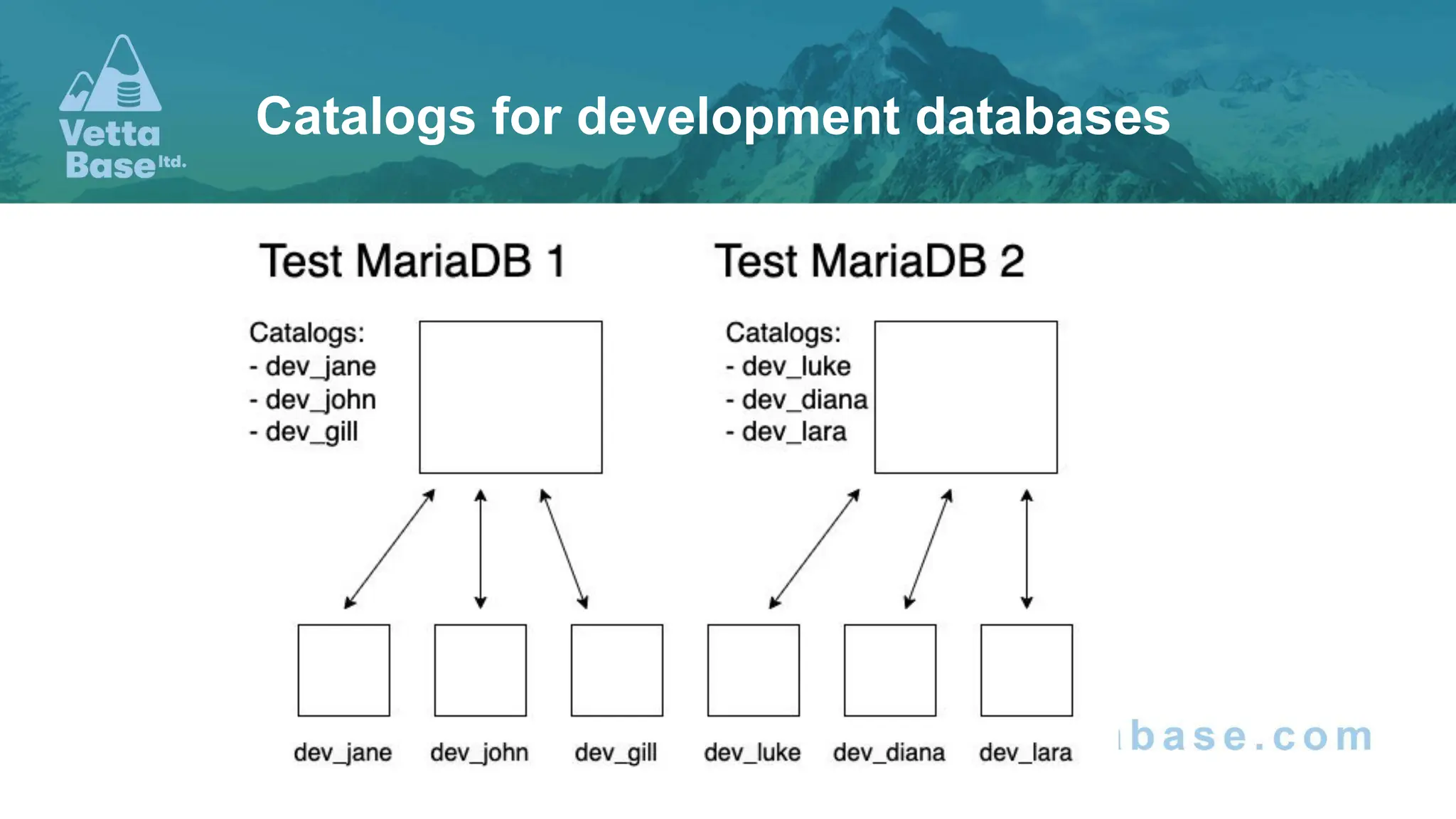
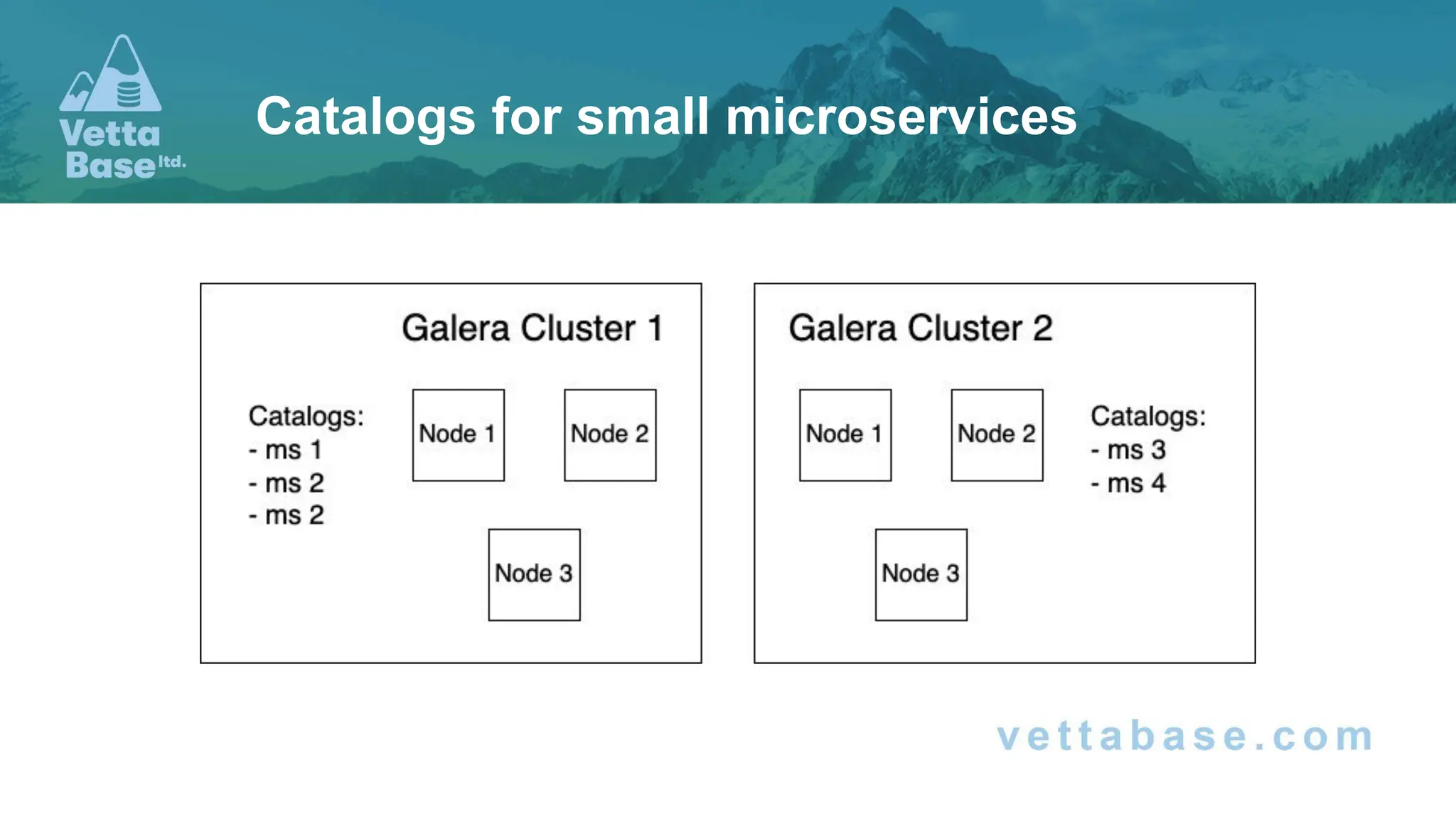
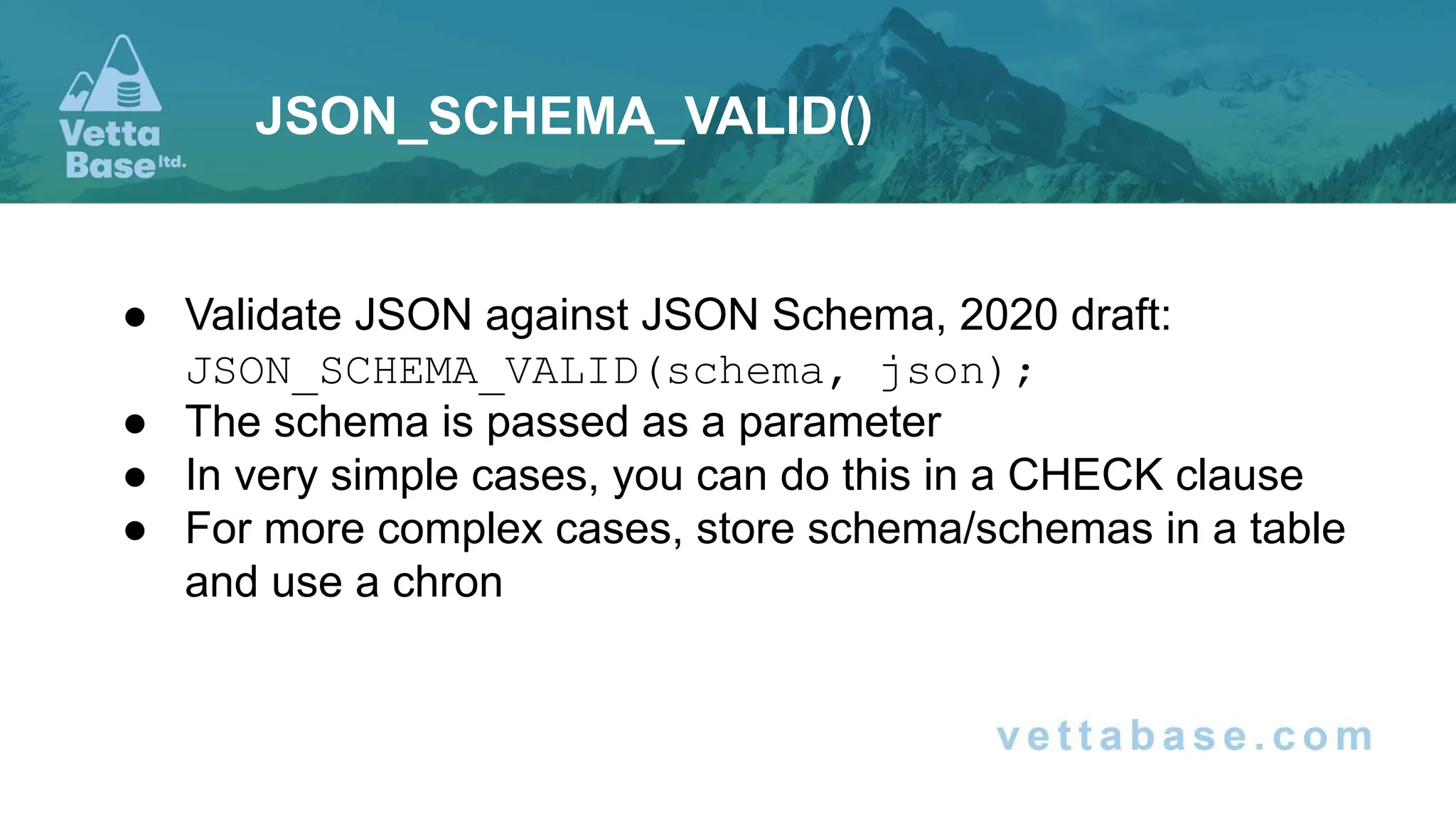
The document discusses new features in MariaDB 11.x, including the introduction of catalogs that offer improved isolation for databases and schemas, and enhanced support for microservices. Key updates include non-locking alter table operations, automatic SSL configuration, and new JSON functions for enhanced data manipulation. Additionally, changes to the optimizer and added capabilities for monitoring query performance are highlighted.






























![● JSON_OBJECT_FILTER_KEYS(obj, array_keys)
Returns an object with only the keys that are in the array
● JSON_OBJECT_TO_ARRAY(obj)
Transforms an object into an array in the form:
[ ["key1", "value1"], … ]
● JSON_ARRAY_INTERSECT(array1, array2)
Returns the intersection of 2 arrays
MDEV-26182
More JSON functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-afirstlookatmariadb11-231124084755-5f8ec69e/75/A-first-look-at-MariaDB-11-x-features-and-ideas-on-how-to-use-them-34-2048.jpg)

