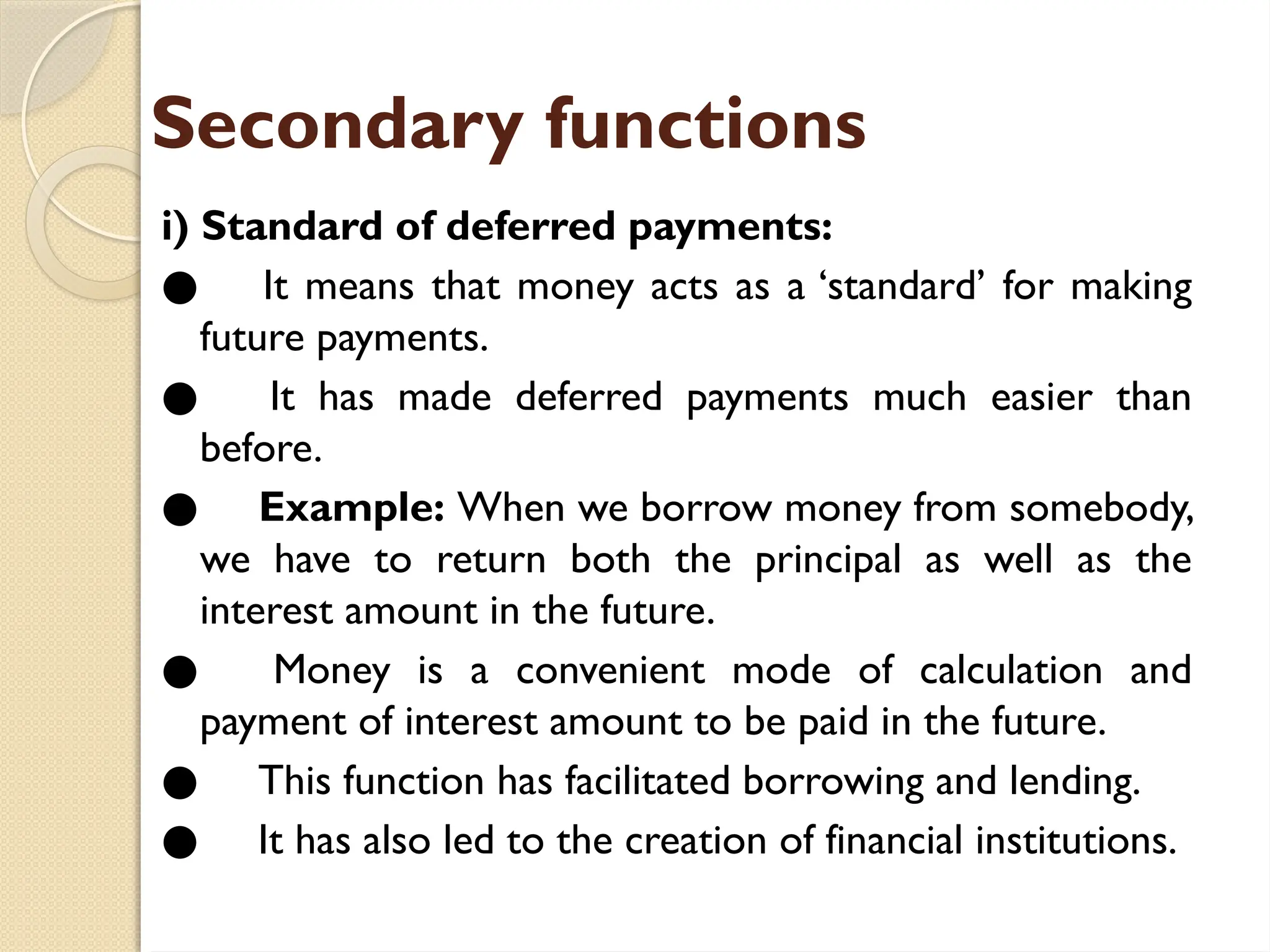
Money serves as a medium of exchange, allowing transactions and representing value, evolving from bartering systems. Its primary functions include facilitating payments and measuring value, while secondary functions encompass standards for future payments, storing value, and transferring value both domestically and internationally.