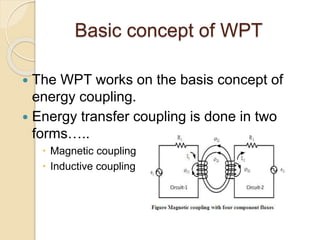
This document discusses wireless power transmission (WPT). It begins with an overview and objectives, then discusses the history of WPT from Tesla's experiments in the late 19th century. The document explains that WPT works via magnetic or inductive coupling and describes various methods like atmospheric conduction, microwave transmission, and laser transmission. It notes applications like electric vehicle charging and transmitting power to remote areas. In closing, it outlines advantages like efficiency and flexibility and disadvantages like high initial costs.