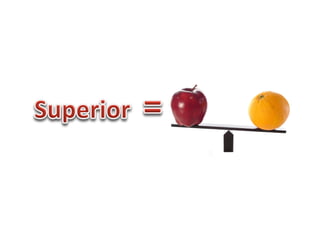
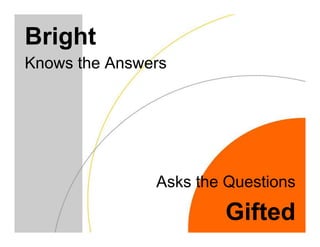
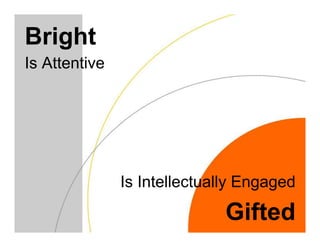
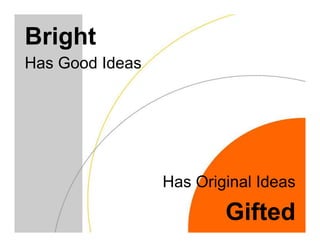
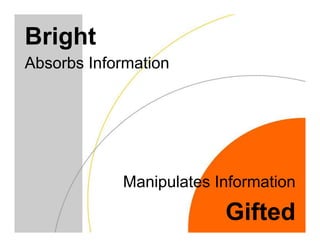
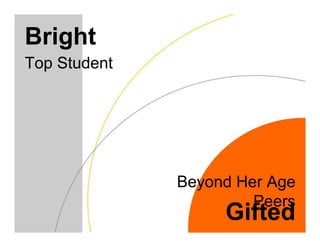
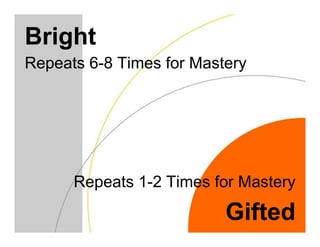
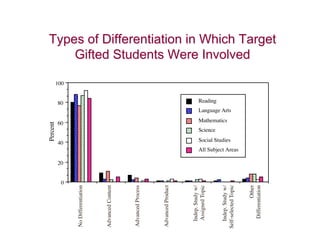
This document discusses academically and intellectually gifted students. It begins by noting that gifted students are highly diverse, with a wide variety of abilities, skills, backgrounds, and characteristics. The document then discusses common traits of gifted students, such as advanced language skills, reasoning ability, memory, and abstract/complex thinking. It also notes potential issues like asynchronous development and underachievement. The document emphasizes that giftedness manifests differently in each student and recommends differentiation strategies like curriculum compacting to meet student needs.