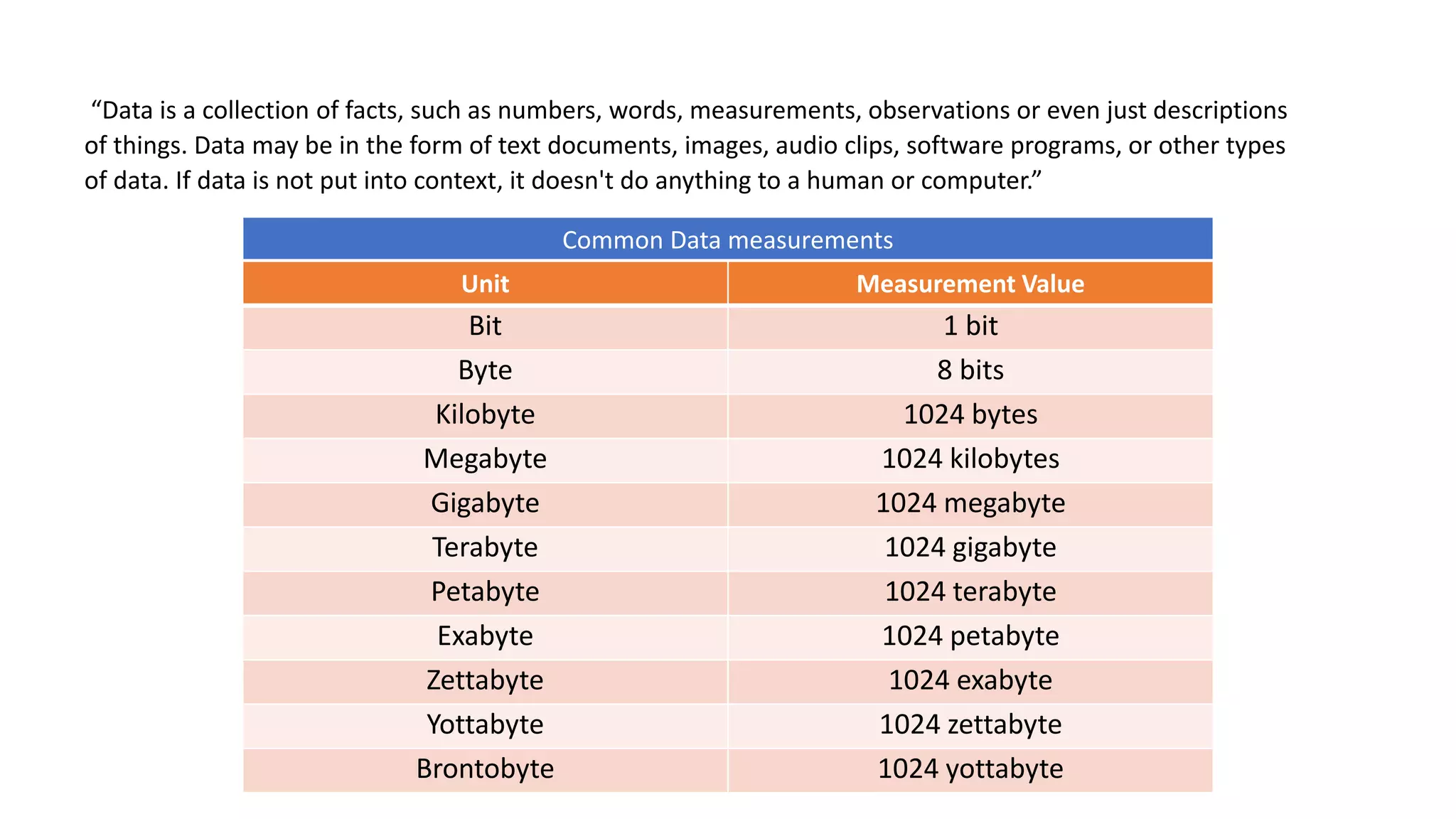
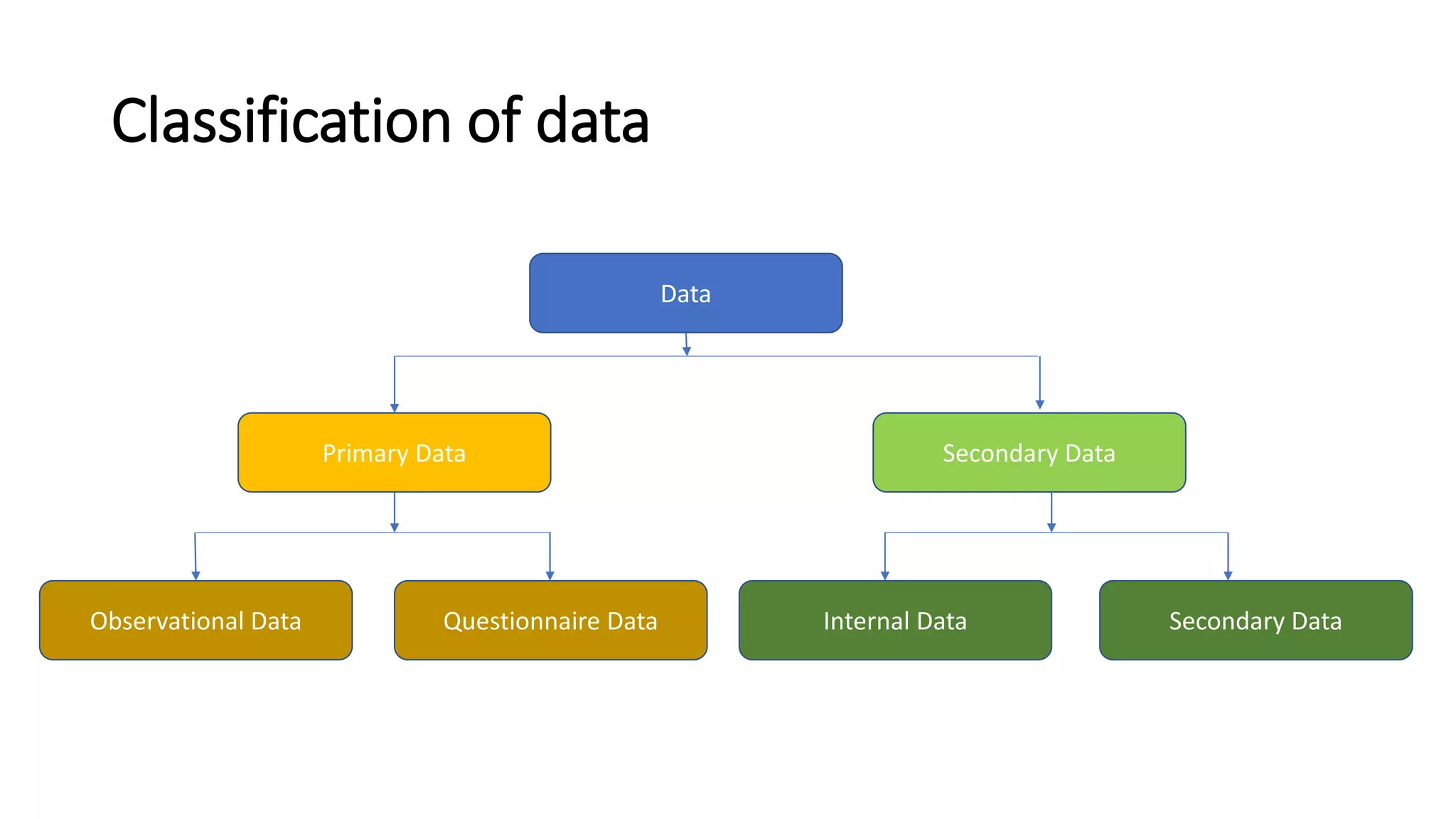
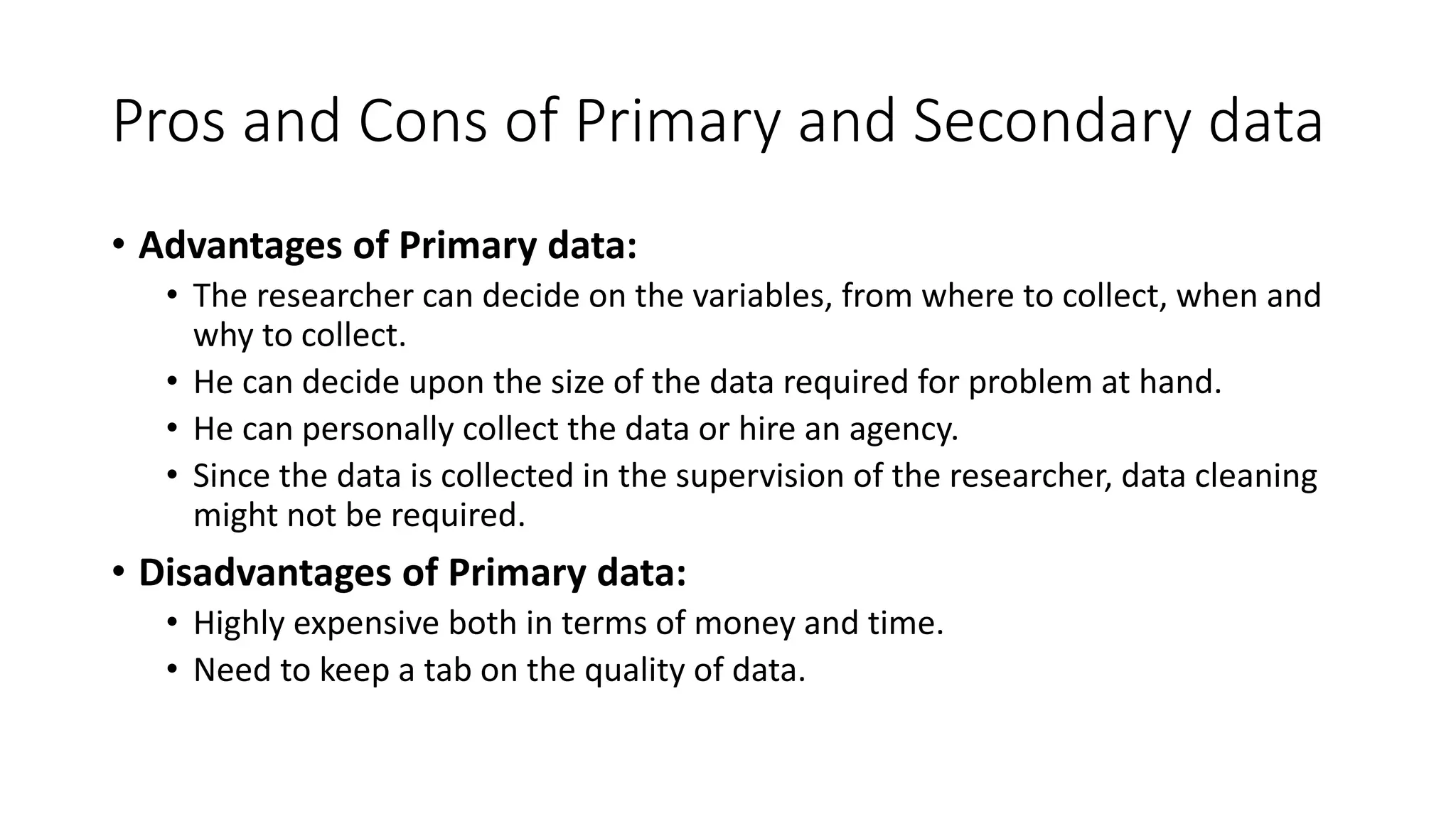
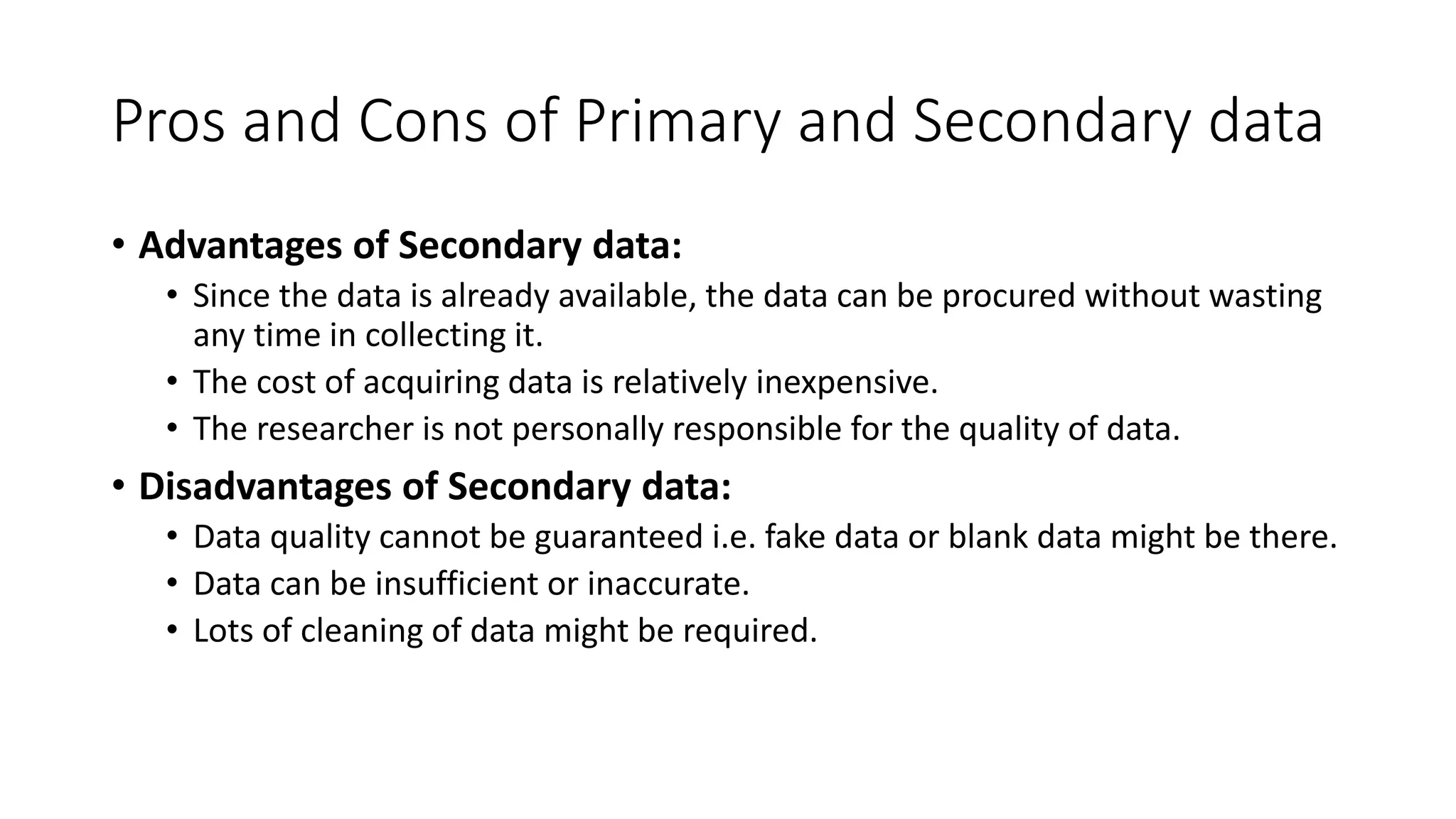
The document discusses data as a vital resource in the modern world, emphasizing its significance over traditional resources like oil. It classifies data into primary and secondary types, explaining their respective advantages and disadvantages, and further distinguishes between structured and unstructured data. Additionally, it outlines various methods of data collection, storage formats, and applications in different systems.