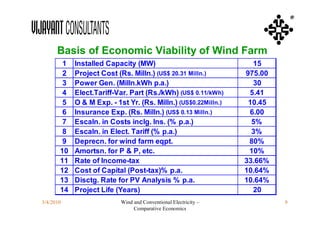
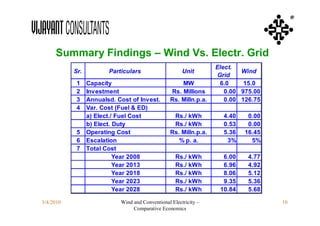
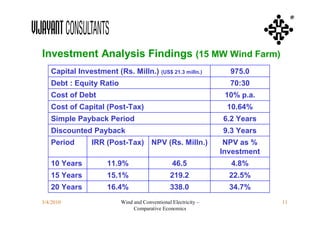
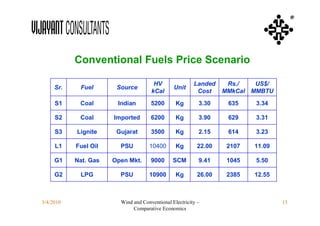
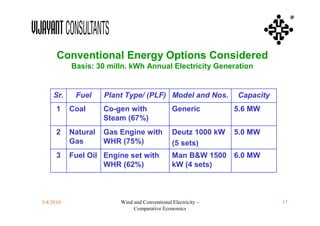
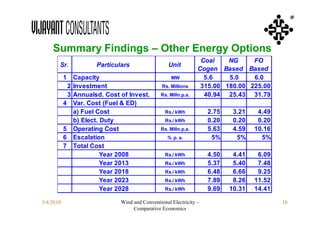
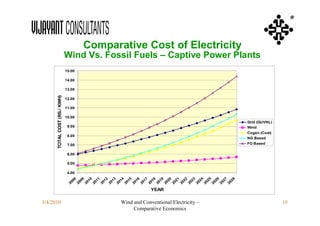
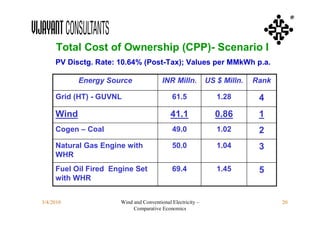
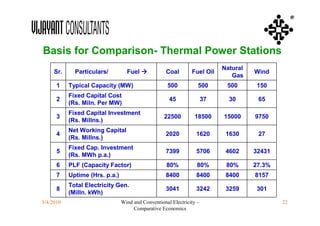
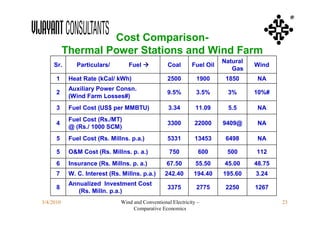
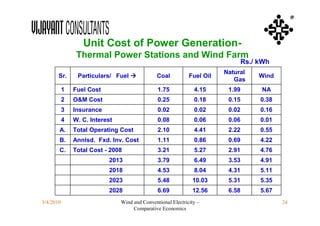
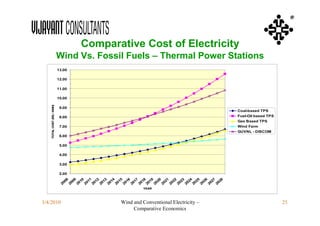
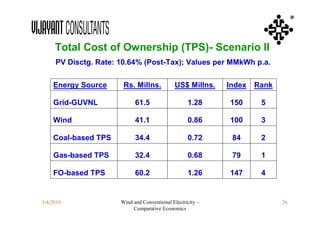
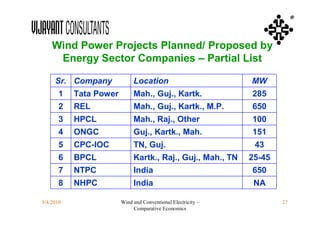
This document compares the economics of wind electricity to conventional electricity sources for captive power plants and utility companies. It presents the capital and operating costs of a 15 MW wind farm and different conventional options. Scenario I compares the levelized cost of electricity for wind vs. coal cogeneration, natural gas engines, and fuel oil engines for captive power plants over 20 years. Scenario II evaluates the costs for utility-scale coal, gas, and fuel oil plants vs. a 150 MW wind farm. The wind farm has lower lifetime costs per MWh than all fossil fuel options considered for both scenarios.