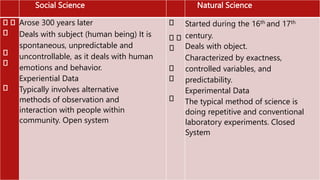
This document provides an introduction to social sciences, distinguishing it from natural sciences and humanities. It defines social sciences as the study of society and how individuals relate within societies. Natural sciences deal with the physical world through empirical evidence and experimentation, while humanities study aspects of human culture through fields like philosophy, history and art. Both social sciences and humanities are concerned with humans, but social sciences take a more scientific approach using empirical data and testing of theories, while humanities take a more interpretive approach. The document provides examples of branches within natural sciences and describes similarities and differences between social sciences, natural sciences and humanities.