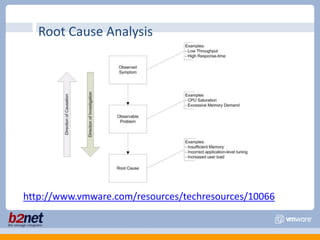
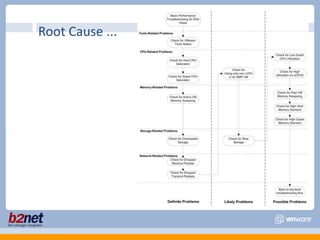
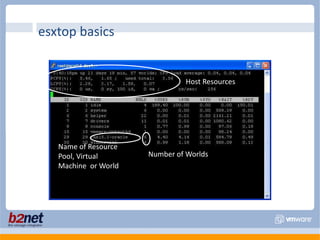
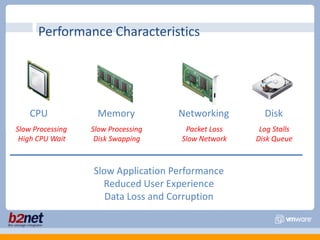
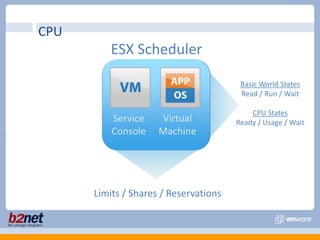
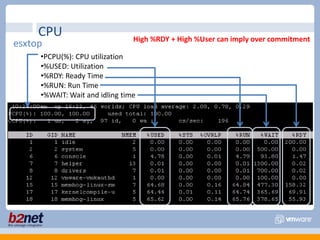
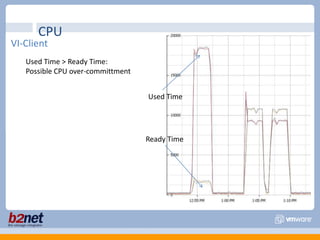
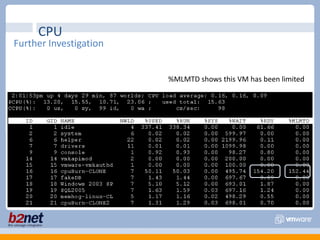
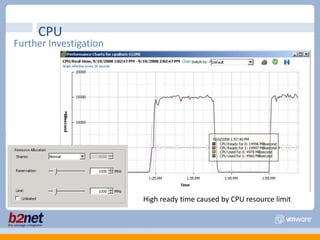
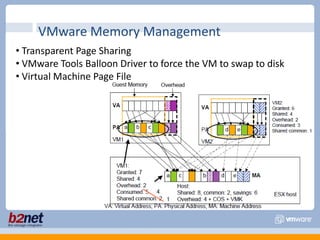
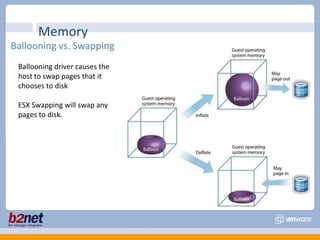
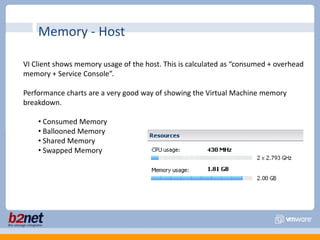
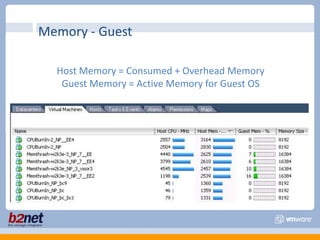
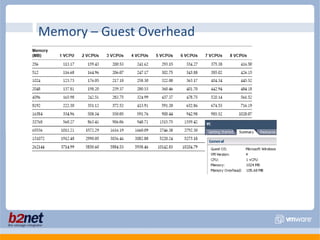
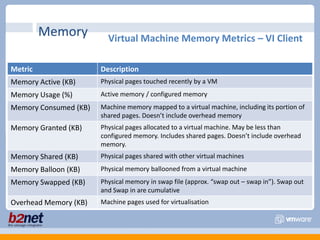
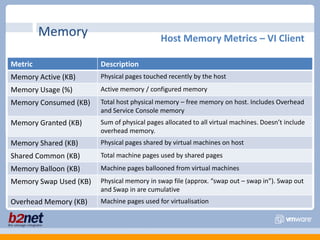
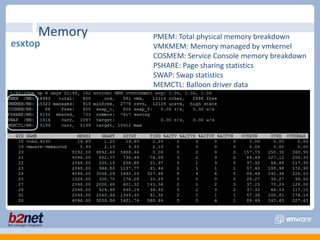
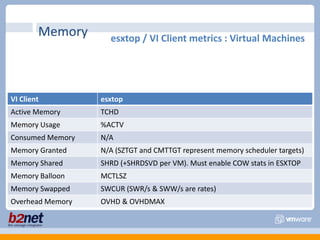
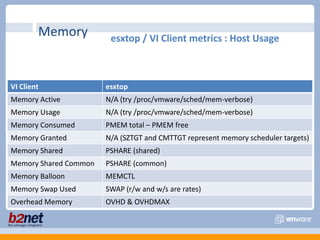
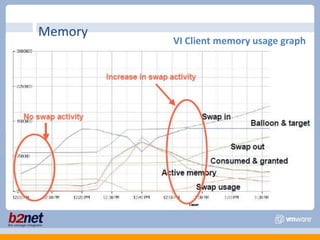
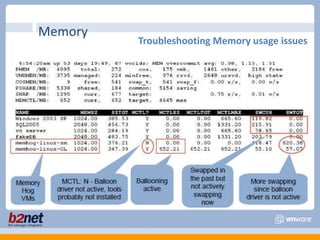
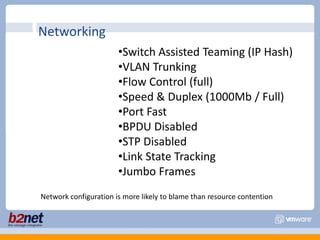
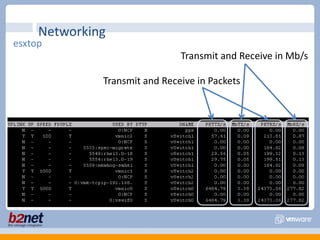
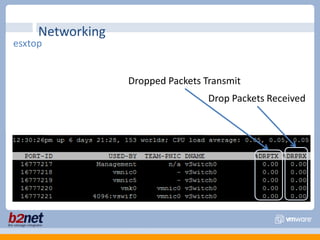
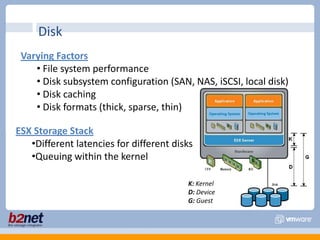
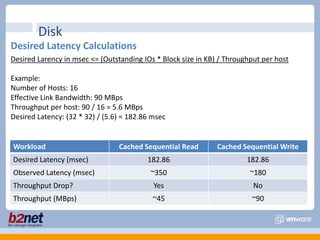
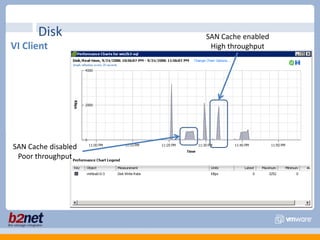
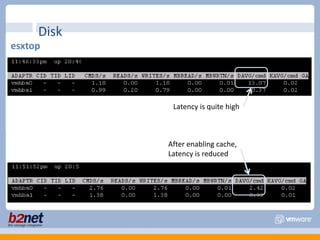
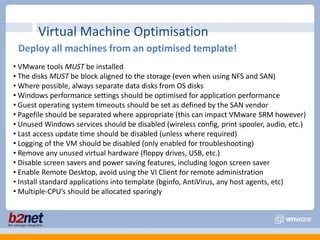
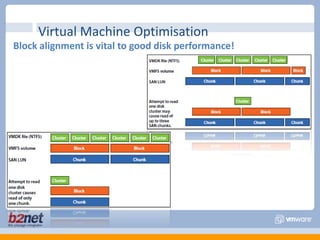
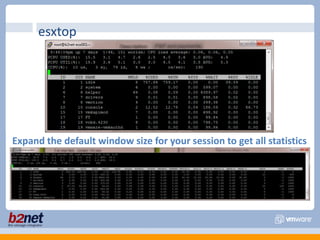
This document discusses VMware performance troubleshooting. It covers topics like root cause analysis, performance characteristics of CPU, memory, disk and networking, and tools like ESXTop, vm-support and the service console. It provides guidelines on capacity planning, virtual machine optimization and design best practices.