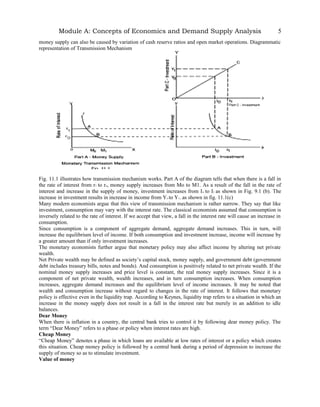
Money has become essential in modern economies. Originally, barter was used for exchange but it had many limitations. Money overcomes the difficulties of barter by serving four main functions: as a medium of exchange, a measure of value, a store of value, and a standard for deferred payments. The Reserve Bank of Bangladesh manages the country's monetary system by controlling various components of the money supply such as currency in circulation (M1), deposits (M2), and total money supply (M3). Monetary policy uses instruments like adjusting bank rates, reserve ratios, and open market operations to influence the money supply and achieve goals like full employment and price stability.