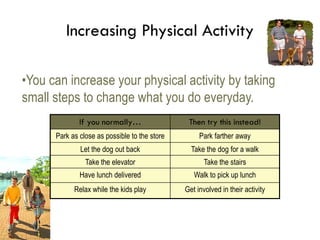
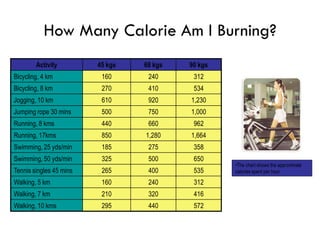
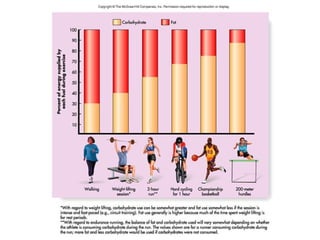
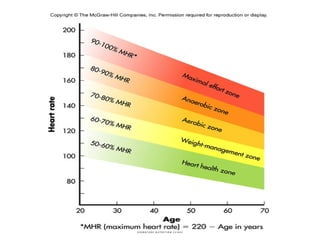
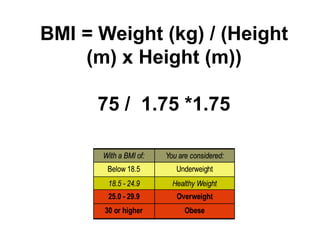
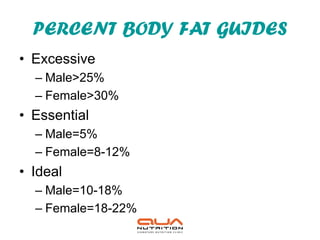
The document discusses weight management strategies including calculating ideal body weight, understanding fat loss, and tailoring diet and exercise programs for weight loss or gain. It emphasizes the importance of a balanced energy equation, sustainable lifestyle changes, and the role of physical activity in maintaining weight. Additionally, it highlights the psychological and physiological challenges individuals face during weight loss and the significance of ongoing support to prevent weight regain.