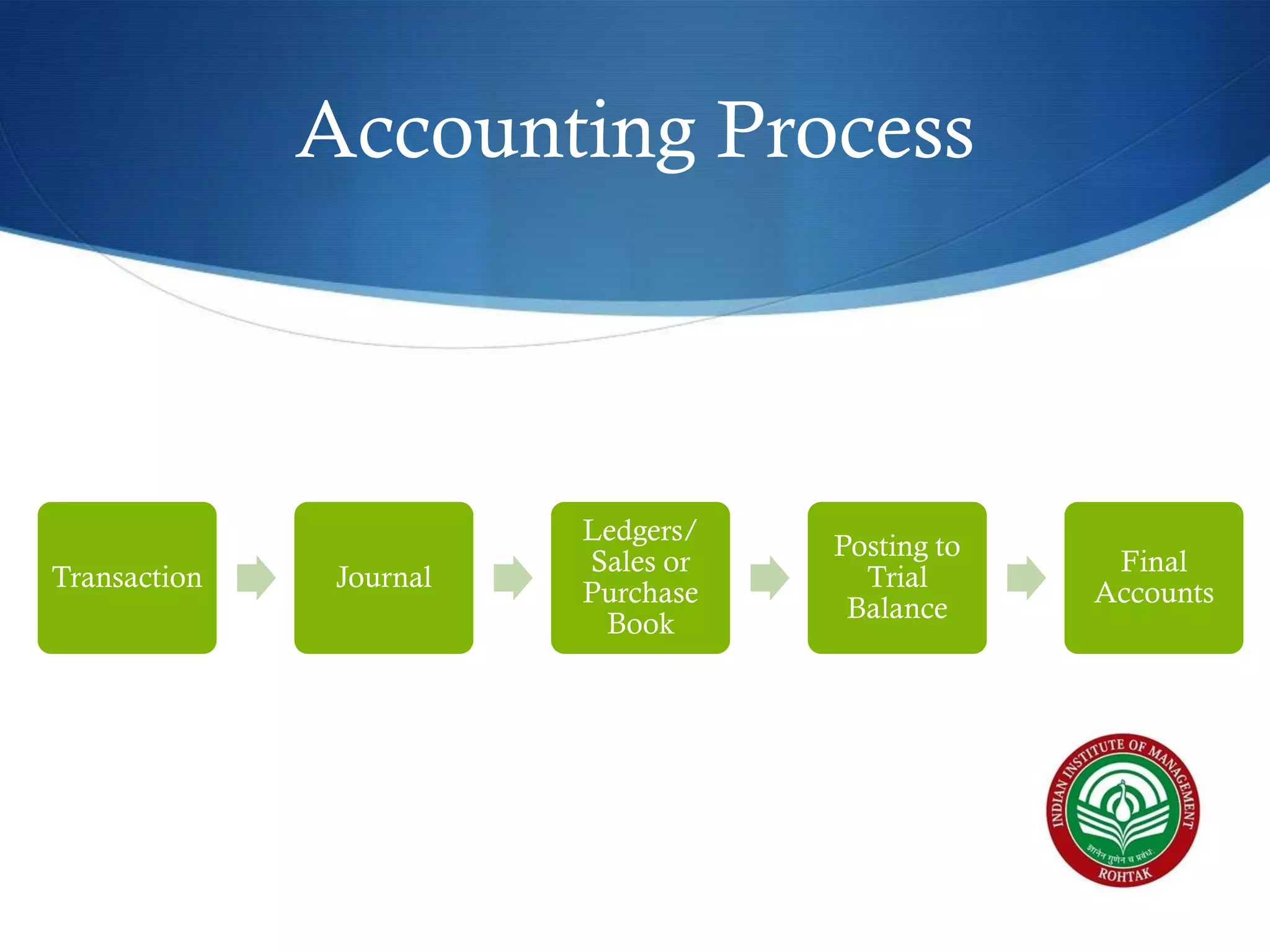
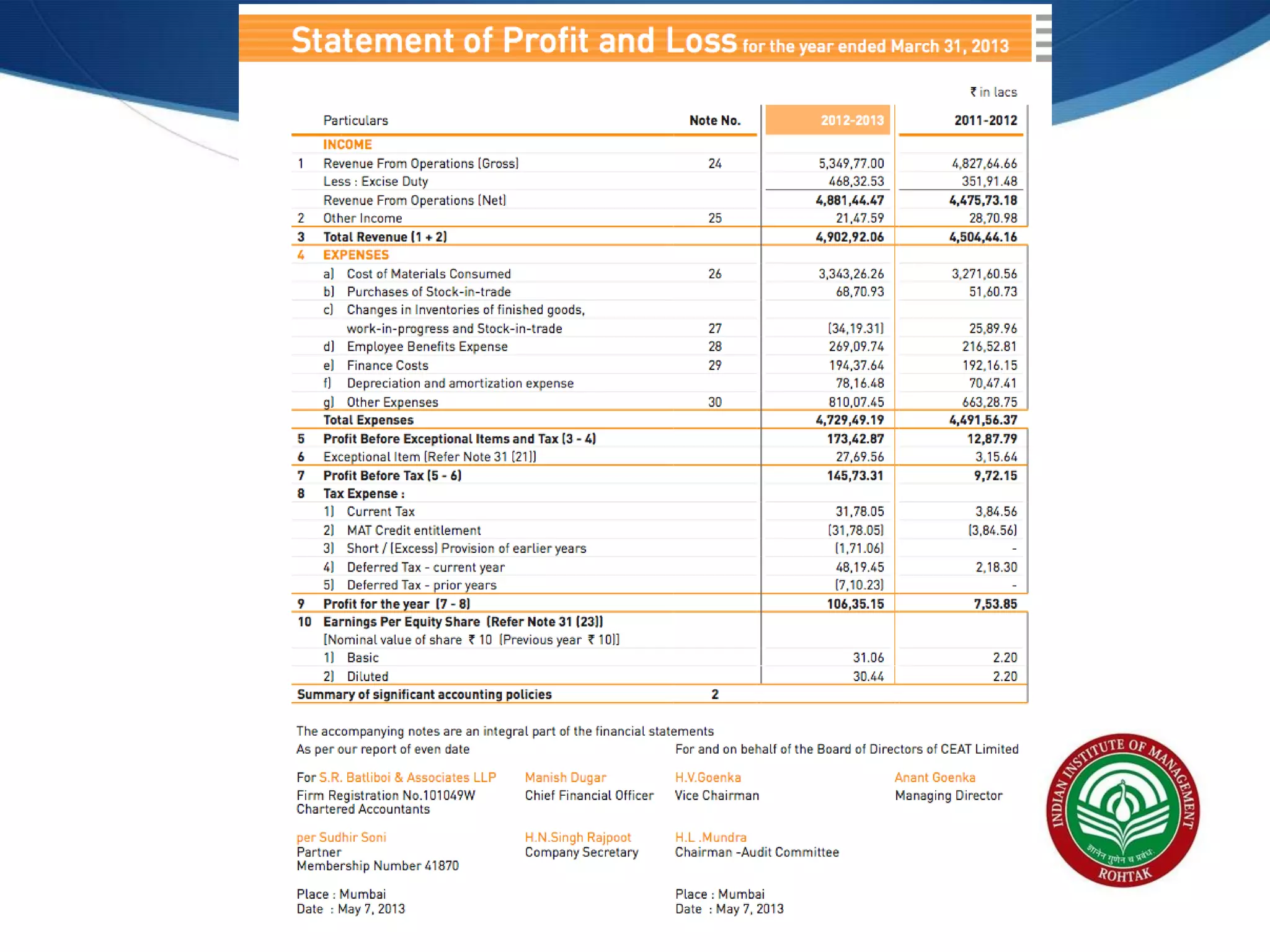
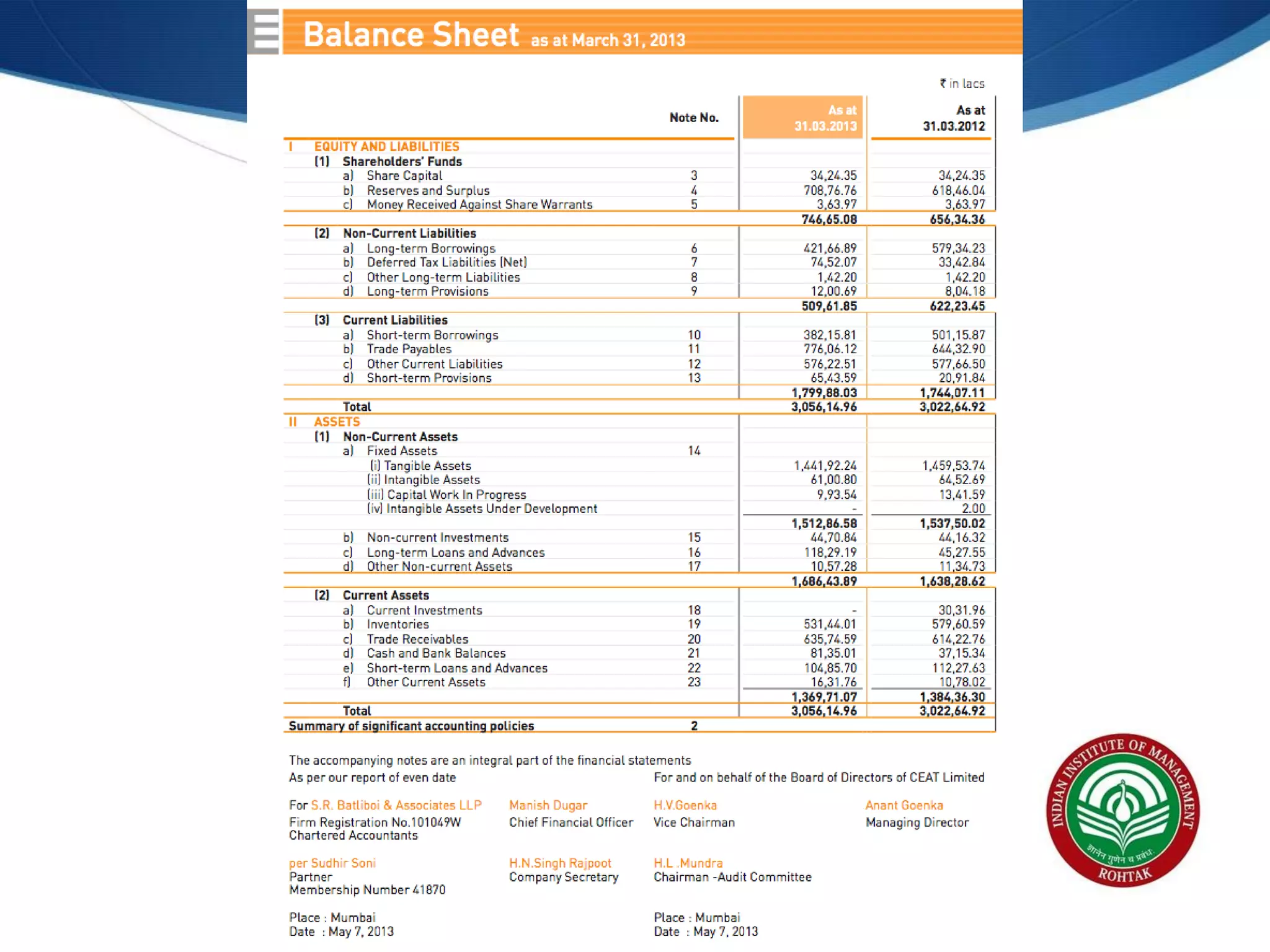
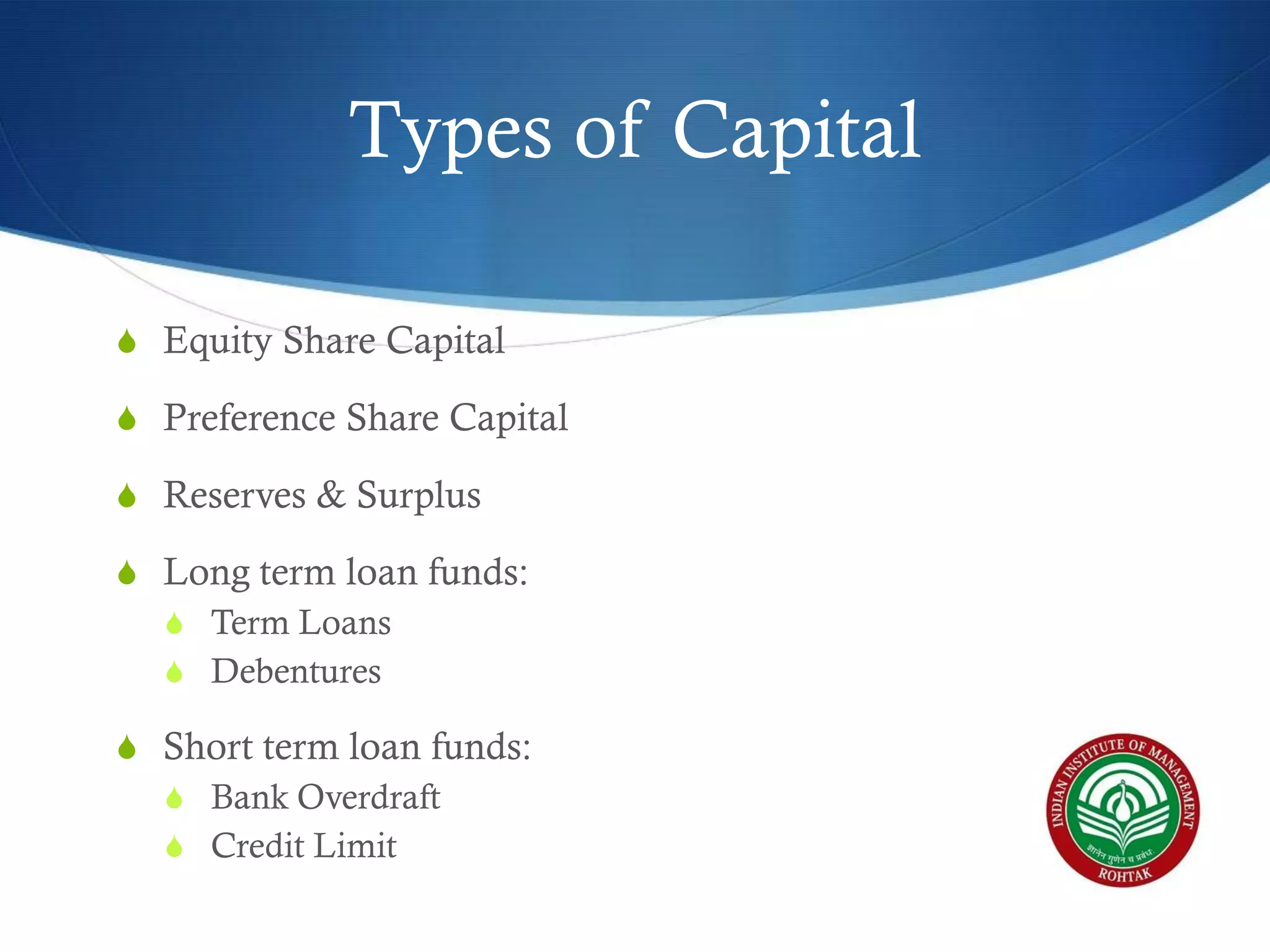
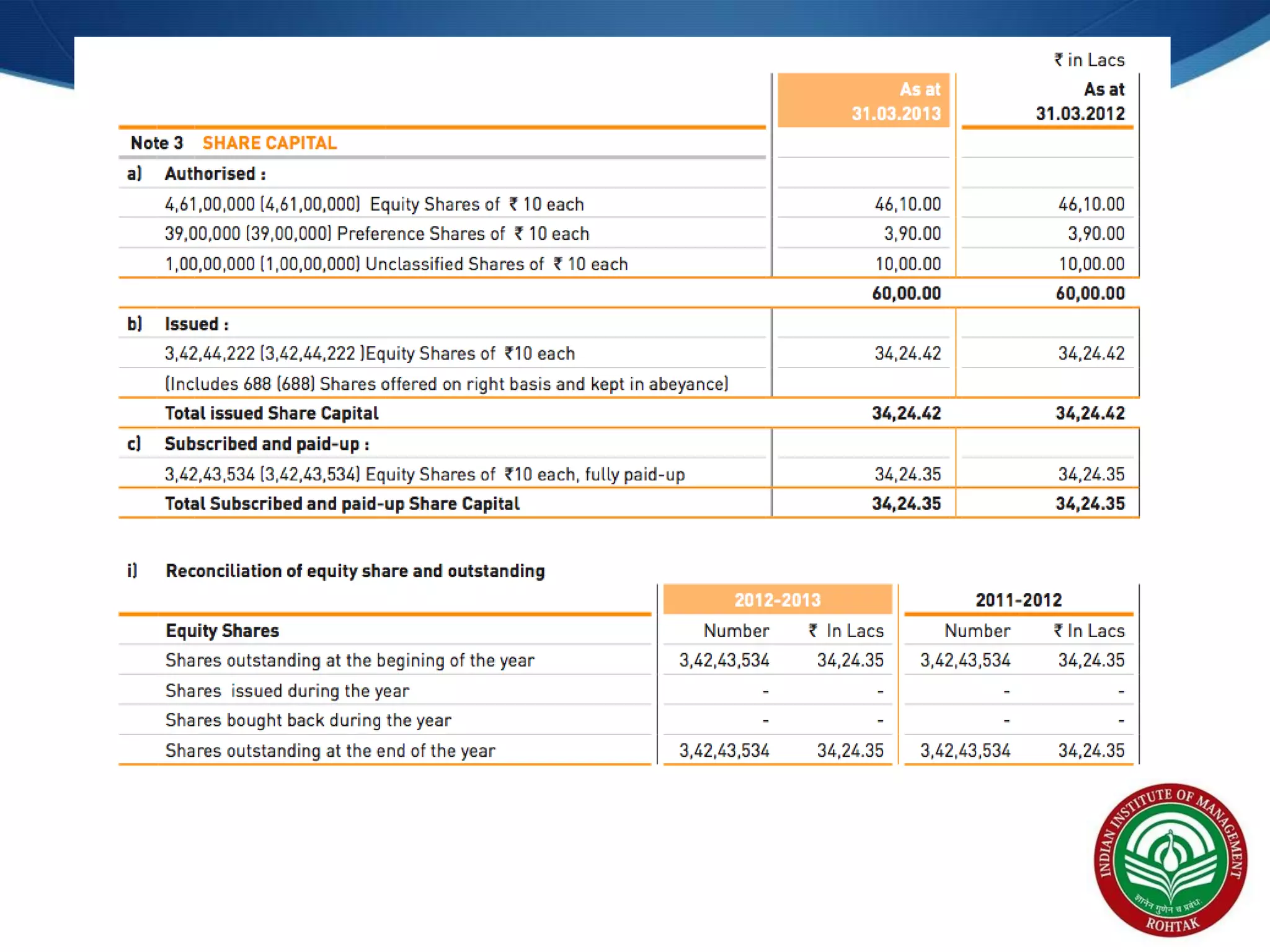
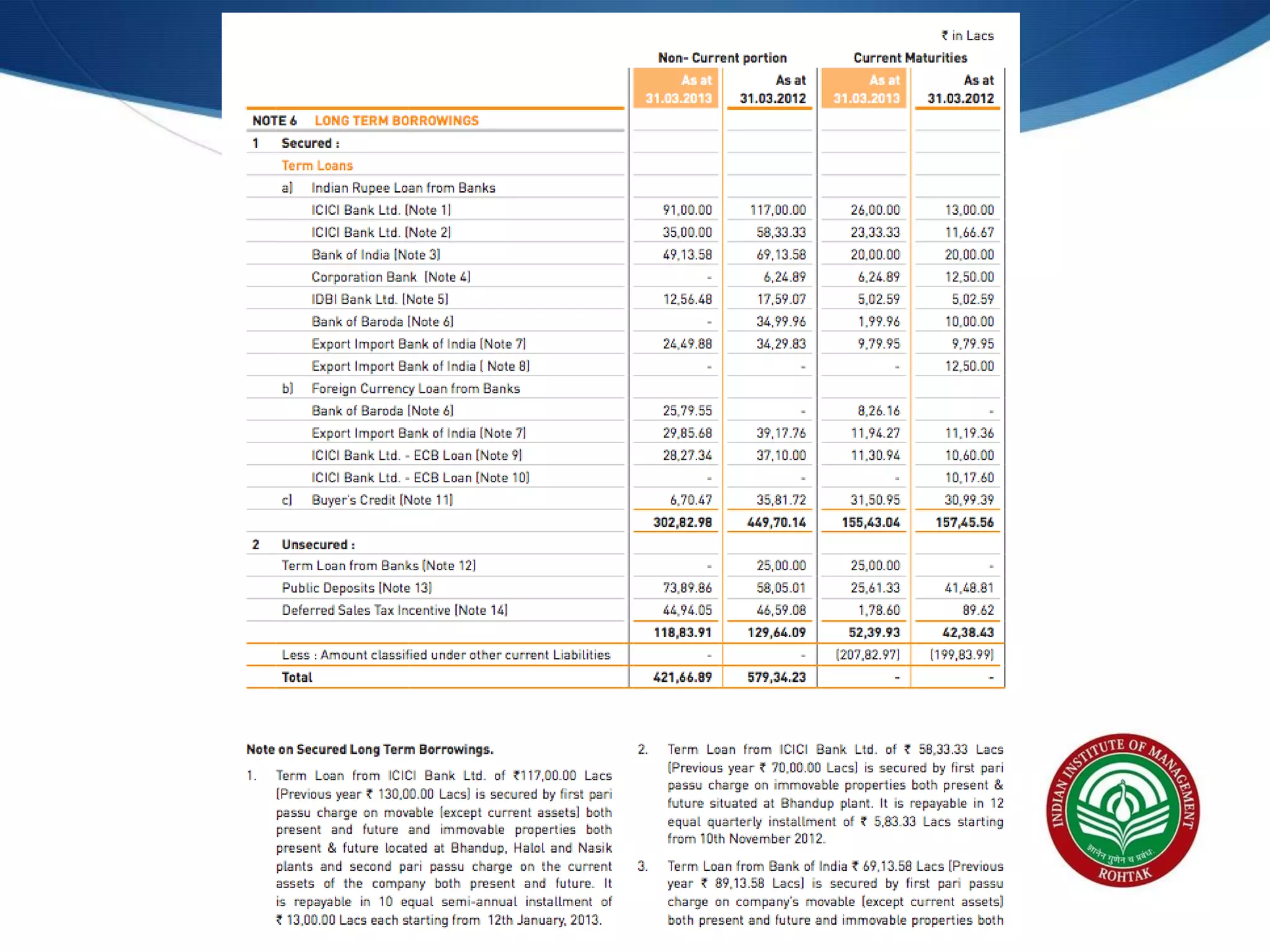
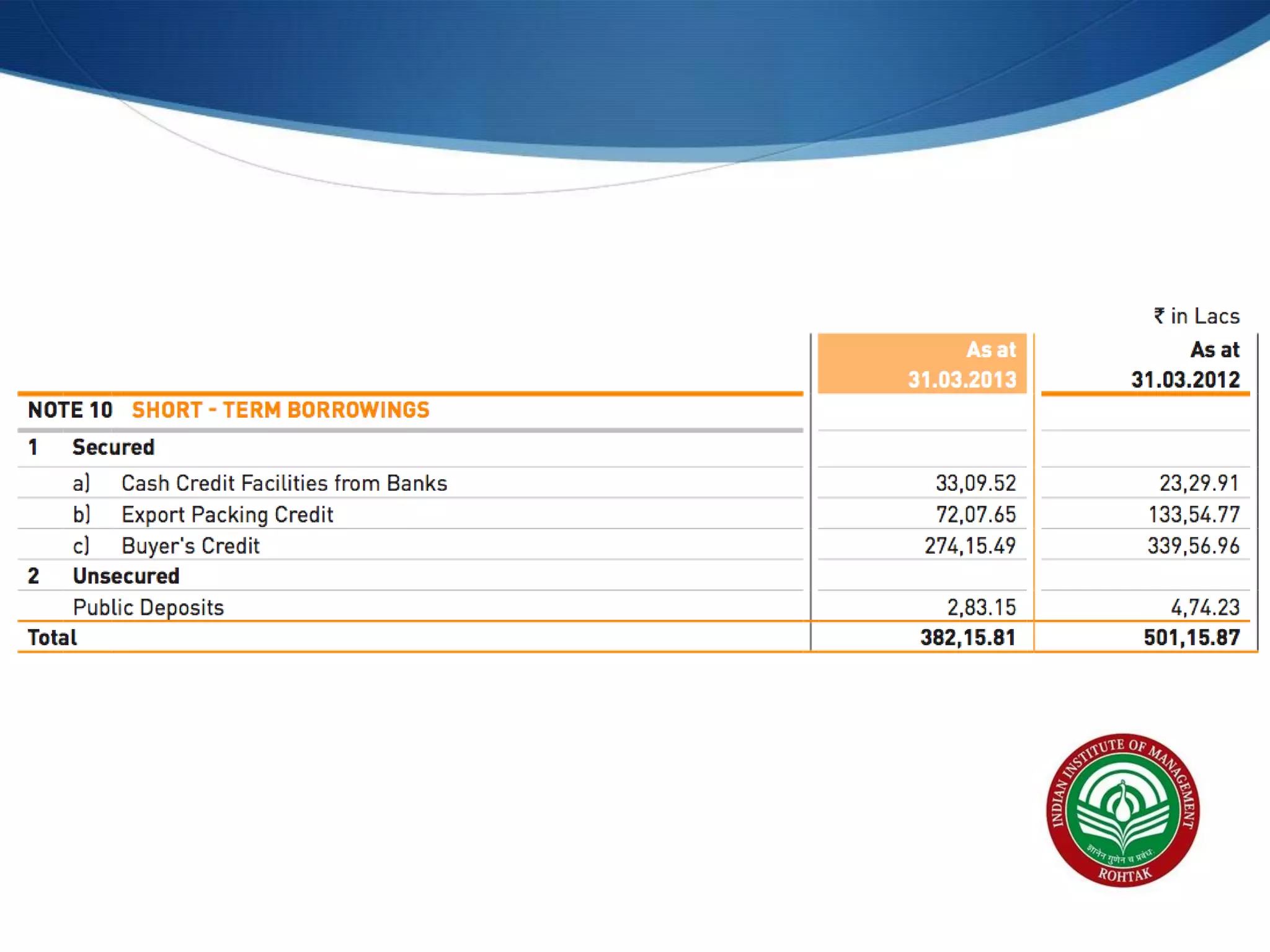
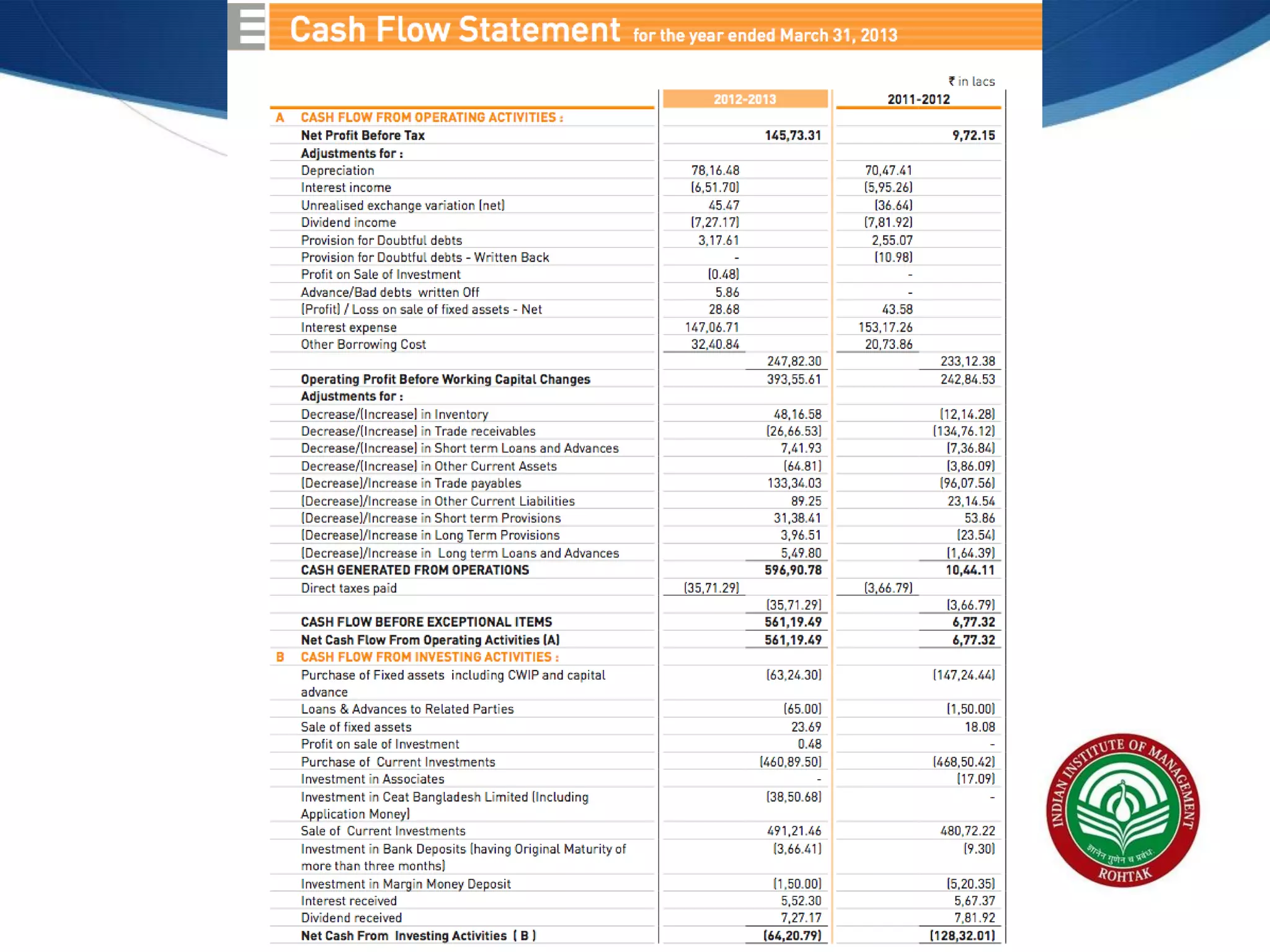
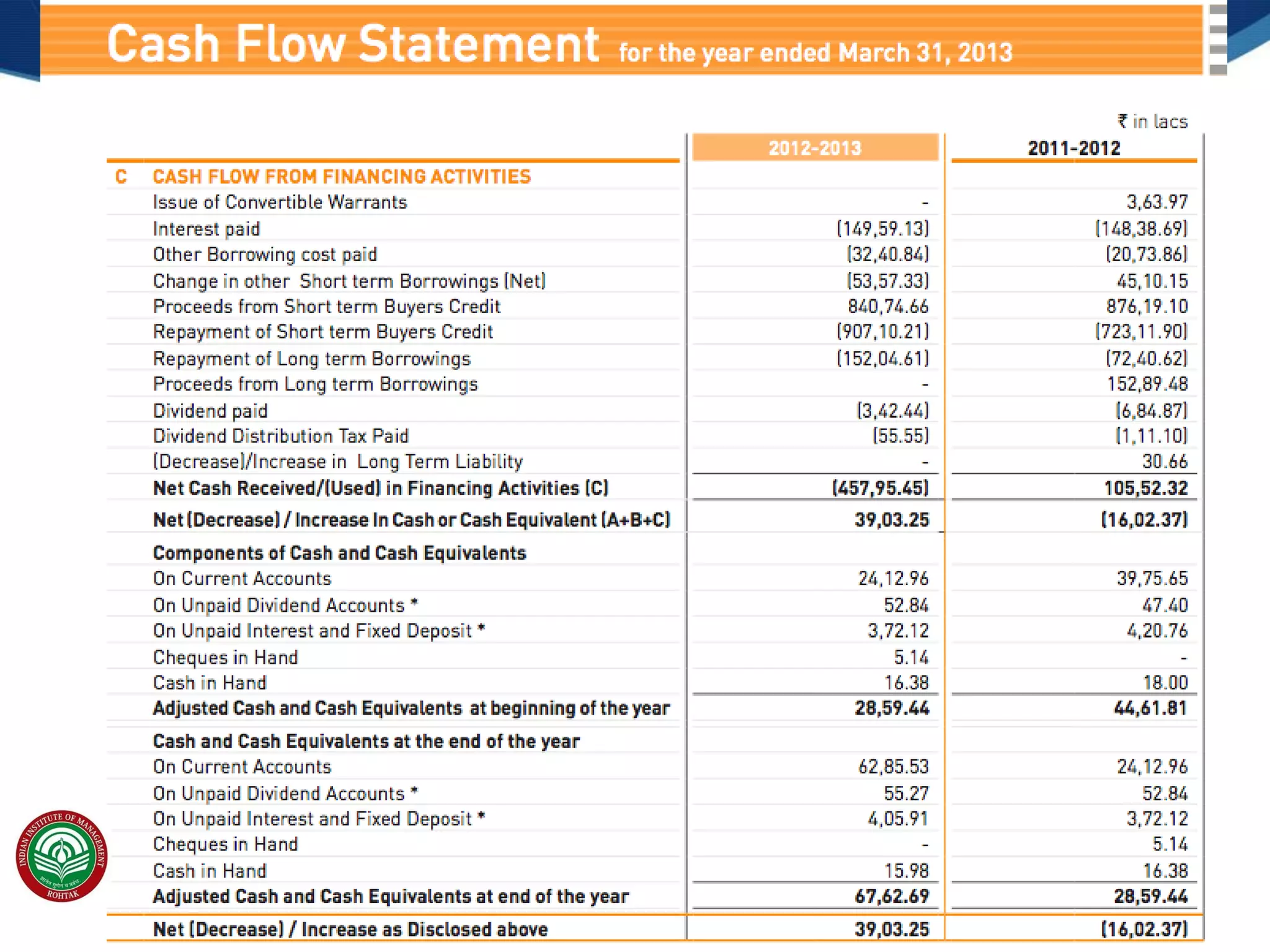
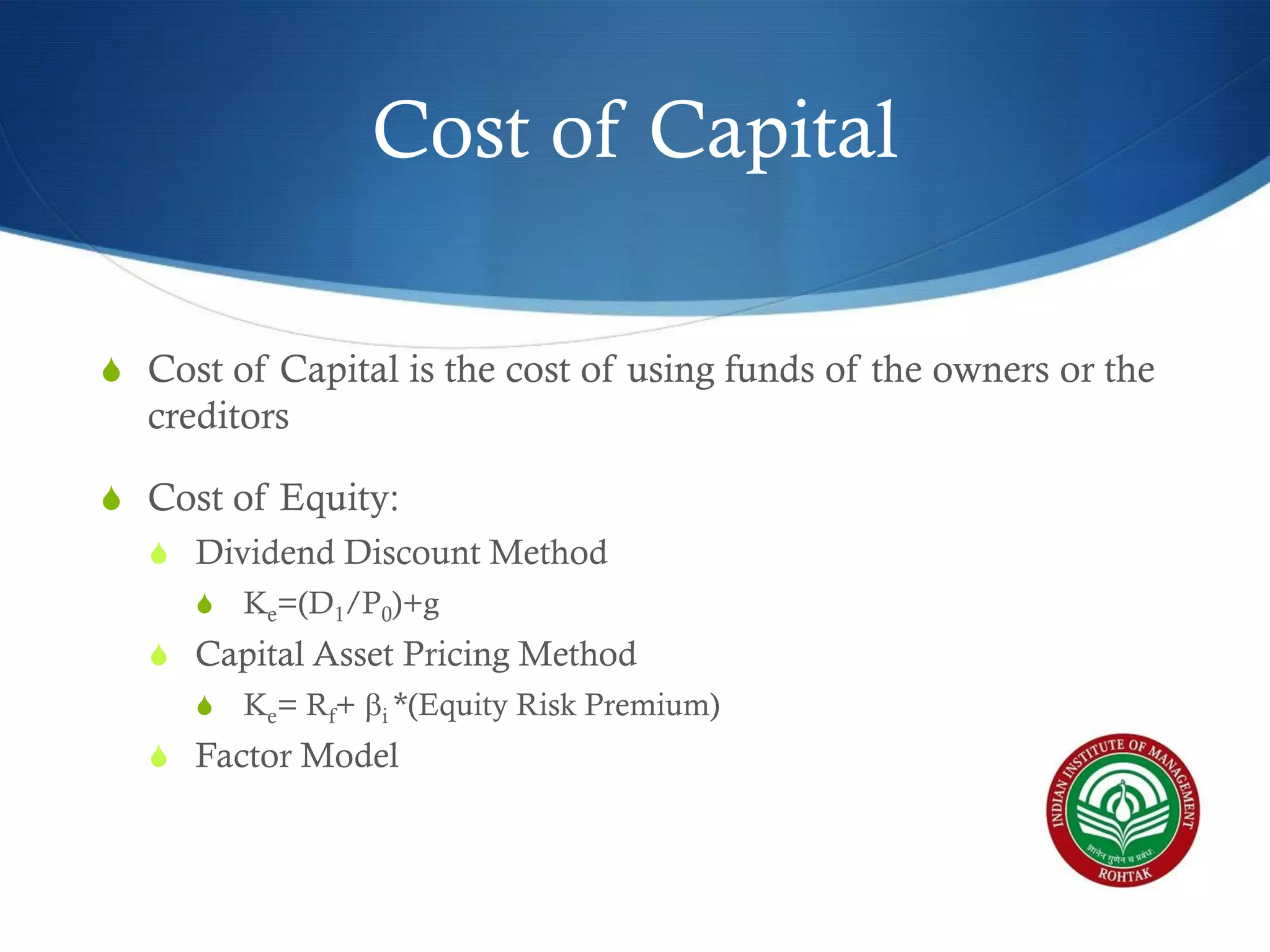
The document covers essential financial concepts in preparation for the WAT-PI process for admissions in 2014, focusing on topics such as accounting, derivatives, and cost of capital. Key areas include financial statements like profit and loss accounts, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, along with various financial ratios. Additionally, it explains derivatives including futures, forwards, options, and swaps, as well as the methods for calculating cost of capital.