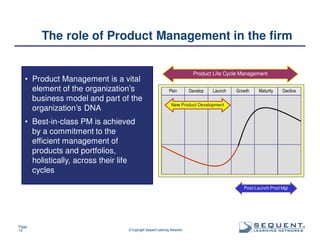
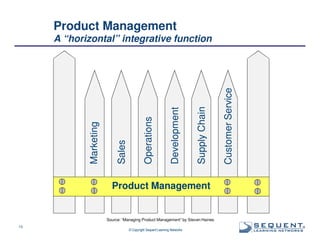
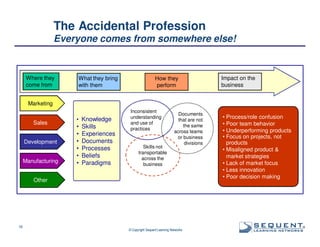
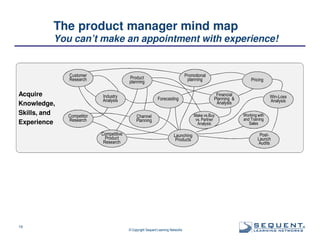
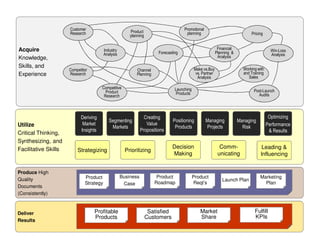
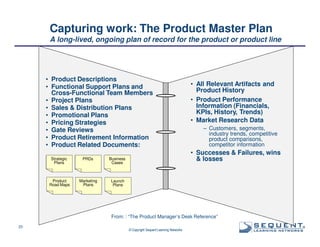
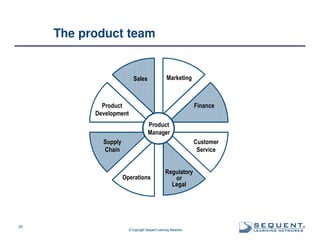
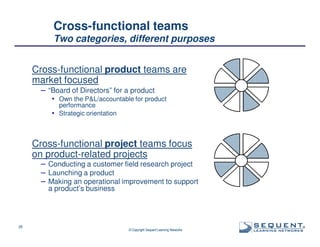
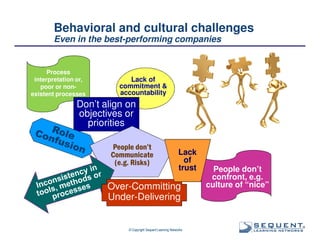
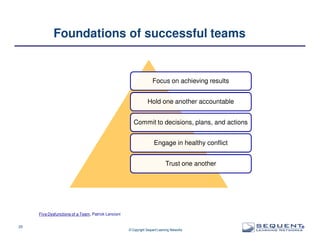
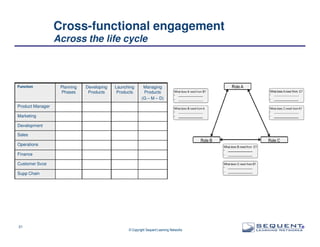
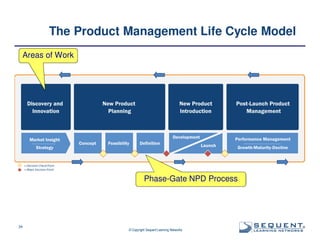
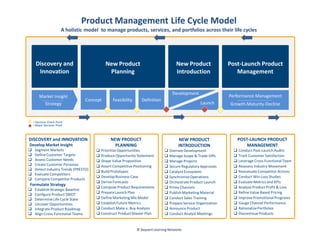
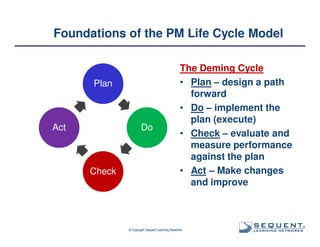
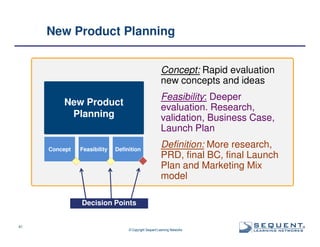
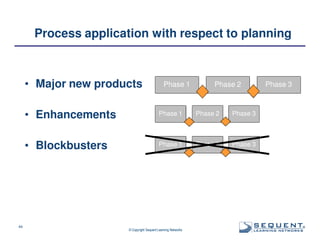
The document outlines the significance of product management and its role in enhancing organizational effectiveness and efficiency. It emphasizes that successful product management is integral to a company’s business model, requiring a commitment to holistic management across the product life cycle. The content also highlights the necessity for strong executive support and a structured governance framework to ensure that product managers can effectively fulfill their roles.