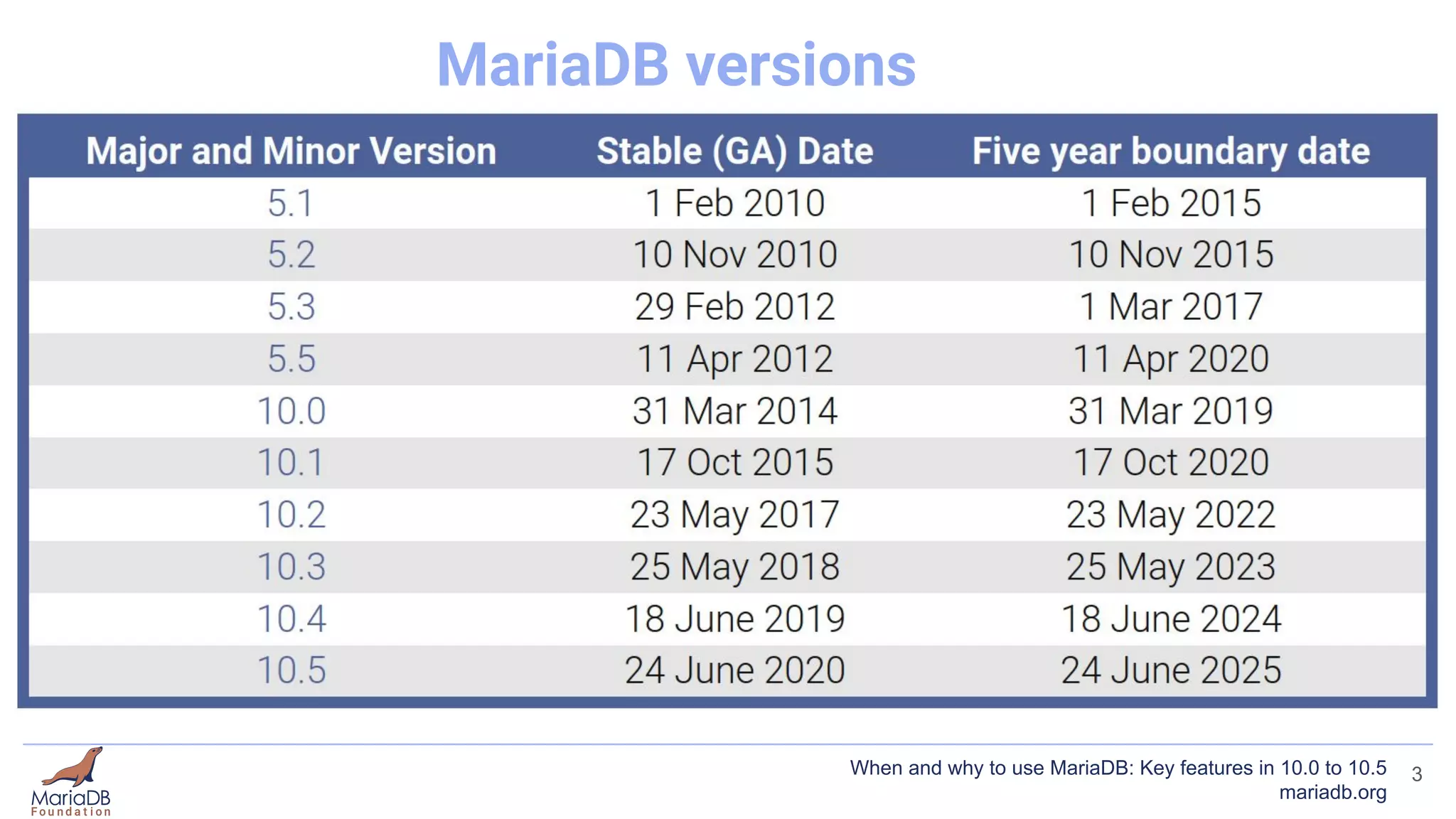
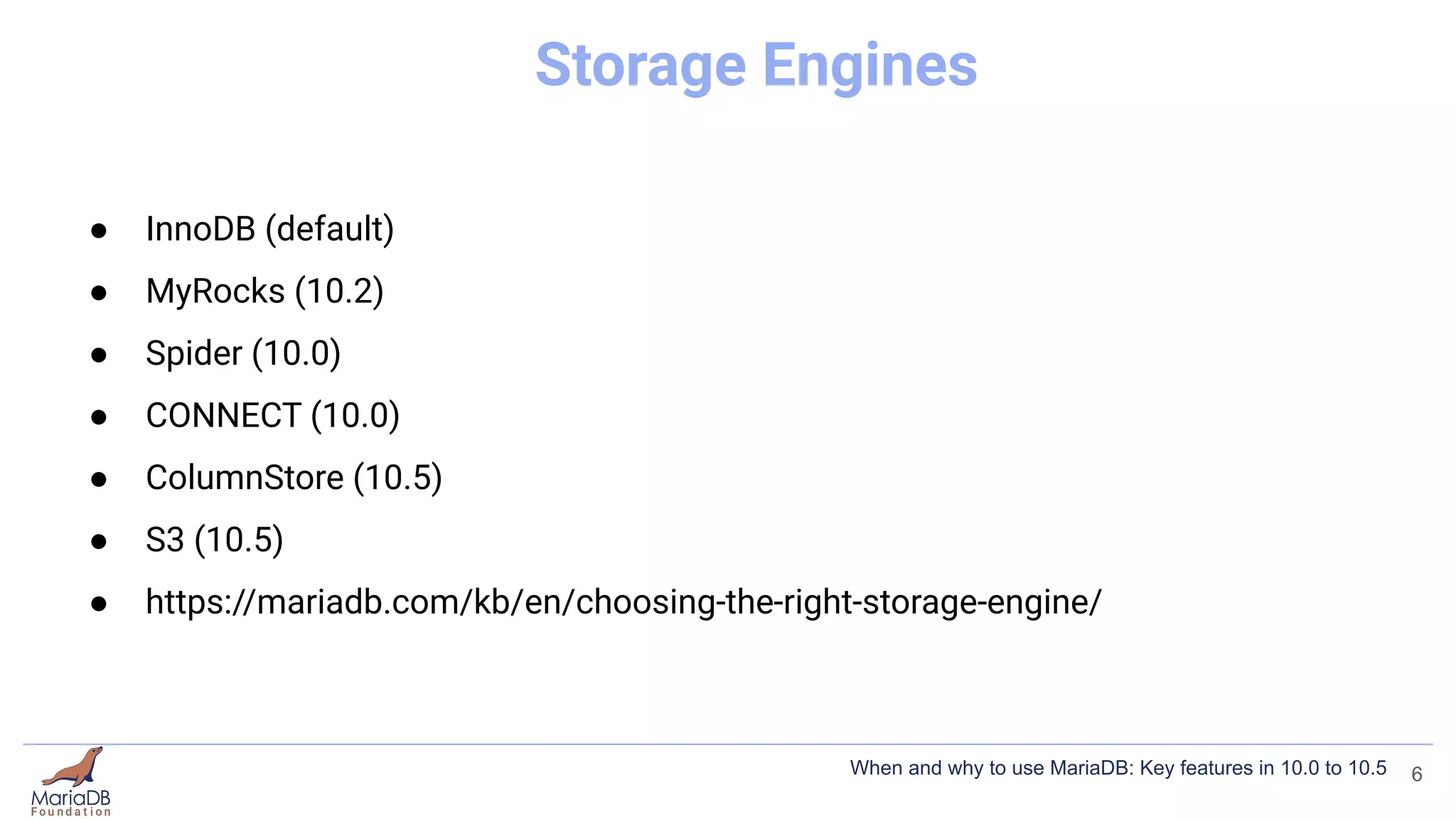
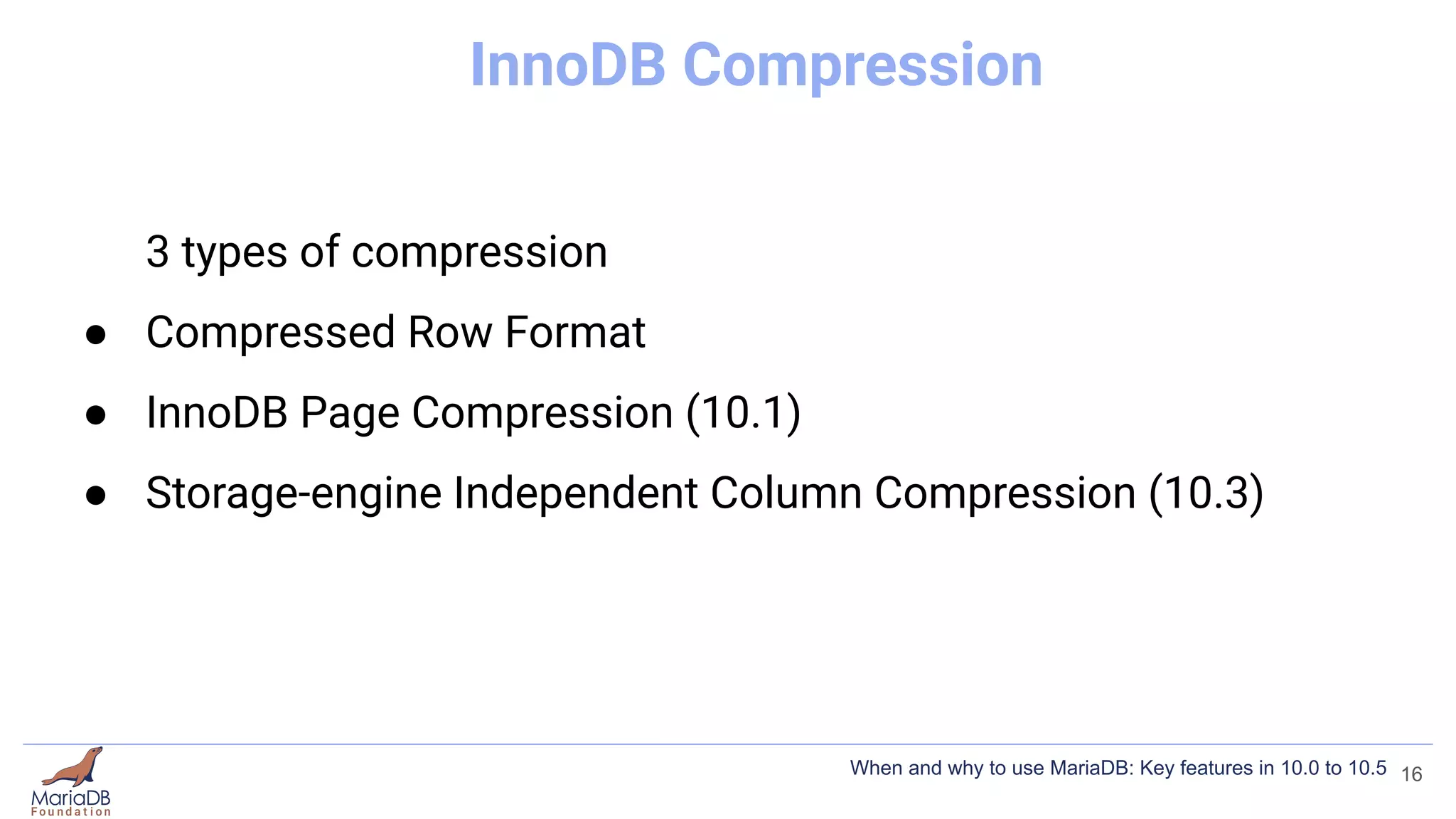
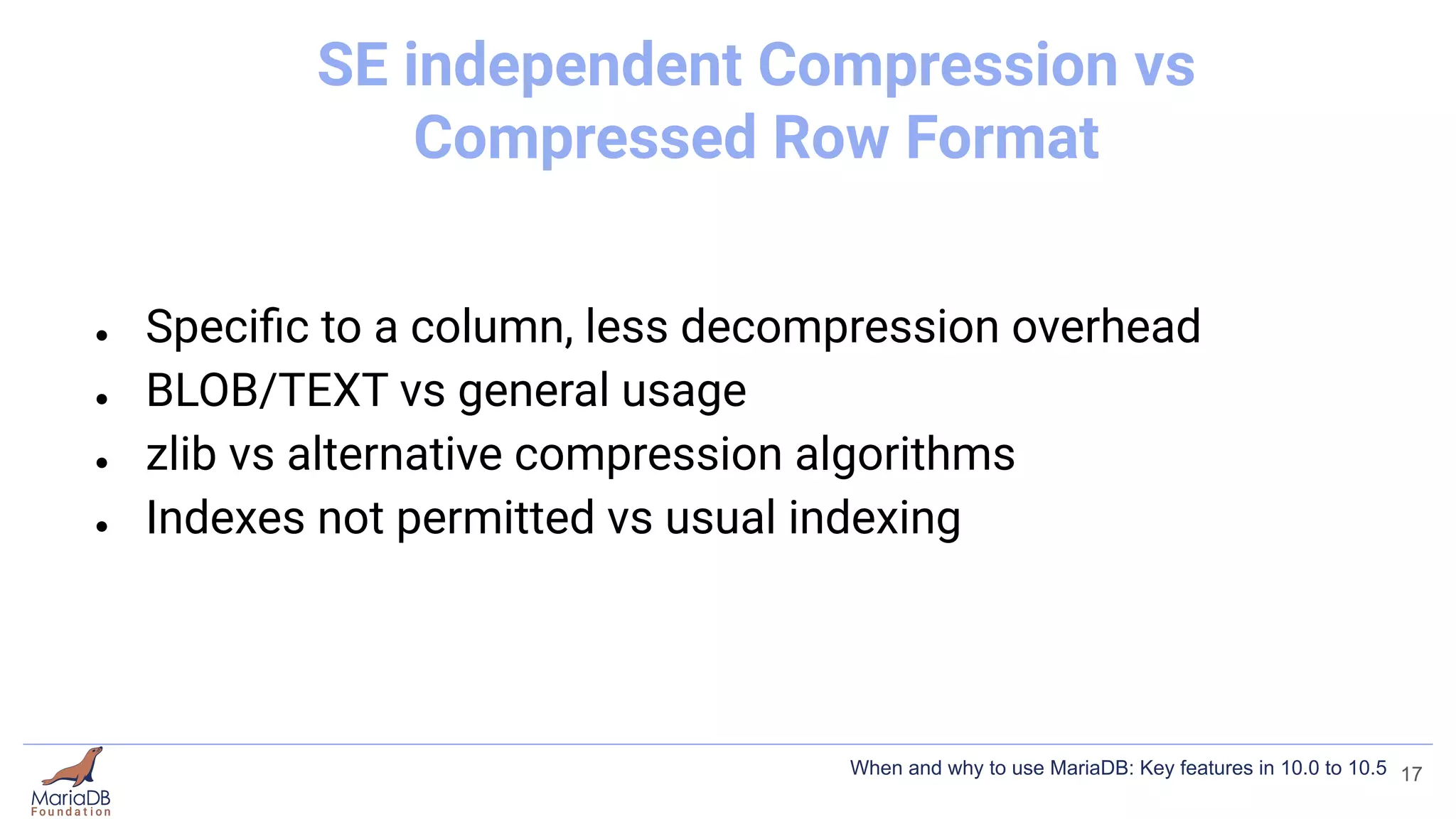
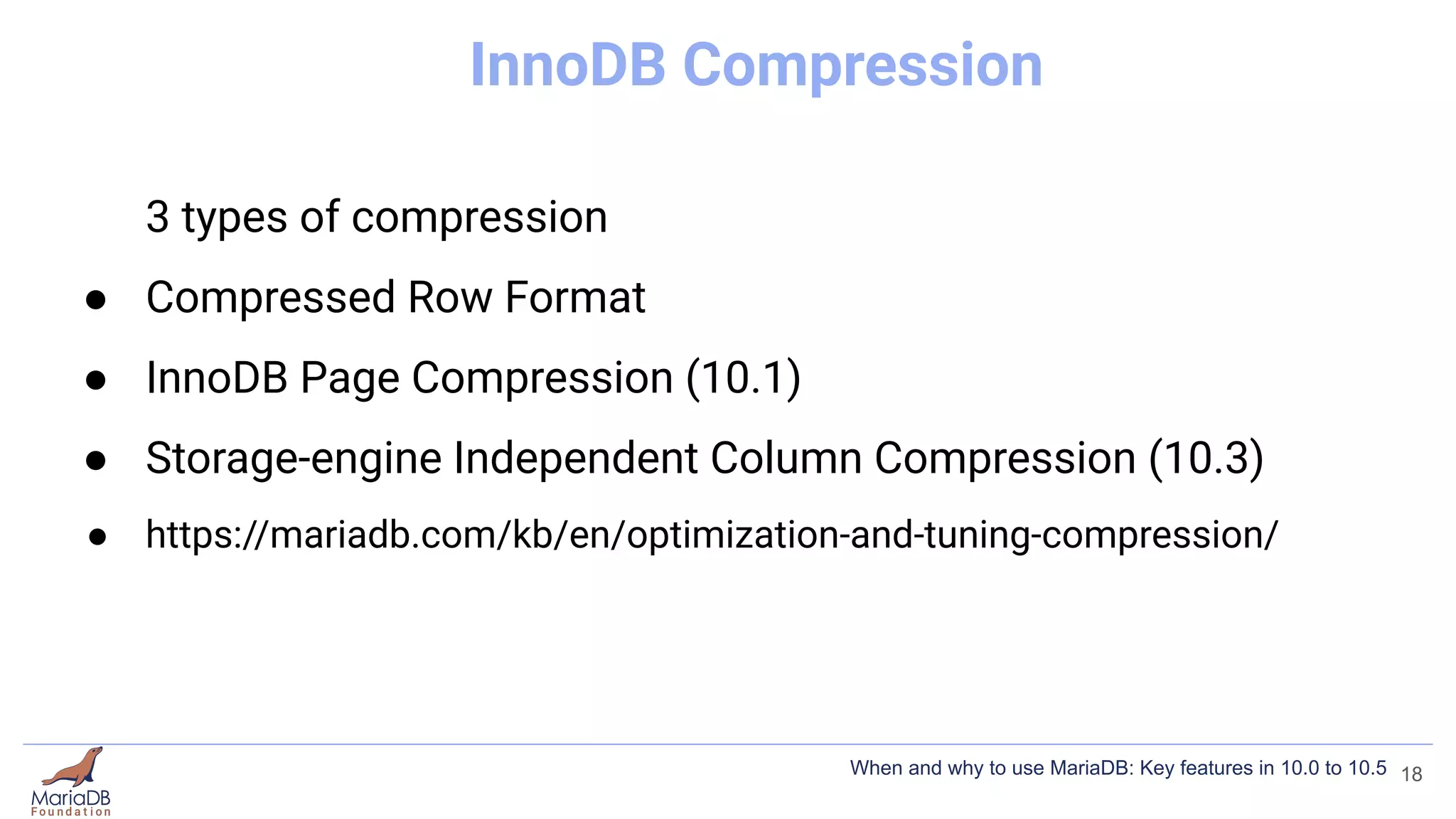
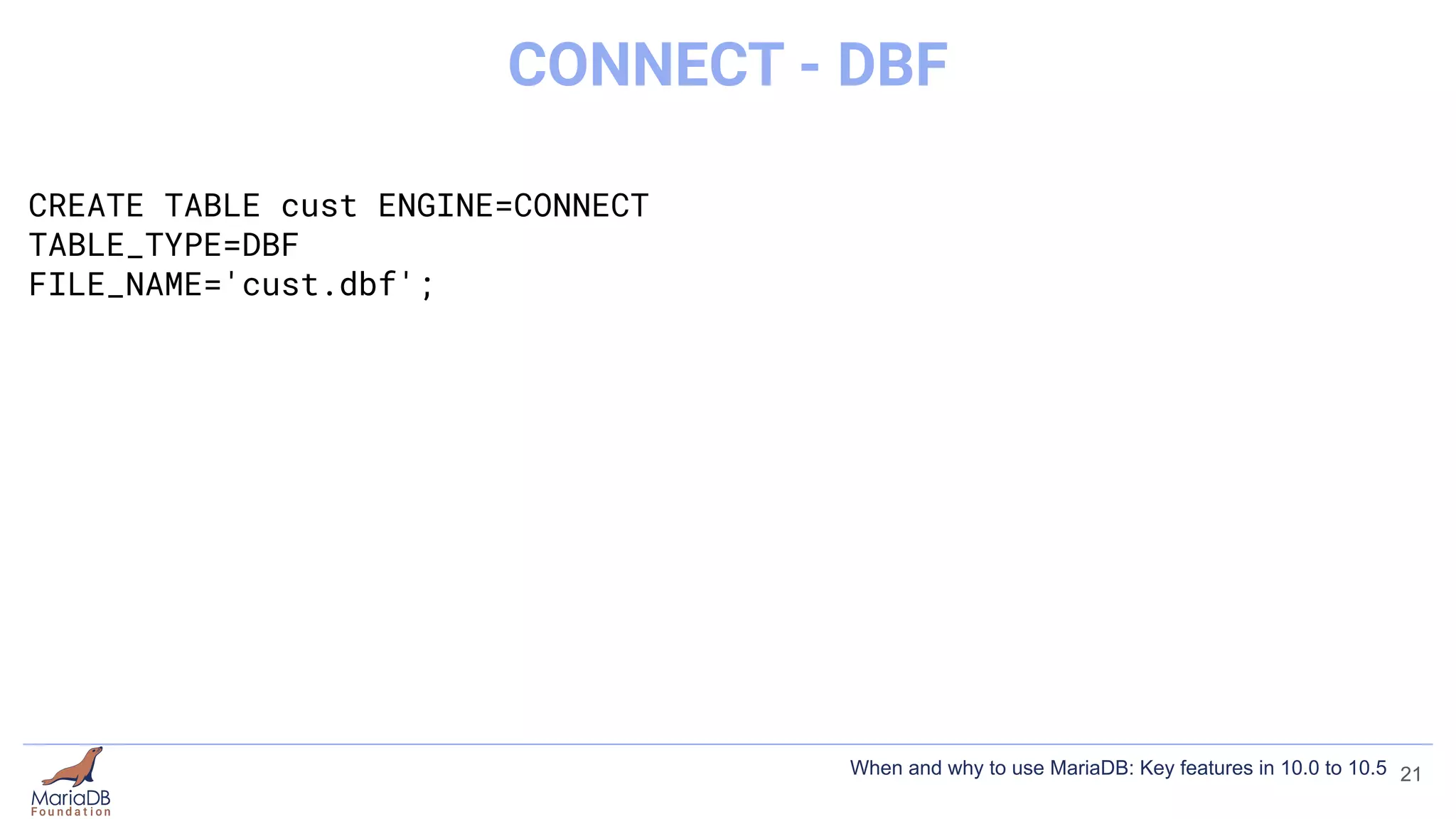
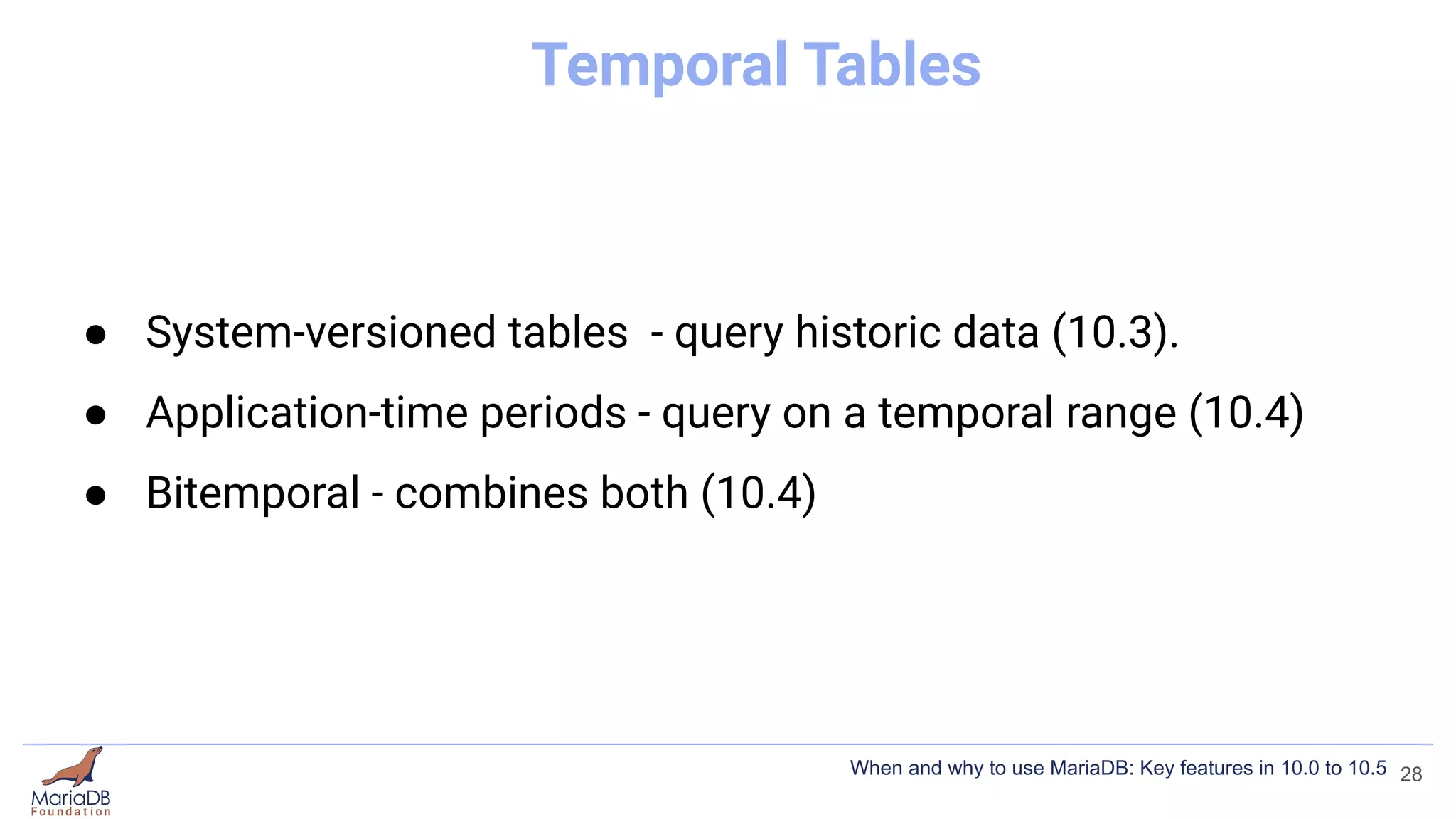
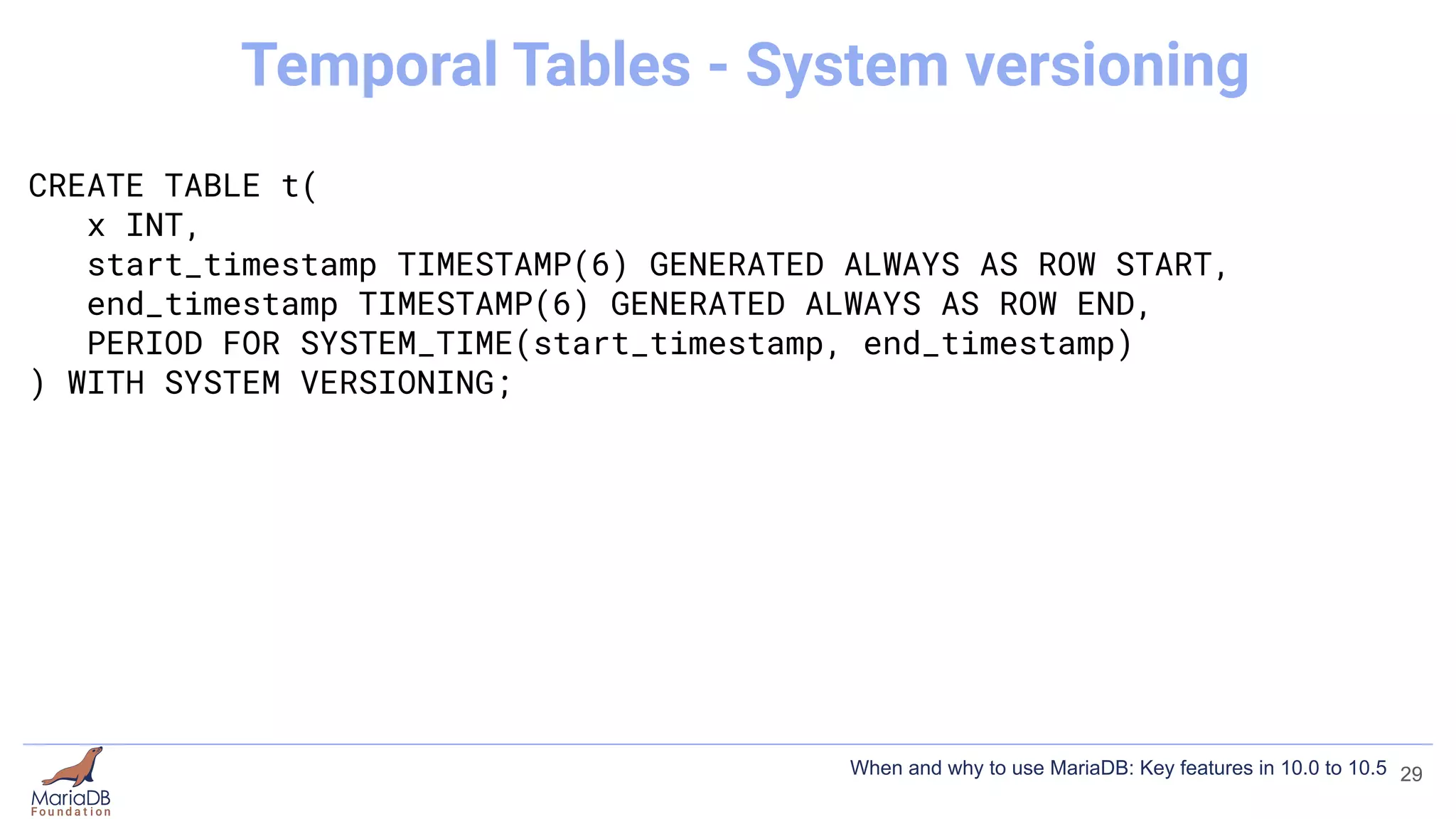
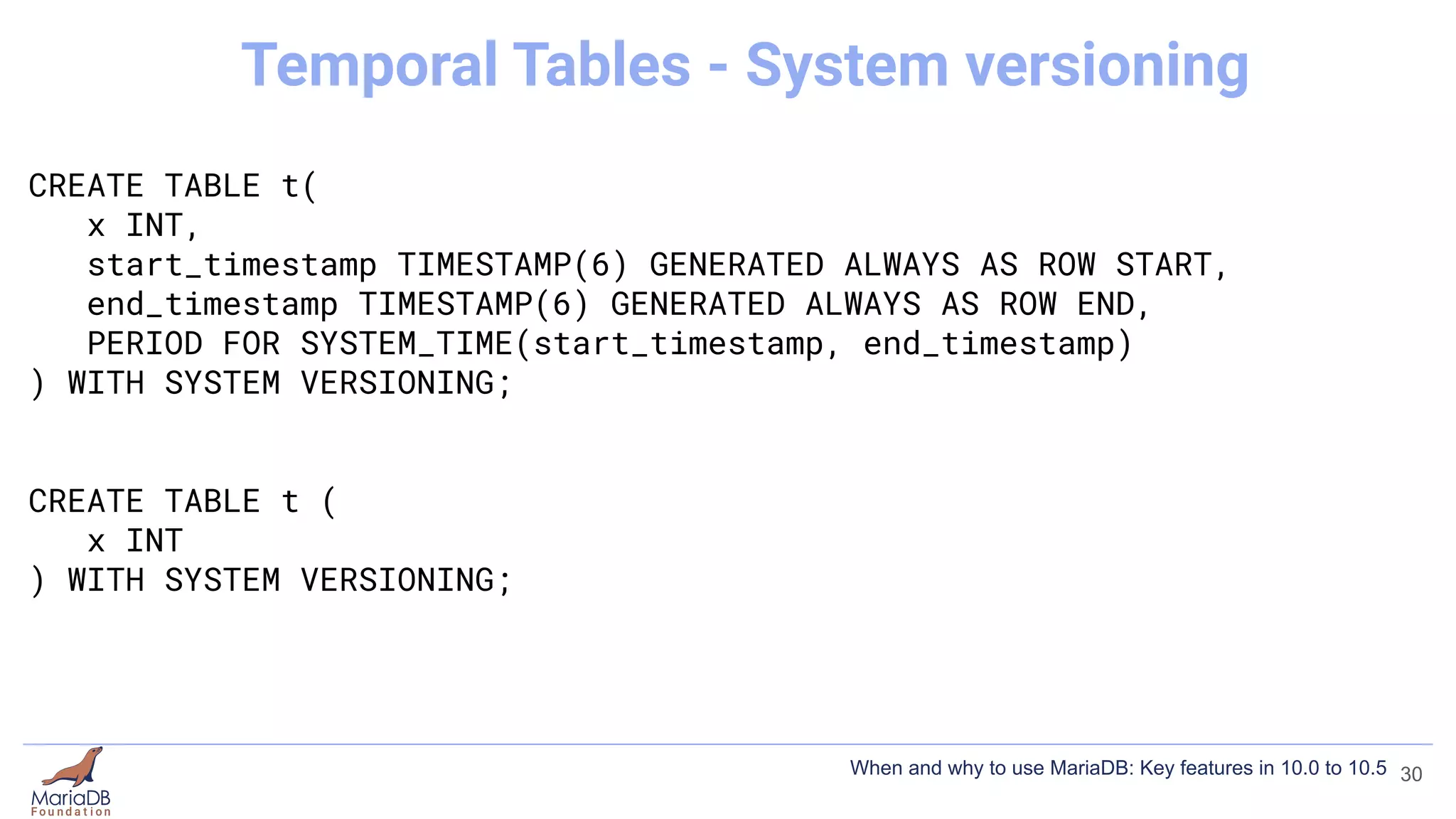
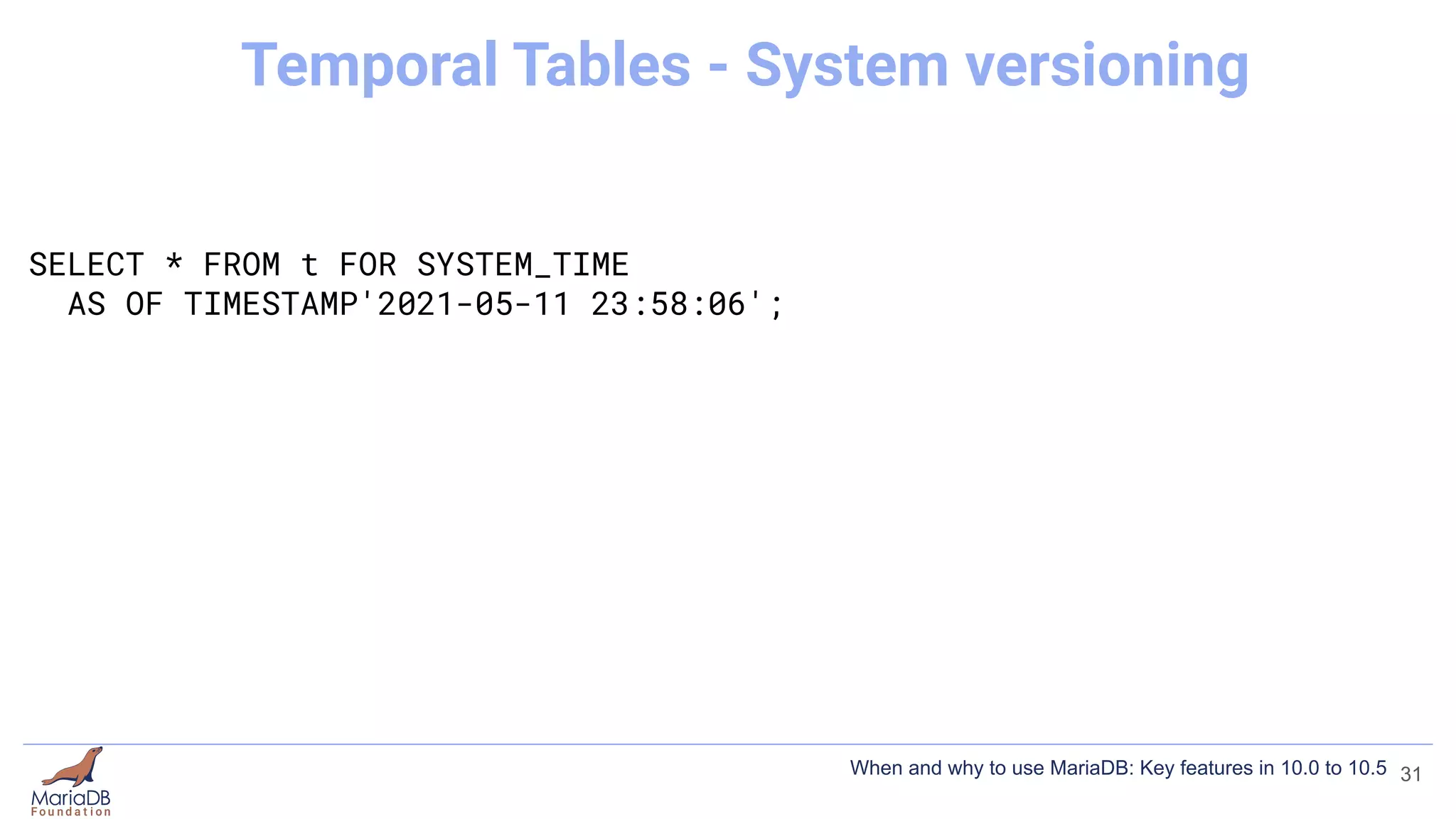
This document summarizes key features introduced in MariaDB versions 10.0 through 10.5, including storage engines like MyRocks, CONNECT, and ColumnStore; compression options for InnoDB; the Spider partitioning storage engine; temporal tables; flashback capabilities; and IF NOT EXISTS and OR REPLACE syntax. It aims to highlight interesting and differentiating features of MariaDB and provide links for further information.






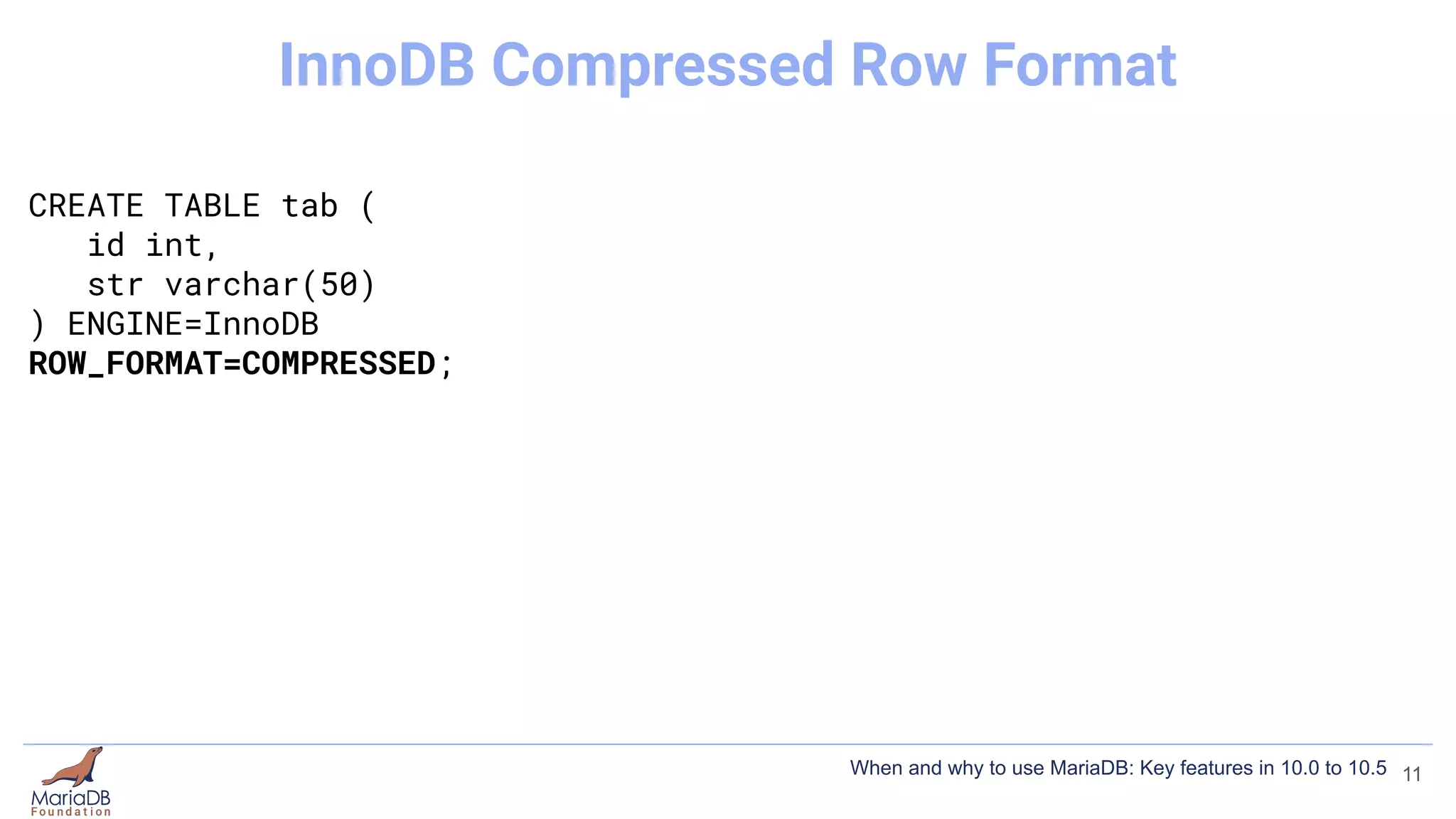
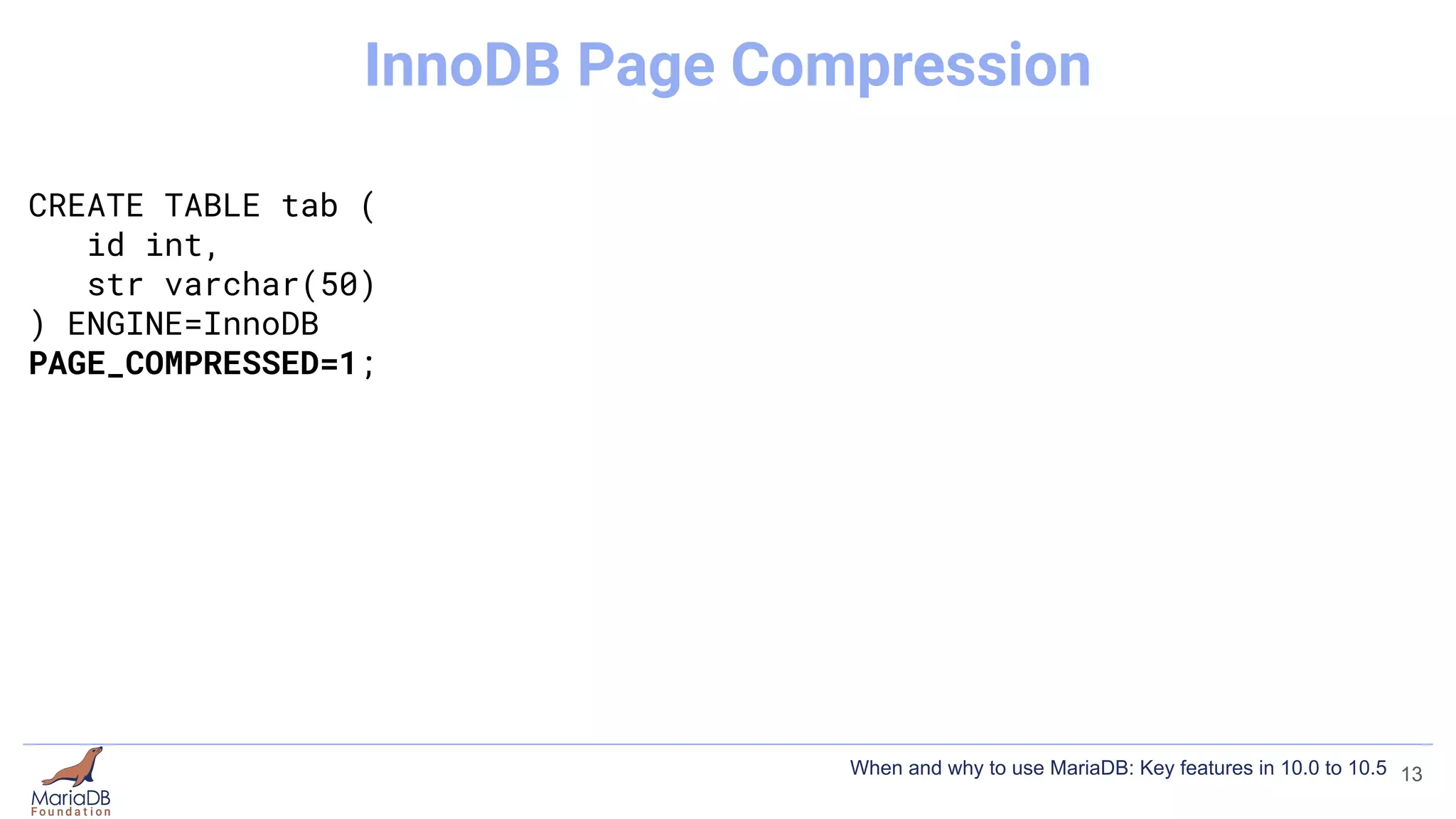
![CREATE TABLE tab (
id int,
str varchar(50)
) ENGINE=InnoDB
PAGE_COMPRESSED=1;
[mariadb]
...
innodb_compression_default=ON
14
InnoDB Page Compression
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-14-2048.jpg)




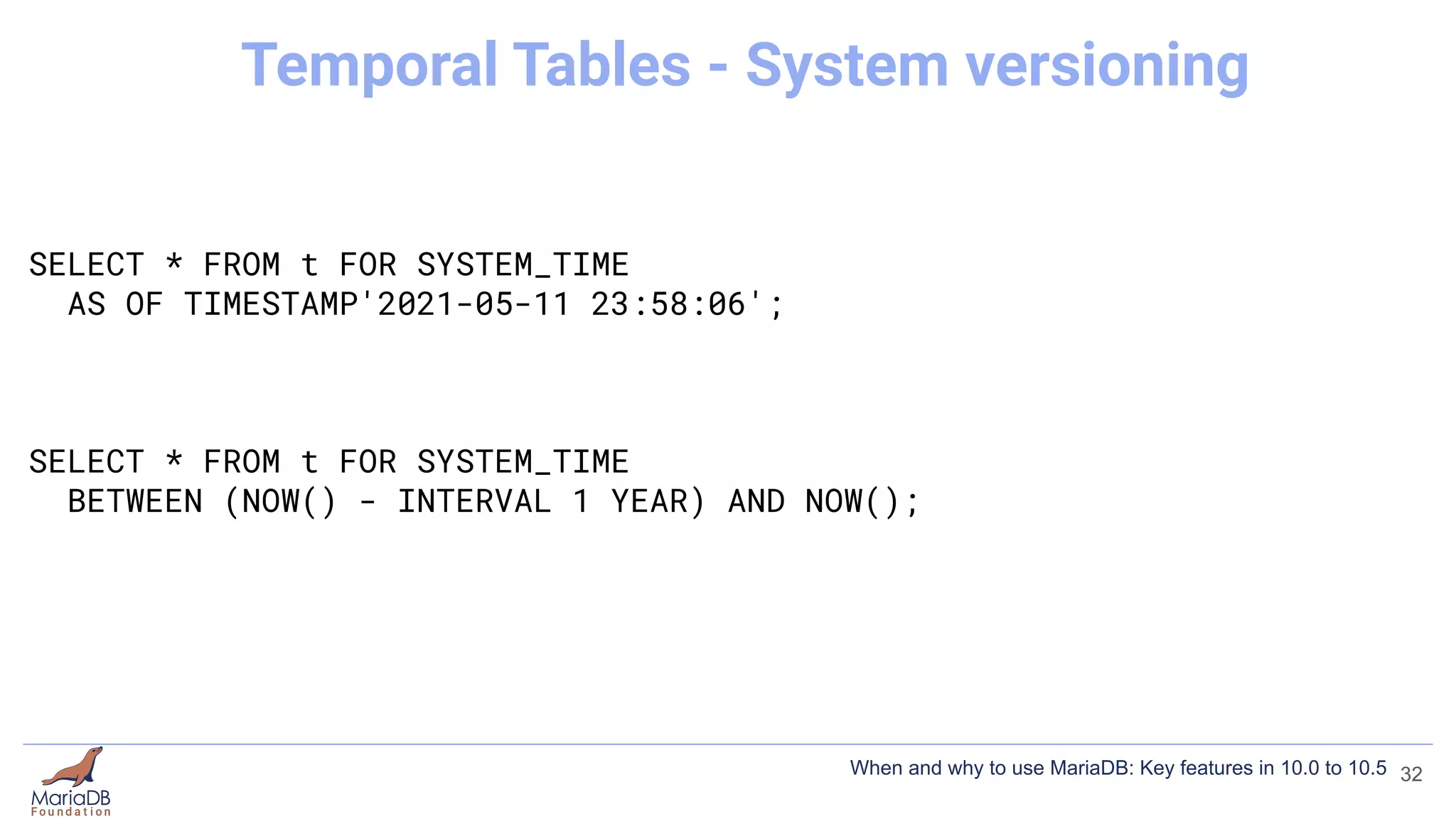
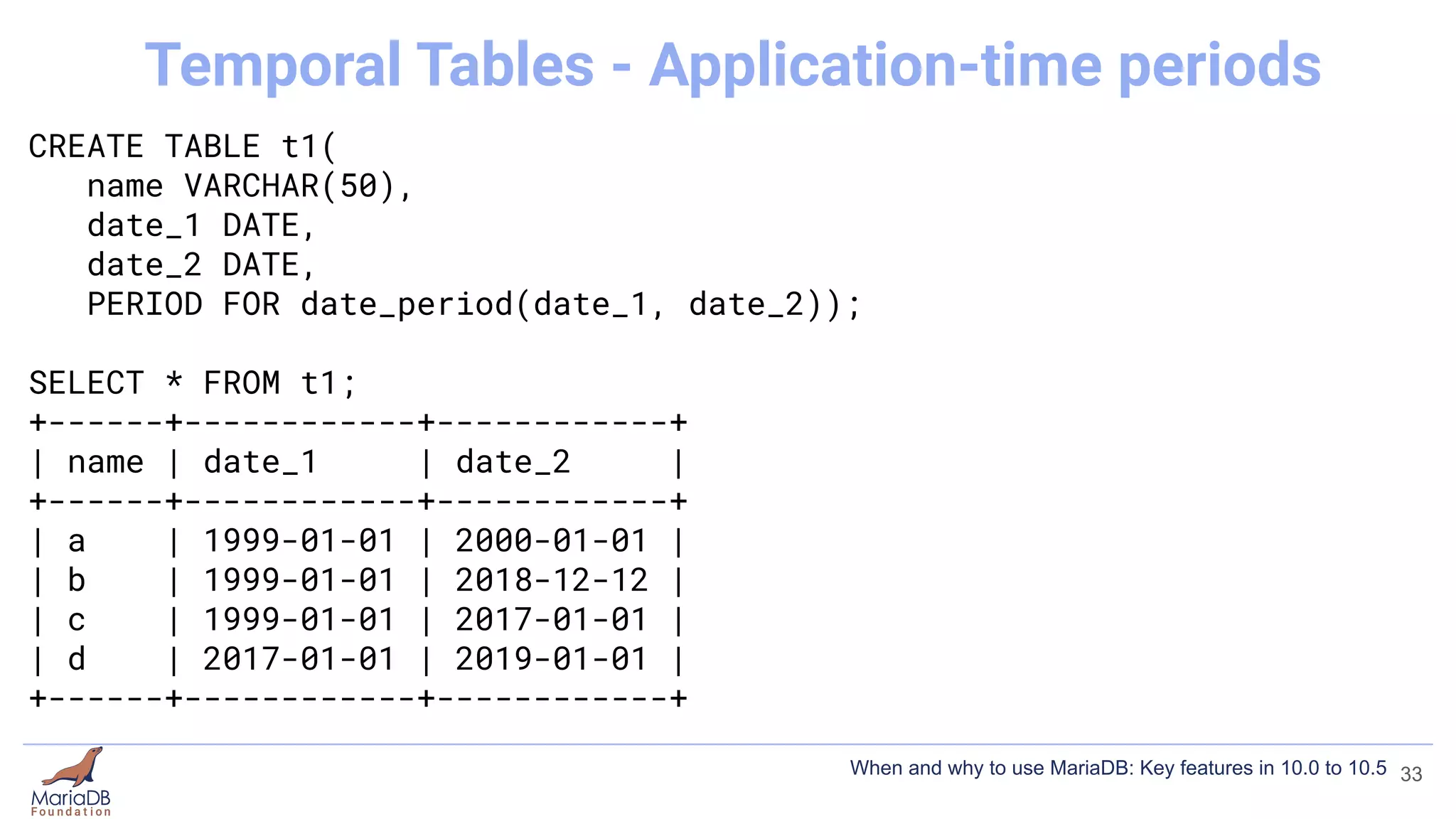
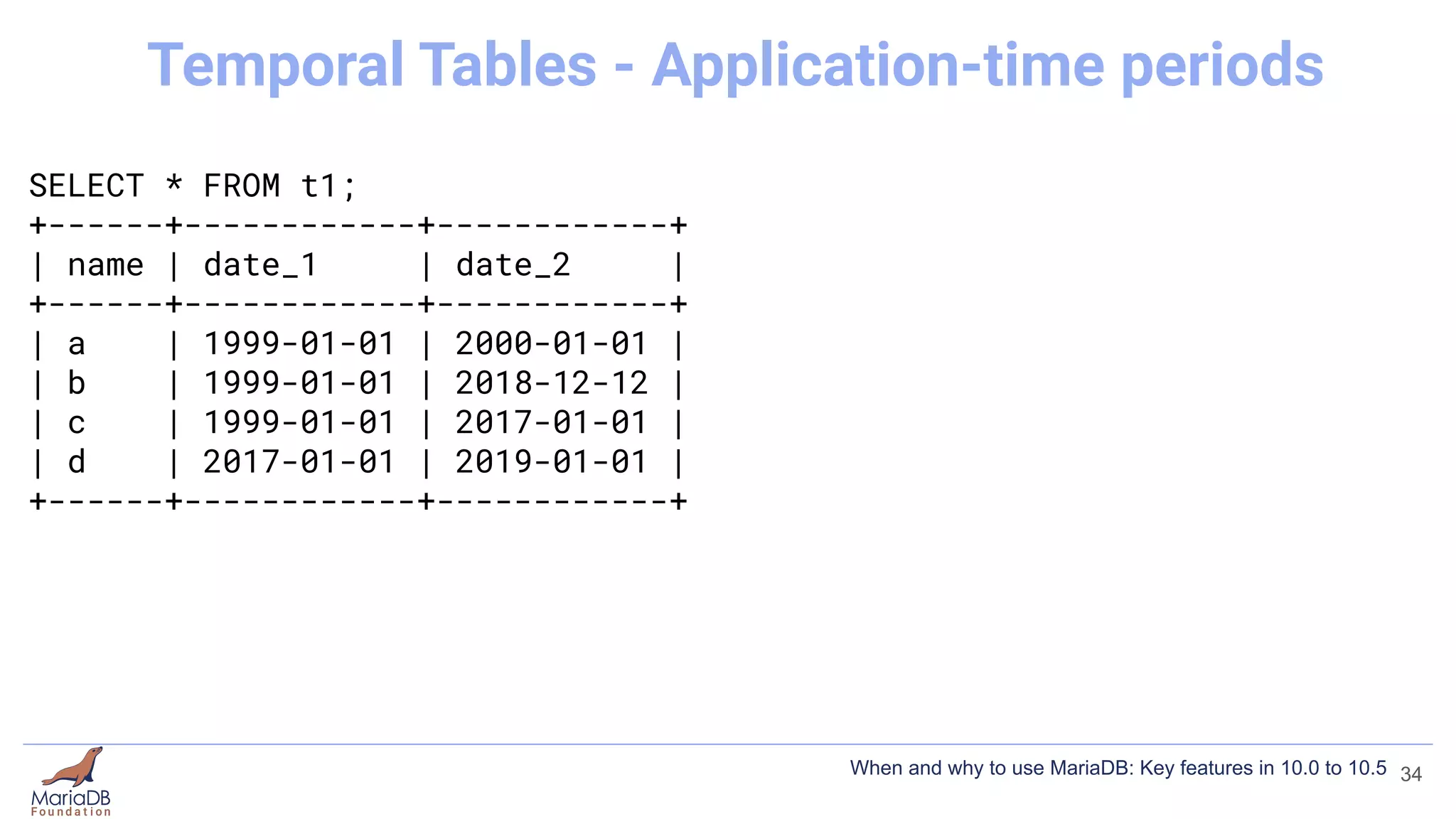
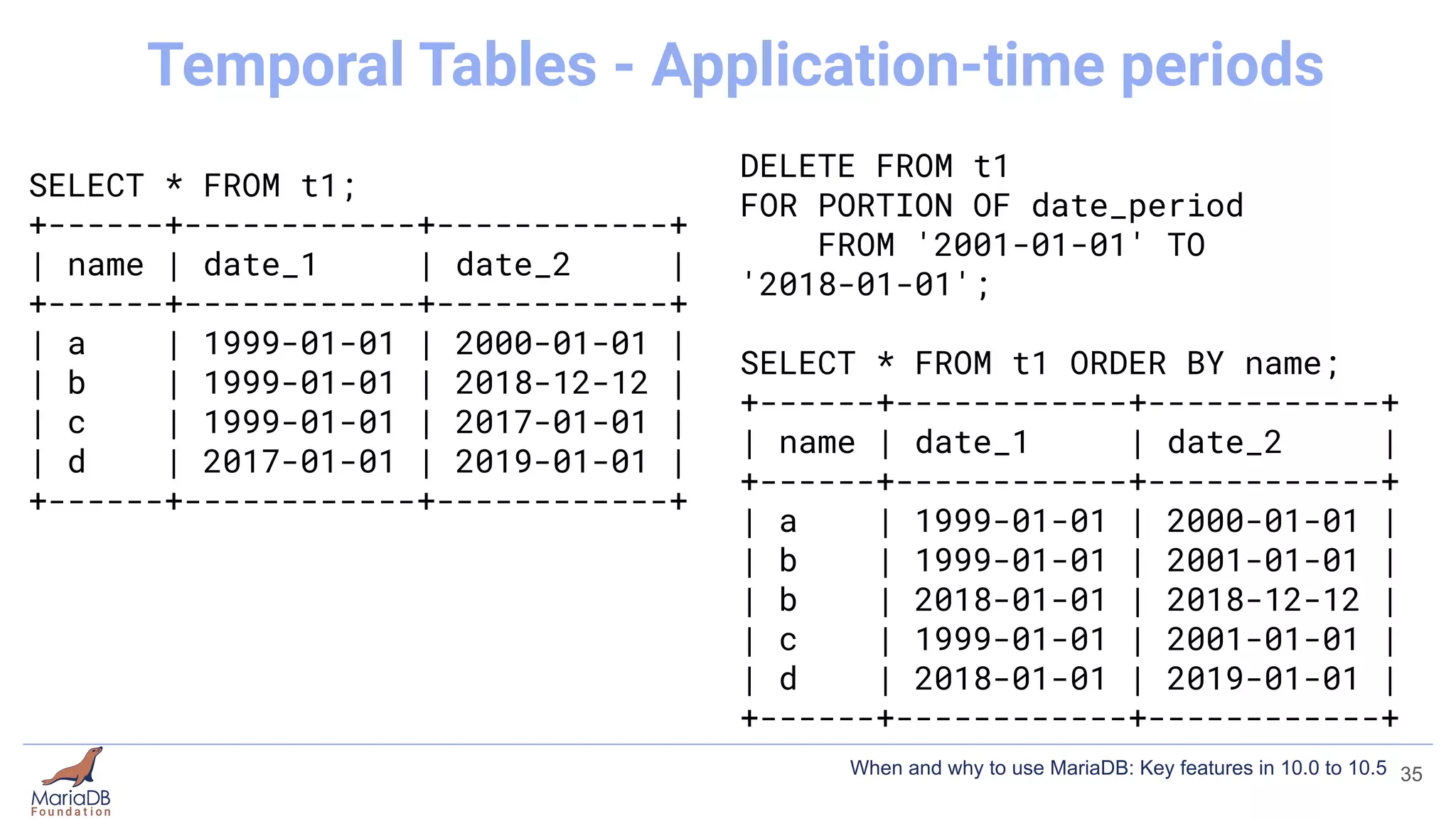

![[mariadb]
...
binlog_format=ROW
binlog_row_image=FULL
mariadb-binlog /var/lib/mysql/mysql-bin.000001
-d test
-T mytable
--start-datetime="2021-05-11 14:54:00"
--flashback
> flashback.sql
41
Flashback
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-41-2048.jpg)
![IF [NOT] EXISTS
● IF [NOT] EXISTS gives a warning instead of an error
● From MariaDB 10.1
42
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-42-2048.jpg)
![DROP USER bob;
ERROR 1396 (HY000): Operation DROP USER failed for 'bob'@'%'
DROP USER IF EXISTS bob;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
SHOW WARNINGS;
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------+
| Note | 1974 | Can't drop user 'bob'@'%'; it doesn't exist |
+-------+------+---------------------------------------------+
43
IF [NOT] EXISTS
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-43-2048.jpg)
![CREATE TABLE t2 (id INT);
ERROR 1050 (42S01): Table 't2' already exists
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t2 (id INT);
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.000 sec)
SHOW WARNINGS;
+-------+------+---------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+---------------------------+
| Note | 1050 | Table 't2' already exists |
+-------+------+---------------------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
44
IF [NOT] EXISTS
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-44-2048.jpg)

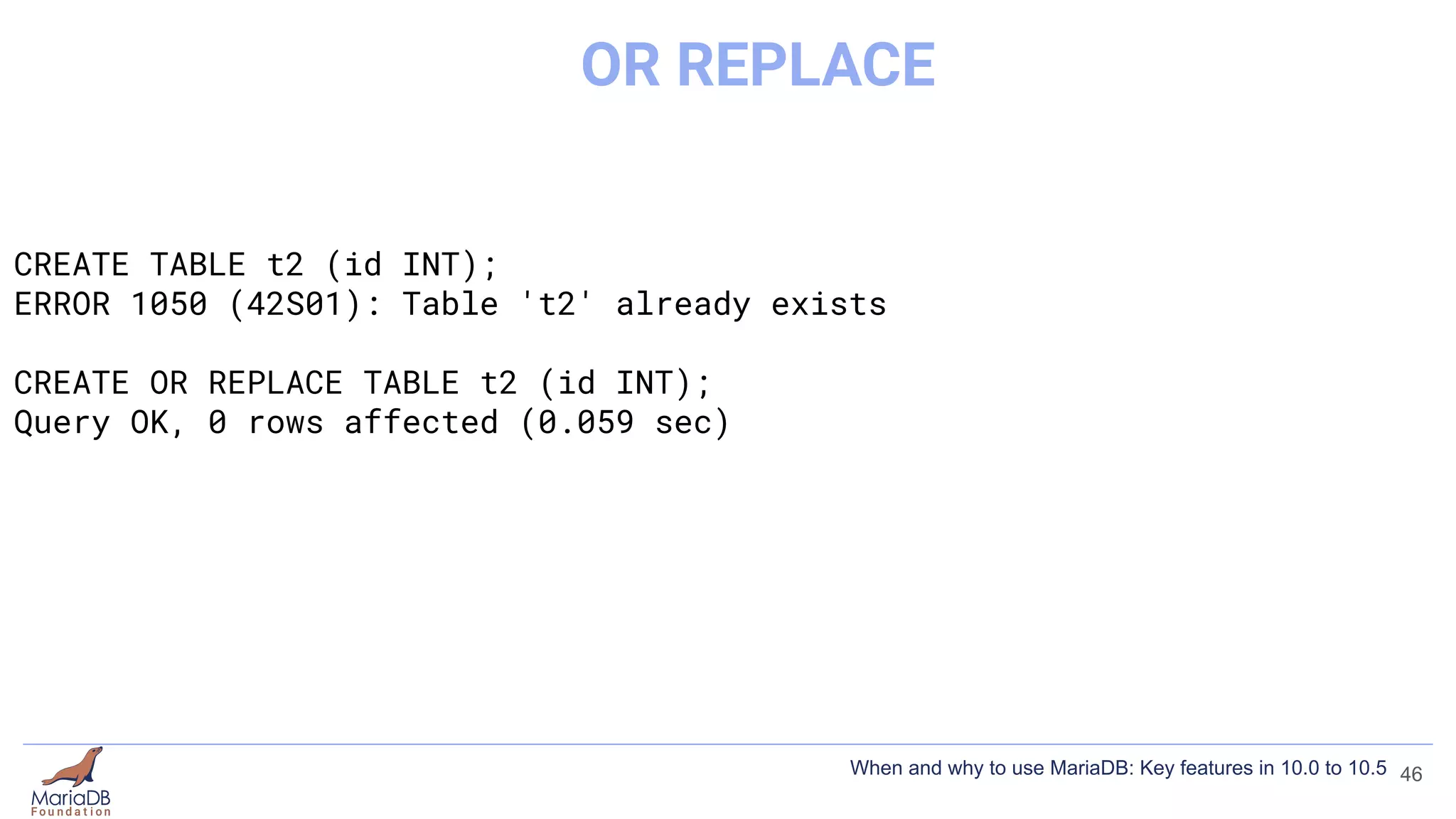
![IF [NOT] EXISTS / OR REPLACE
● OR REPLACE drops and creates instead of giving an error
● From MariaDB 10.1
● https://mariadb.com/kb/en/create-database/
47
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-47-2048.jpg)




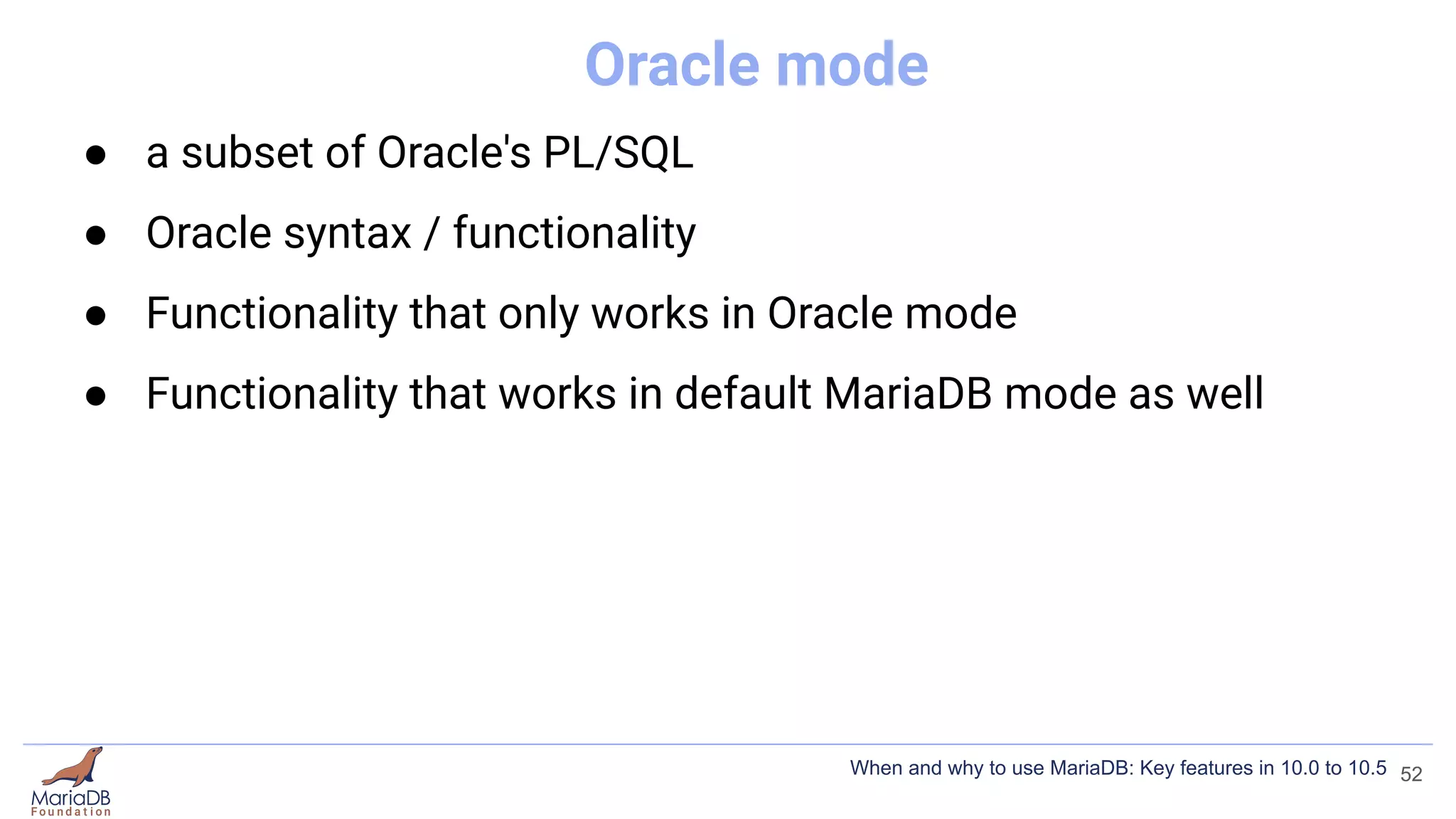
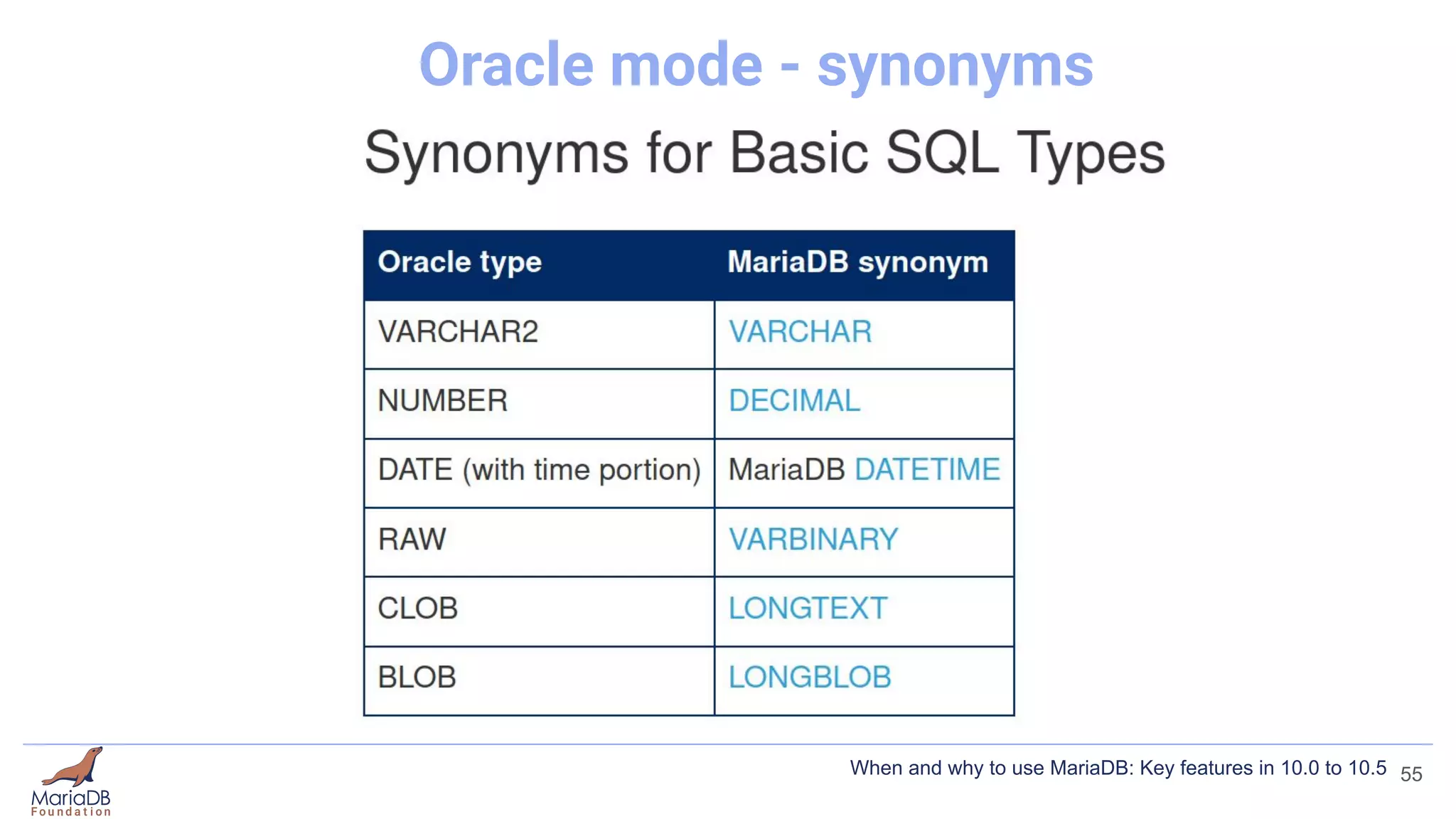
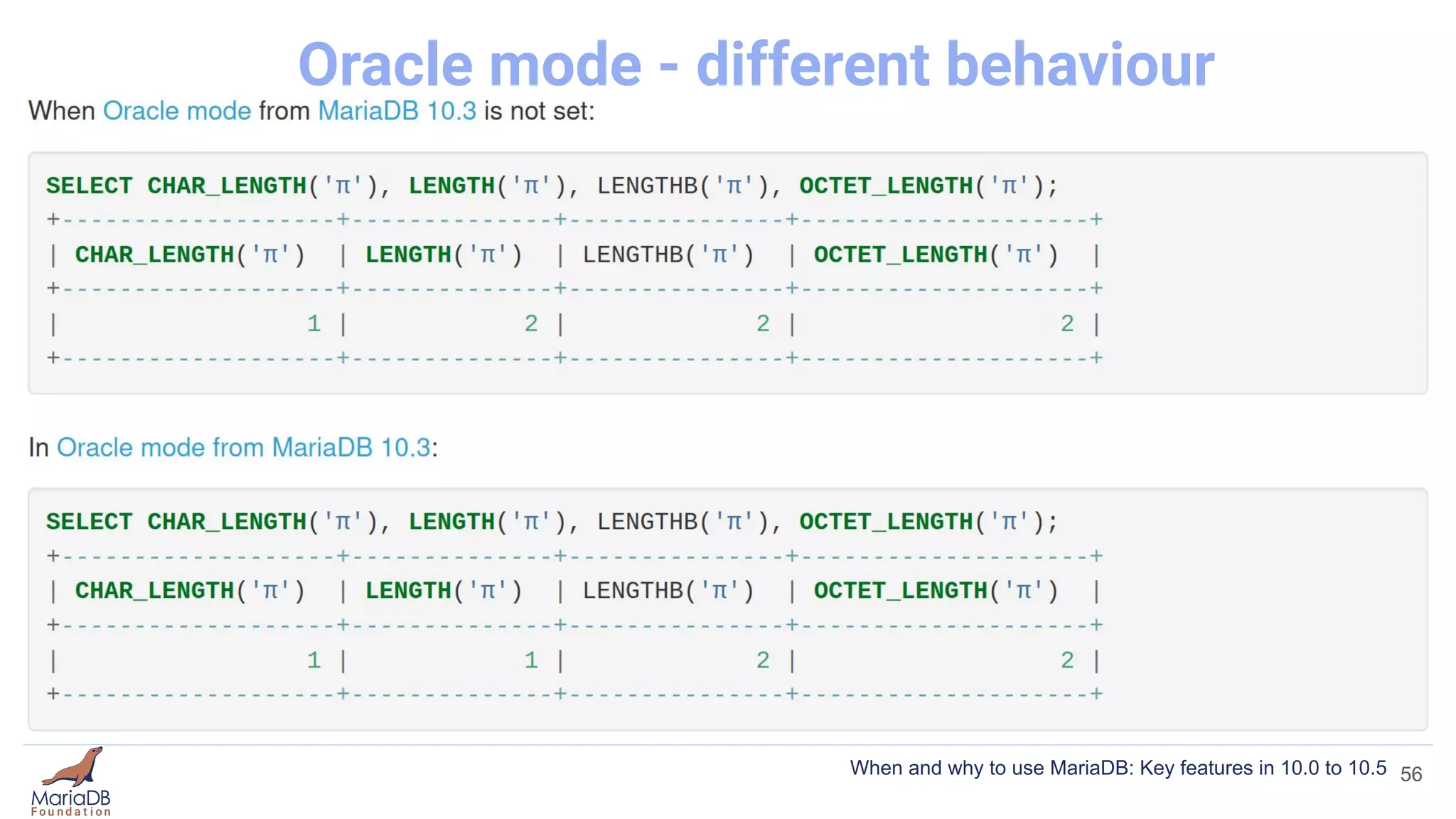
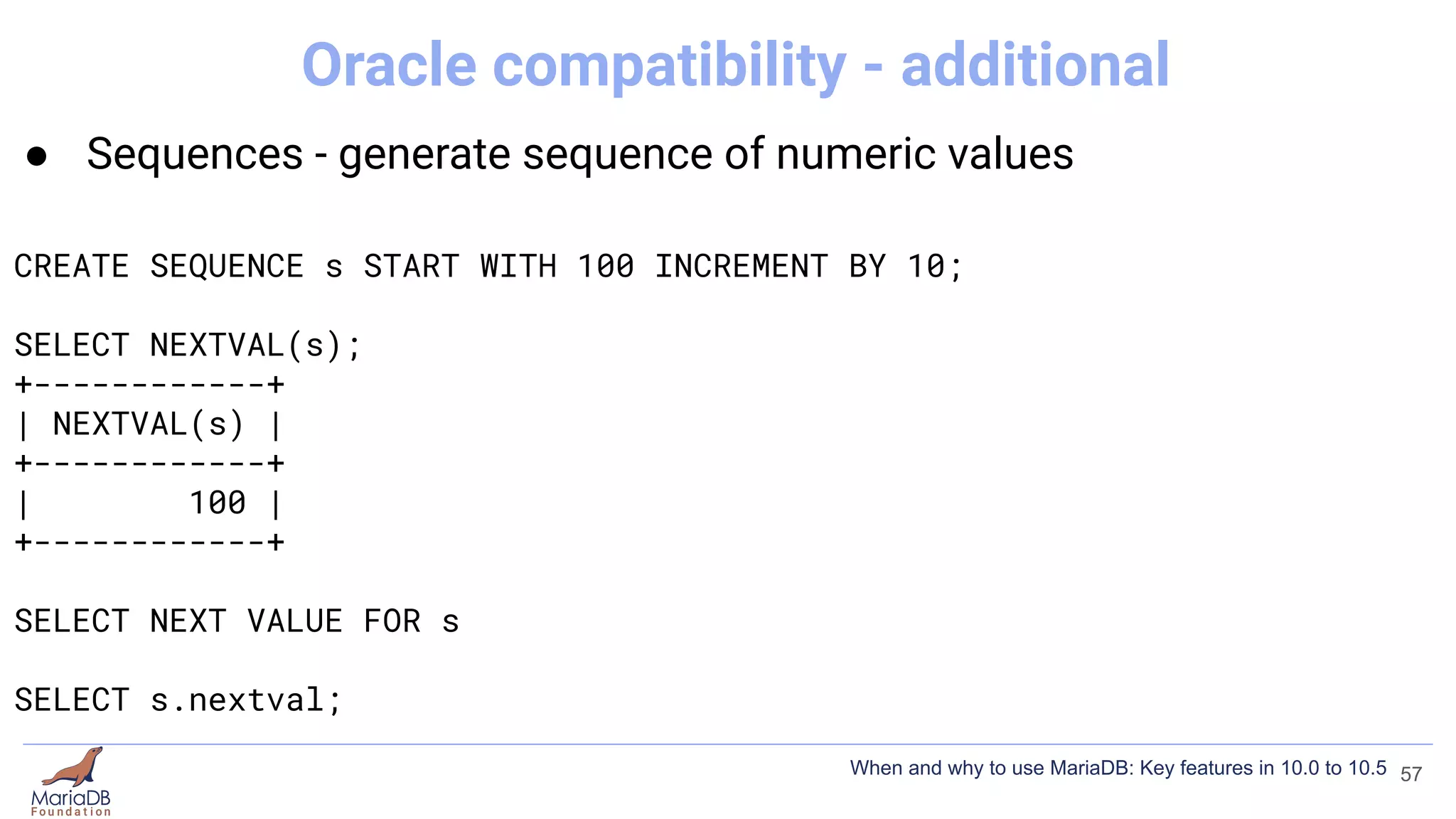
![Oracle mode
● a subset of Oracle's PL/SQL
● Oracle syntax / functionality
● Functionality that only works in Oracle mode
● Functionality that works in default MariaDB mode as well
[mariadb]
sql_mode = ORACLE
53
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-53-2048.jpg)
![Oracle mode
● a subset of Oracle's PL/SQL
● Oracle syntax / functionality
● Functionality that only works in Oracle mode
● Functionality that works in default MariaDB mode as well
[mariadb]
sql_mode = ORACLE
54
When and why to use MariaDB: Key features in 10.0 to 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perconalive2021100105-210513153417/75/When-and-Why-to-Use-MariaDB-New-Features-in-10-0-to-10-5-54-2048.jpg)