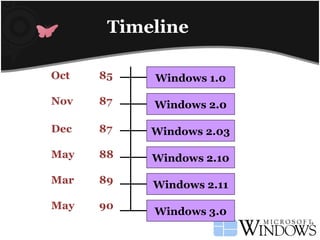
Windows 2.0 was a 16-bit graphical user interface released by Microsoft in October 1987 that allowed overlapping application windows. It introduced more keyboard shortcuts and terms like "Minimize" and "Maximize." Subsequent versions of Windows 2.0 improved support for Intel processors, memory management, and number of supported printers. Windows 2.11, the final version, added driver updates before being superseded by Windows 3.0 in May 1990.