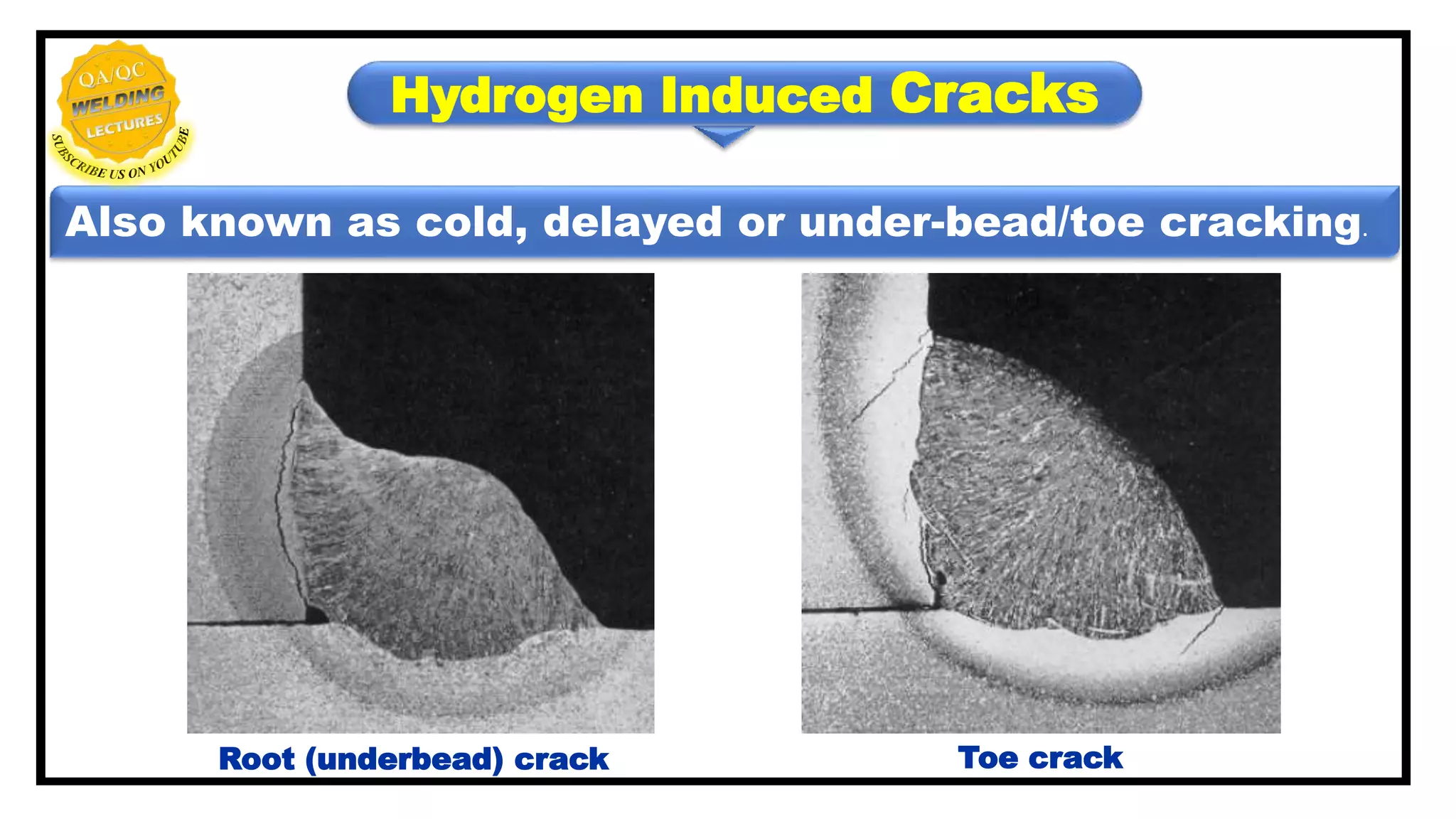
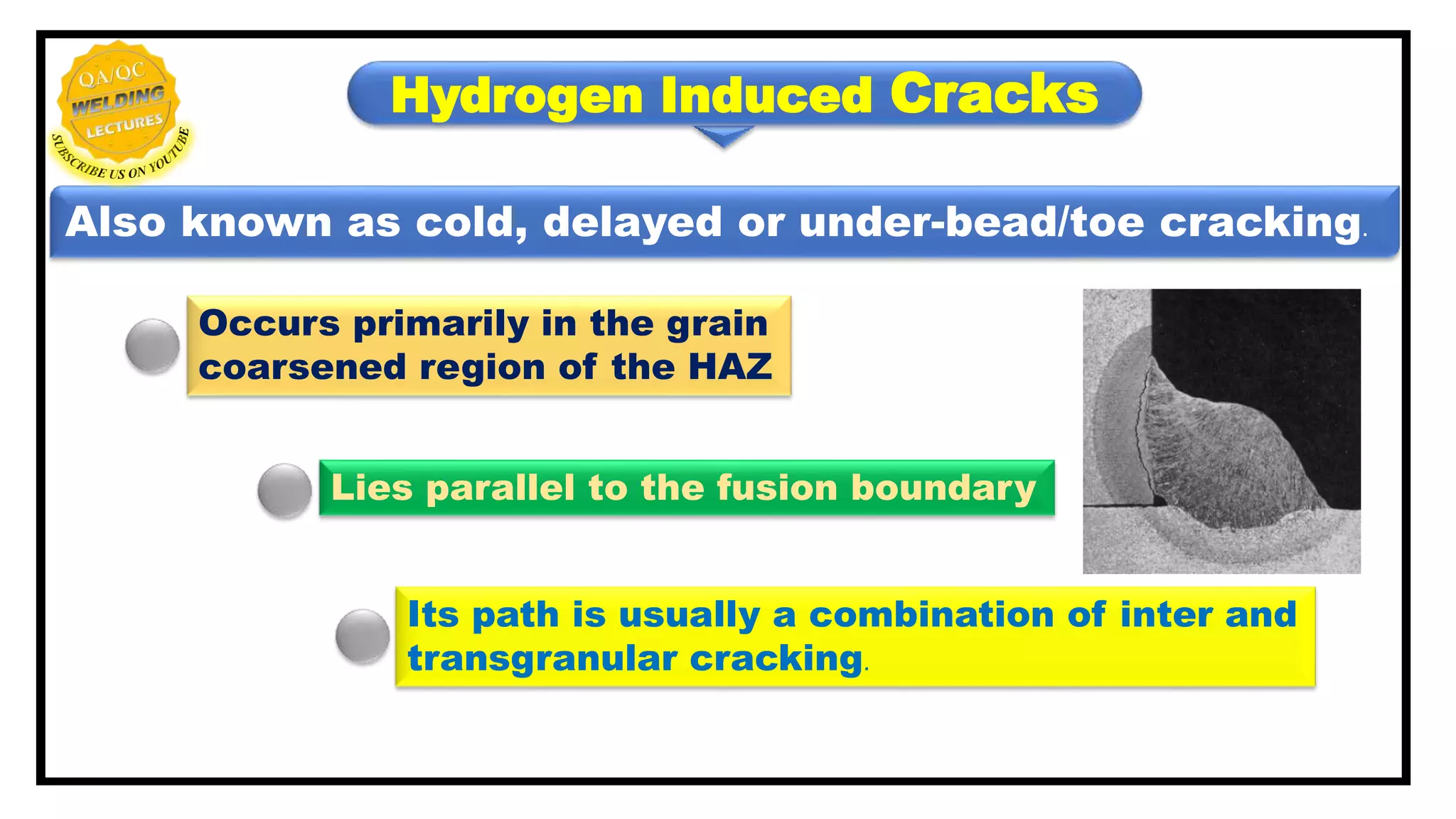
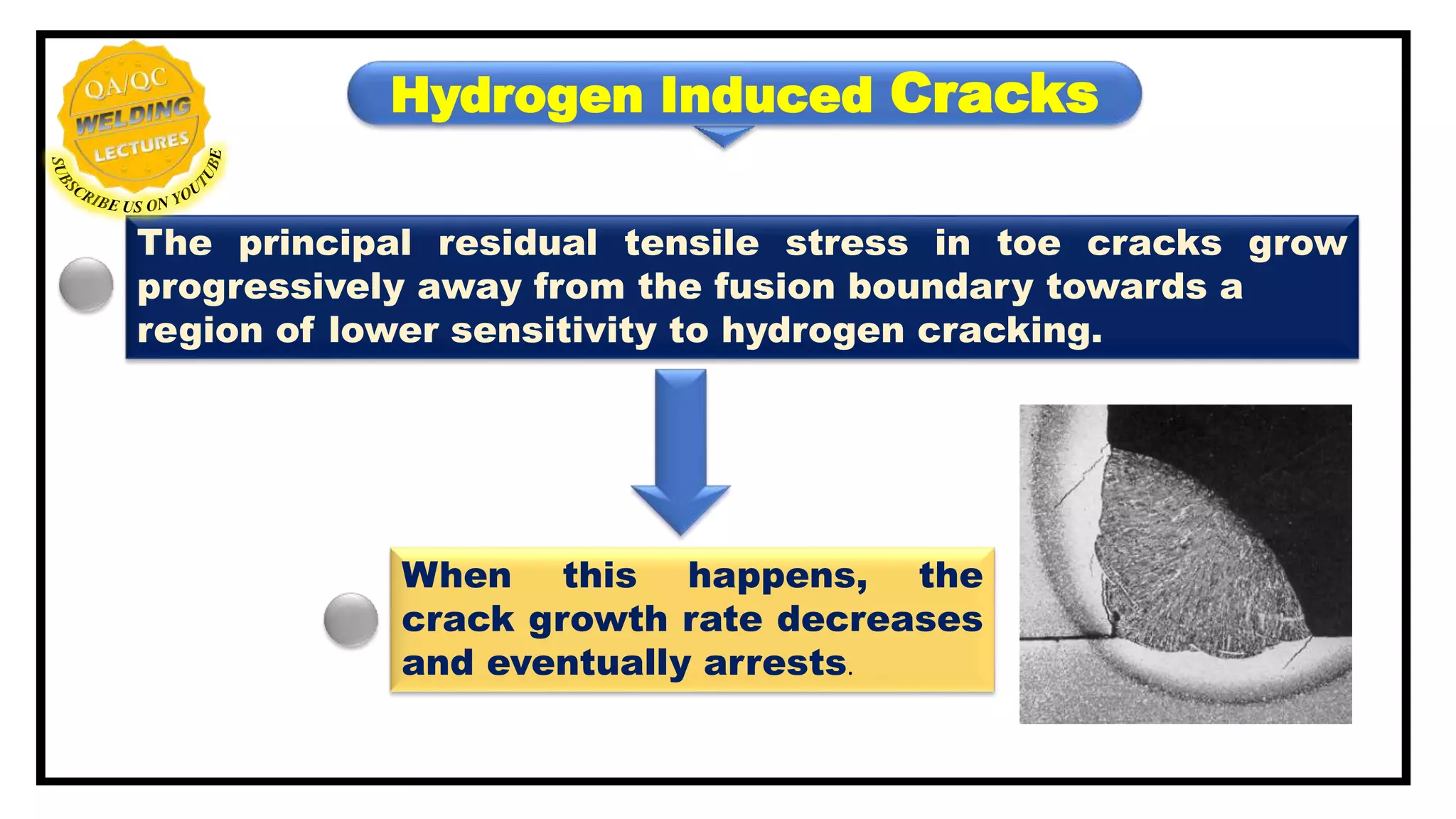
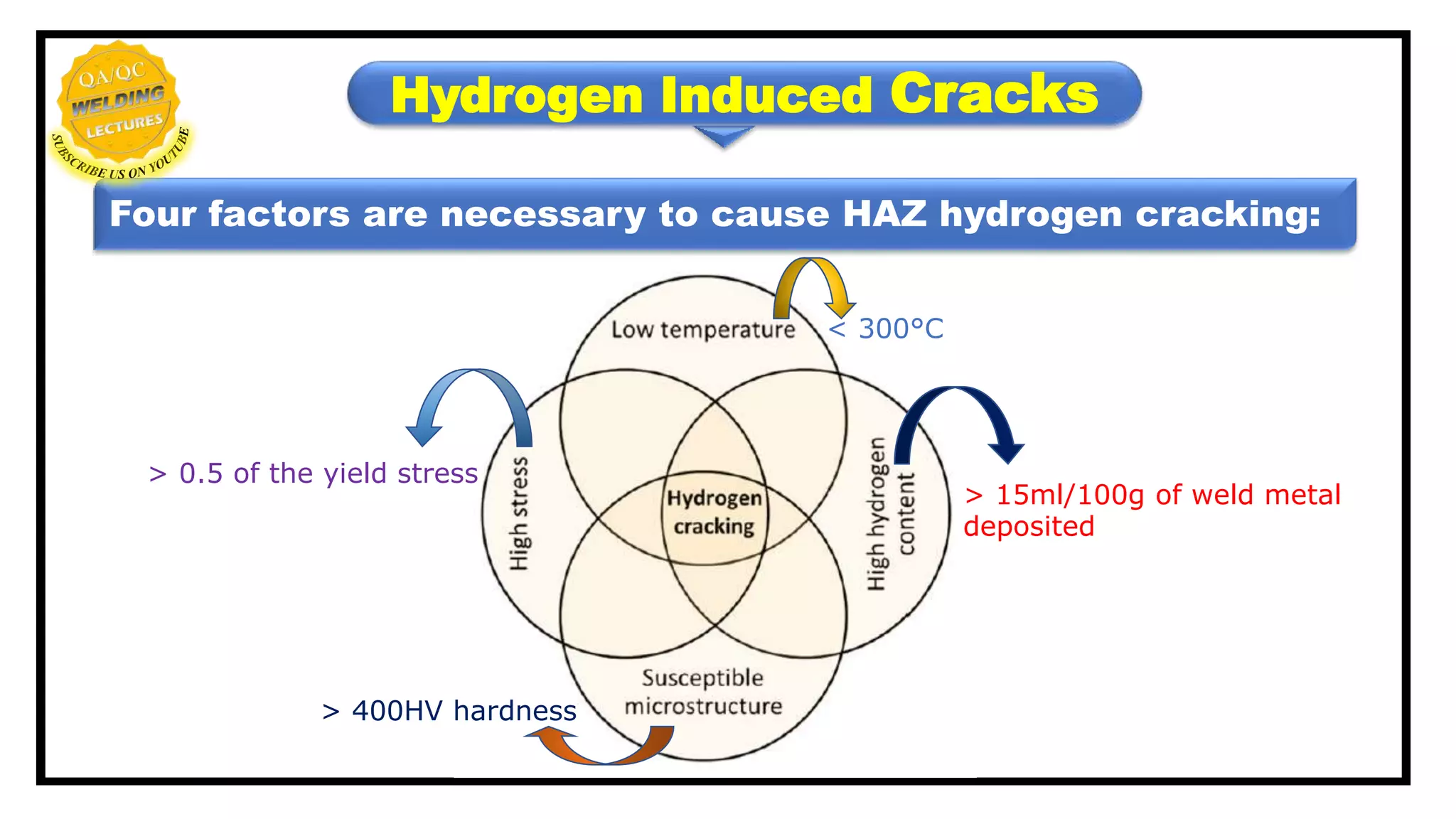
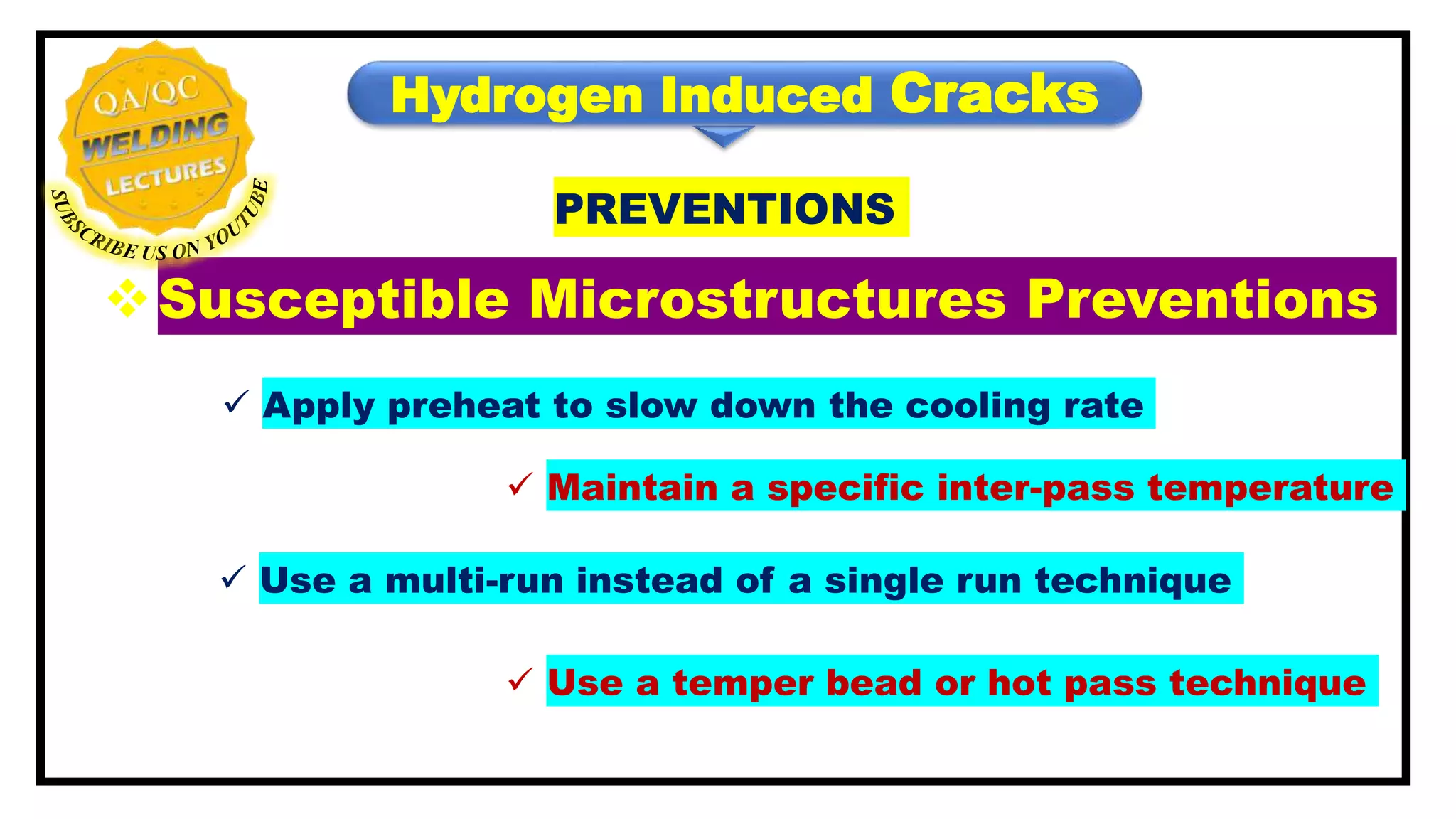
Hydrogen induced cracks, also known as cold, delayed or under-bead/toe cracking, primarily occur in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and result from specific metallurgical conditions and constraints. Four key factors contribute to the formation of these cracks, including deposit composition and residual tensile stress, while prevention strategies involve managing preheat, inter-pass temperature, and cleaning to reduce hydrogen contamination. Techniques such as post-heating and selecting appropriate welding processes also play a critical role in mitigating these cracks.