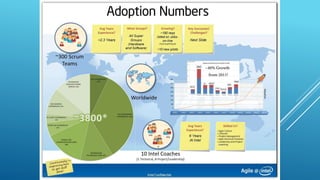
This document discusses how agile principles can help teams that are facing challenges or are in "fire fighting" mode. It recommends focusing on eliminating waste, building quality in, reducing cycle times, continuously learning and improving, making data-driven decisions, engaging everyone on the team, and optimizing the entire system. When coming in to assist a struggling team, the author recommends directly observing the team to understand their needs and culture, using visual tools, gaining management support, establishing a consistent cadence for iterations and reflection, managing interrupts, and celebrating results. The overall message is that agile principles of inspecting and adapting the process as needed can help rescue teams facing difficulties if implemented correctly.