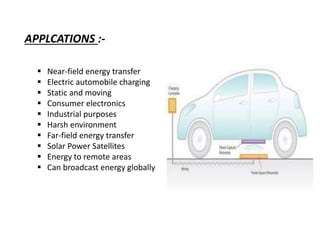
The document discusses wireless power transmission (WPT), detailing its definition, history, types, advantages, and applications. It highlights key technologies such as inductive coupling and resonant inductive coupling, and emphasizes the potential for reduced energy loss compared to traditional wired systems. The conclusion reflects on the efficiency and practicality of WPT, despite challenges like high initial costs and distance constraints.