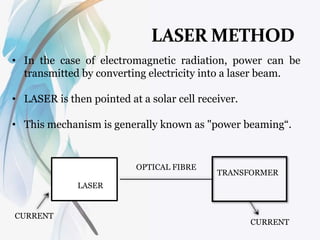
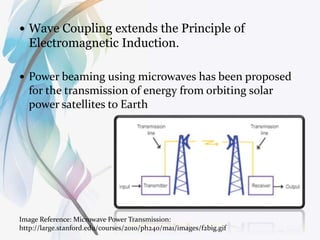
The document discusses wireless power transmission (WPT), explaining its definition, historical context, and various methods such as atmospheric conduction and electromagnetic induction. It highlights the benefits of WPT, including reduced energy loss compared to traditional wired systems, as well as challenges like cost and atmospheric interference. Various applications and future implications of WPT are also covered, emphasizing its potential to revolutionize energy transmission.