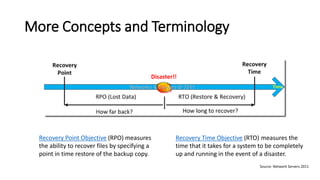
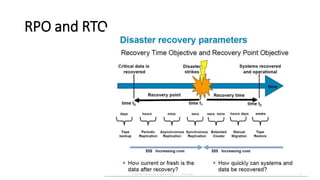
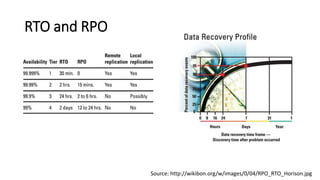
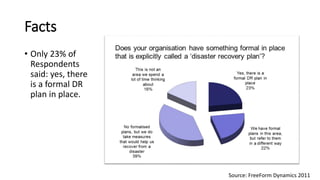
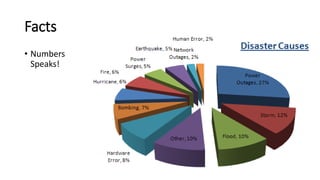
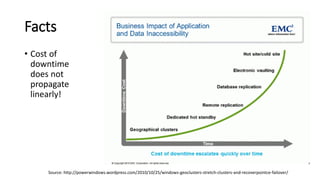
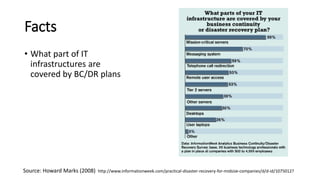
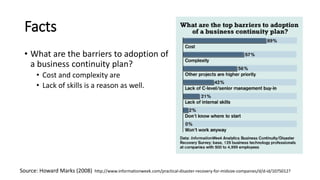
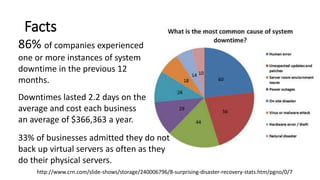
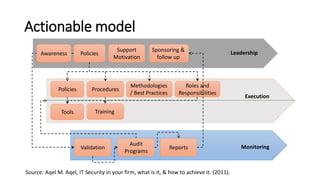
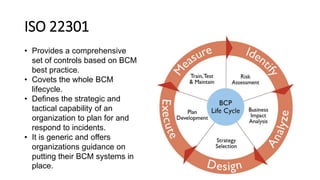
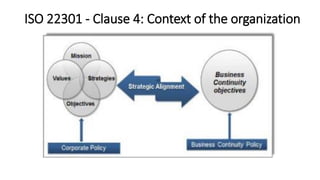
The document discusses the importance of business continuity and disaster recovery planning. It outlines key concepts like business continuity, disaster recovery, recovery point objective (RPO), and recovery time objective (RTO). Statistics are provided showing that 40-60% of businesses that close due to a disaster never reopen, and the average cost of downtime is $366,363 per year. The new global standard, ISO 22301, is also summarized, outlining its key clauses related to leadership, planning, support, operation, and improvement of business continuity management systems.