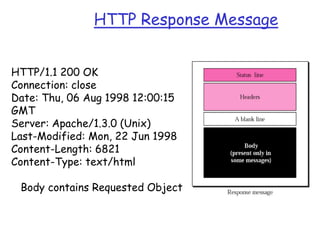
The document describes the structure and components of HTTP request and response messages. It explains that an HTTP request contains a request line with the method, URL and HTTP version, header lines with additional fields like Host and User-Agent, and an optional message body. A response contains a status line with the protocol version, status code and message, header lines including Date, Server and Content-Type, and a message body containing the requested object. Common status codes like 200, 301 and 404 are also defined.