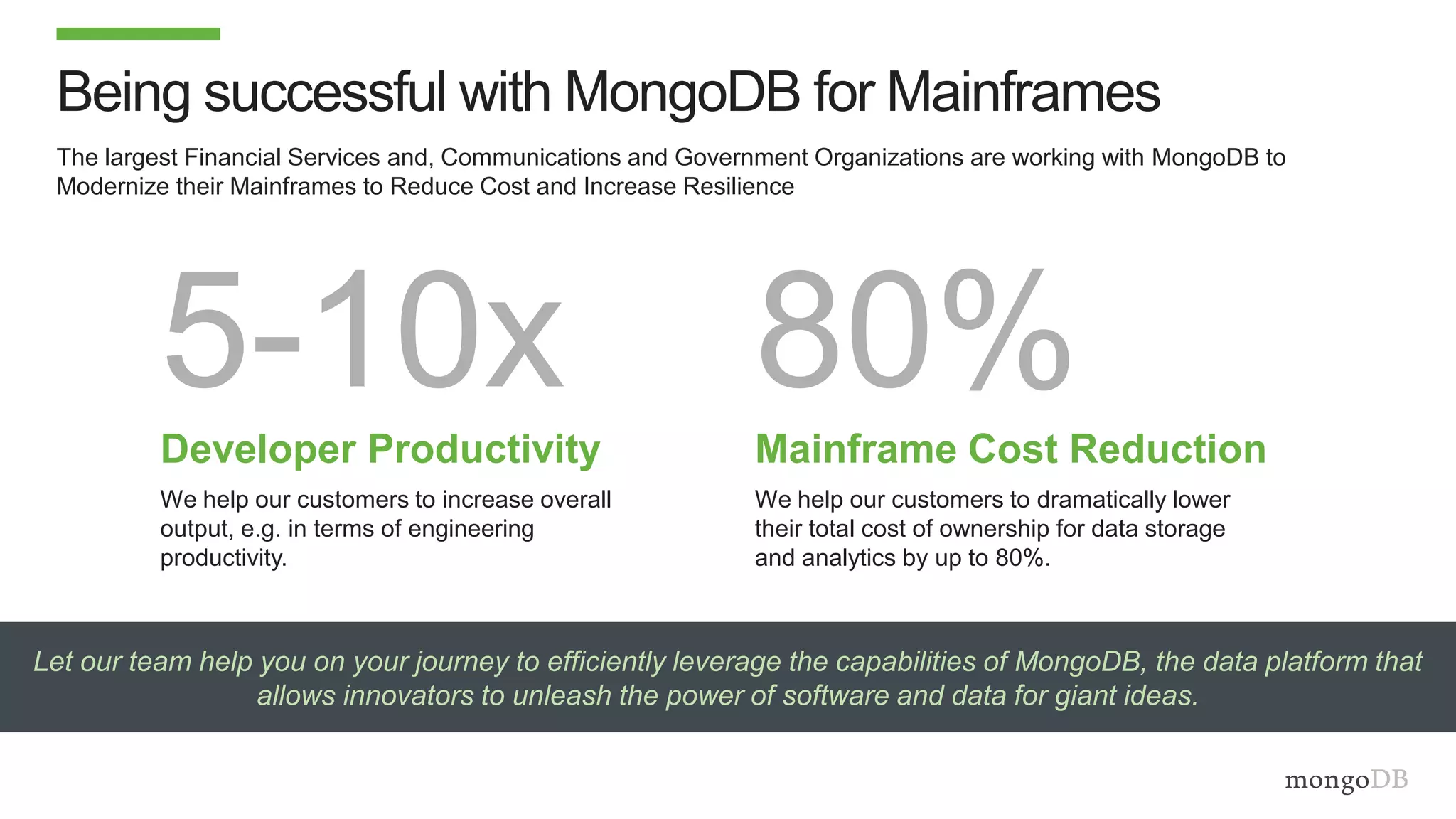
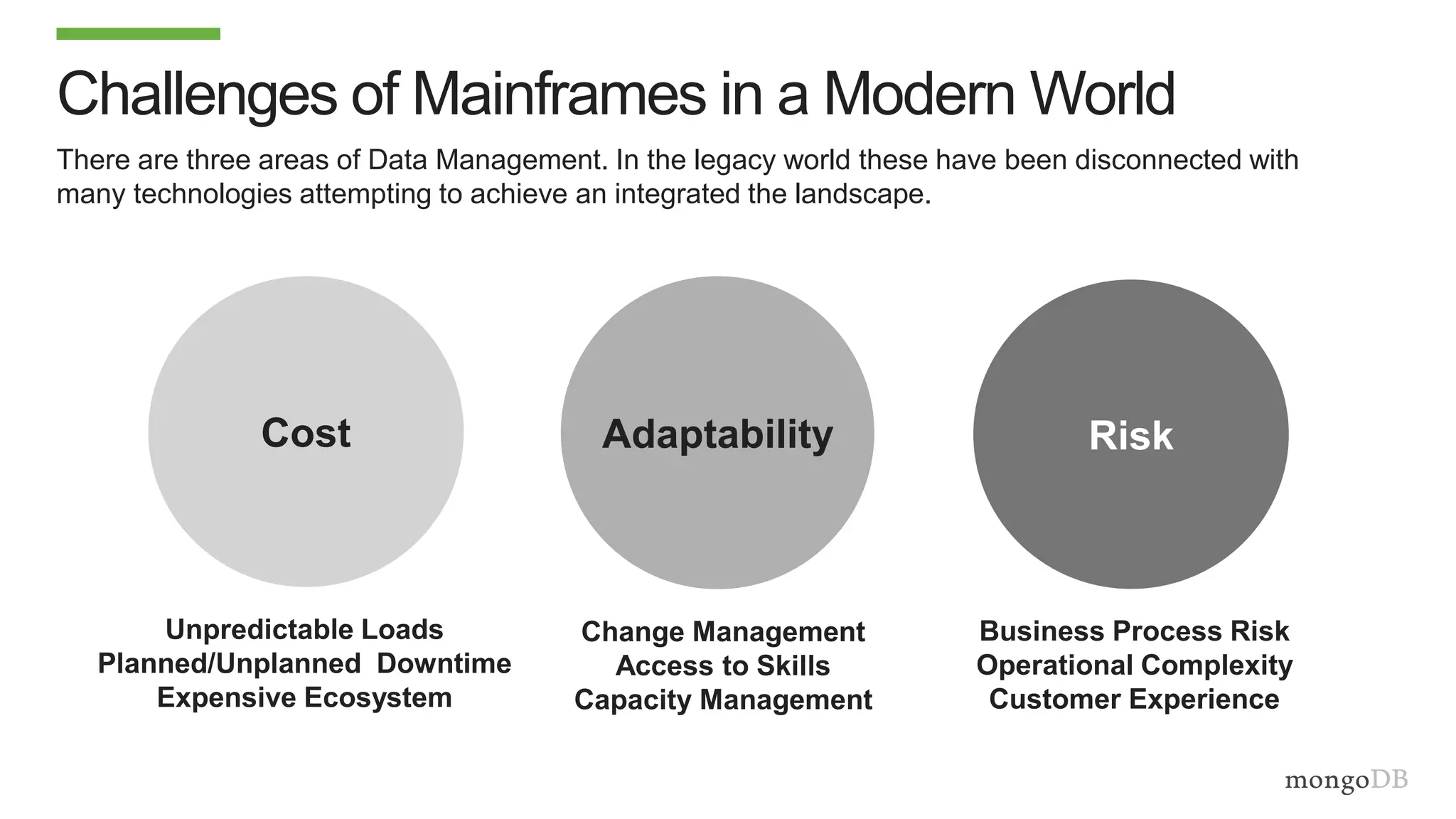
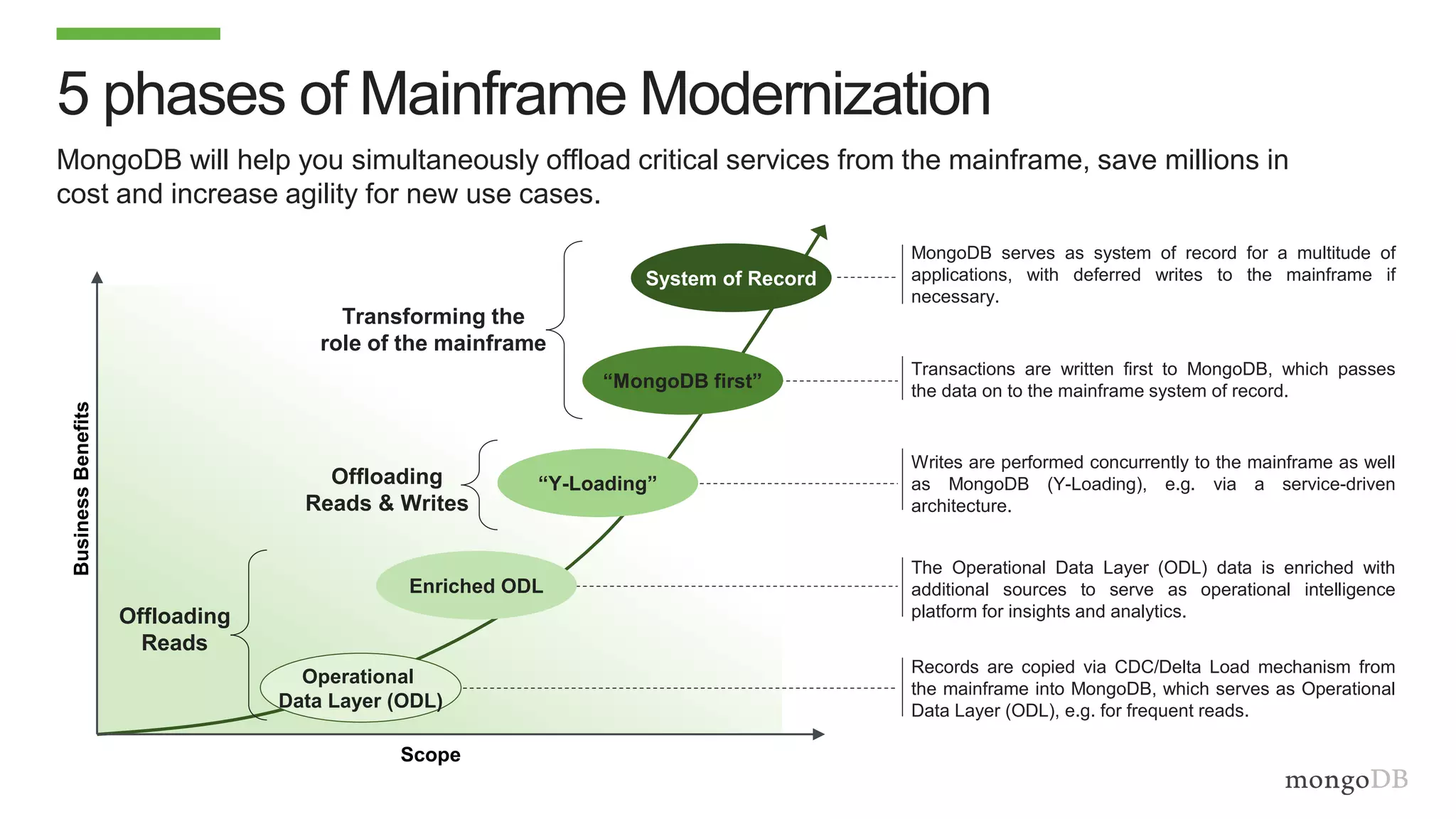
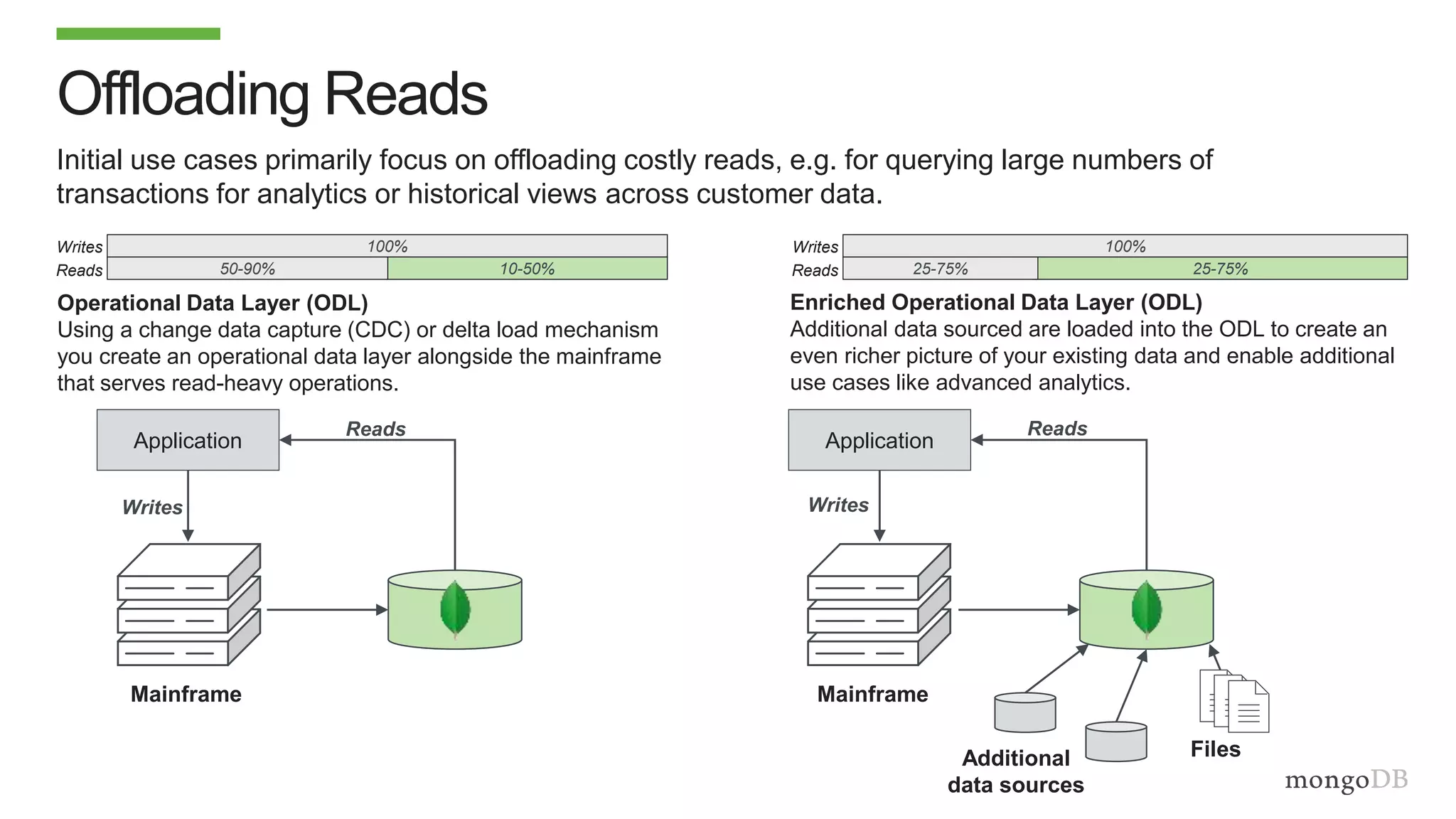
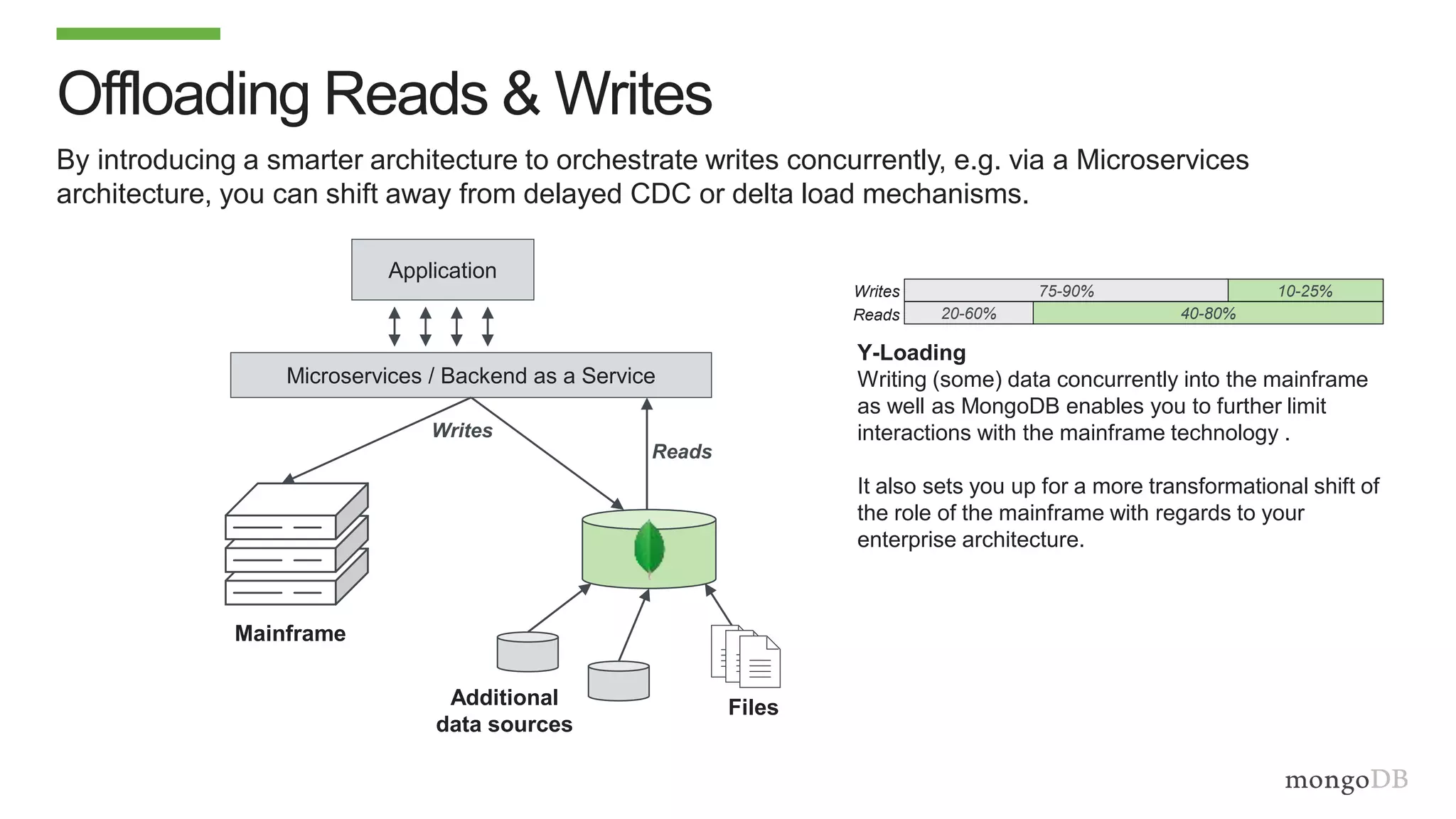
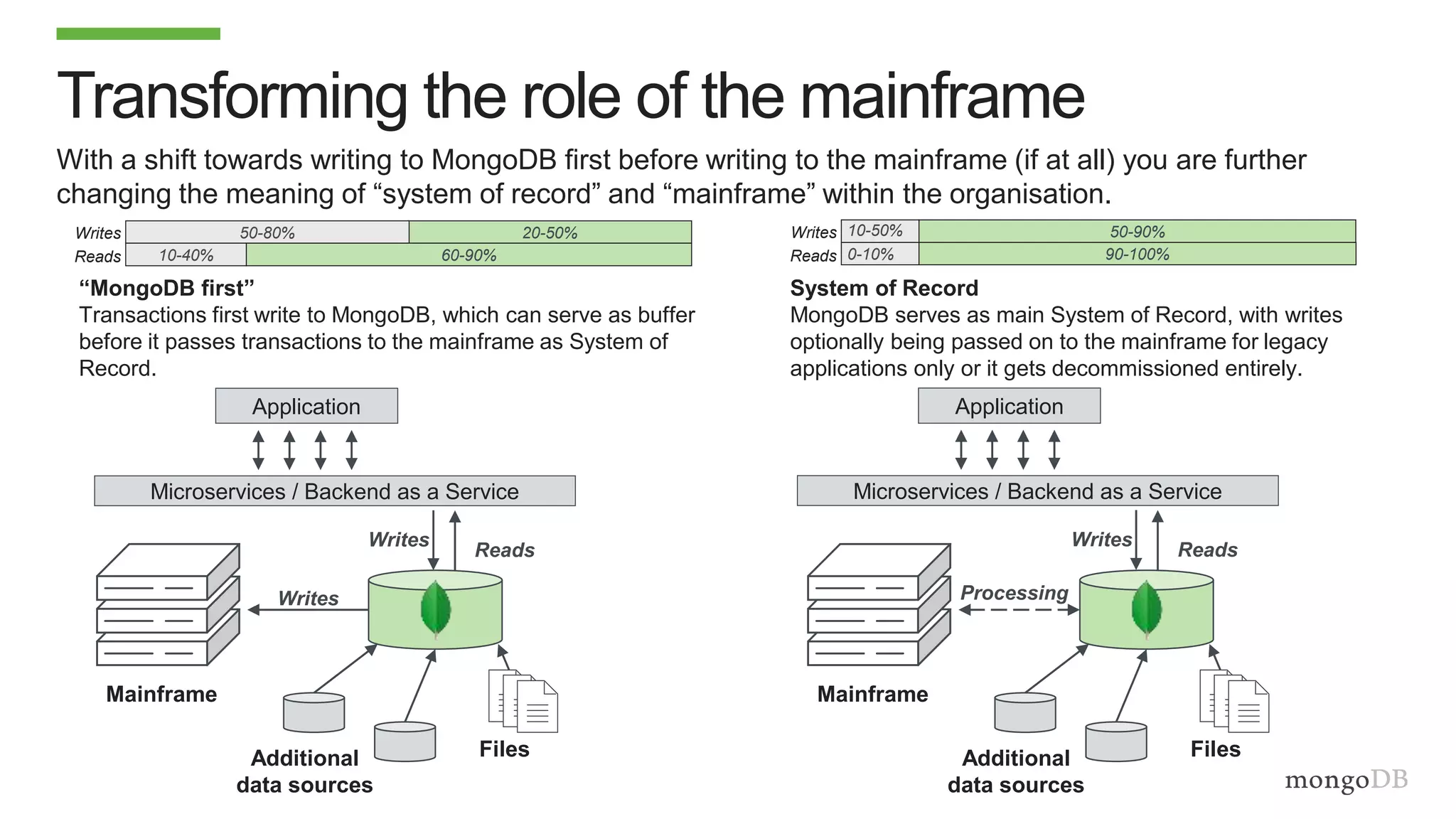
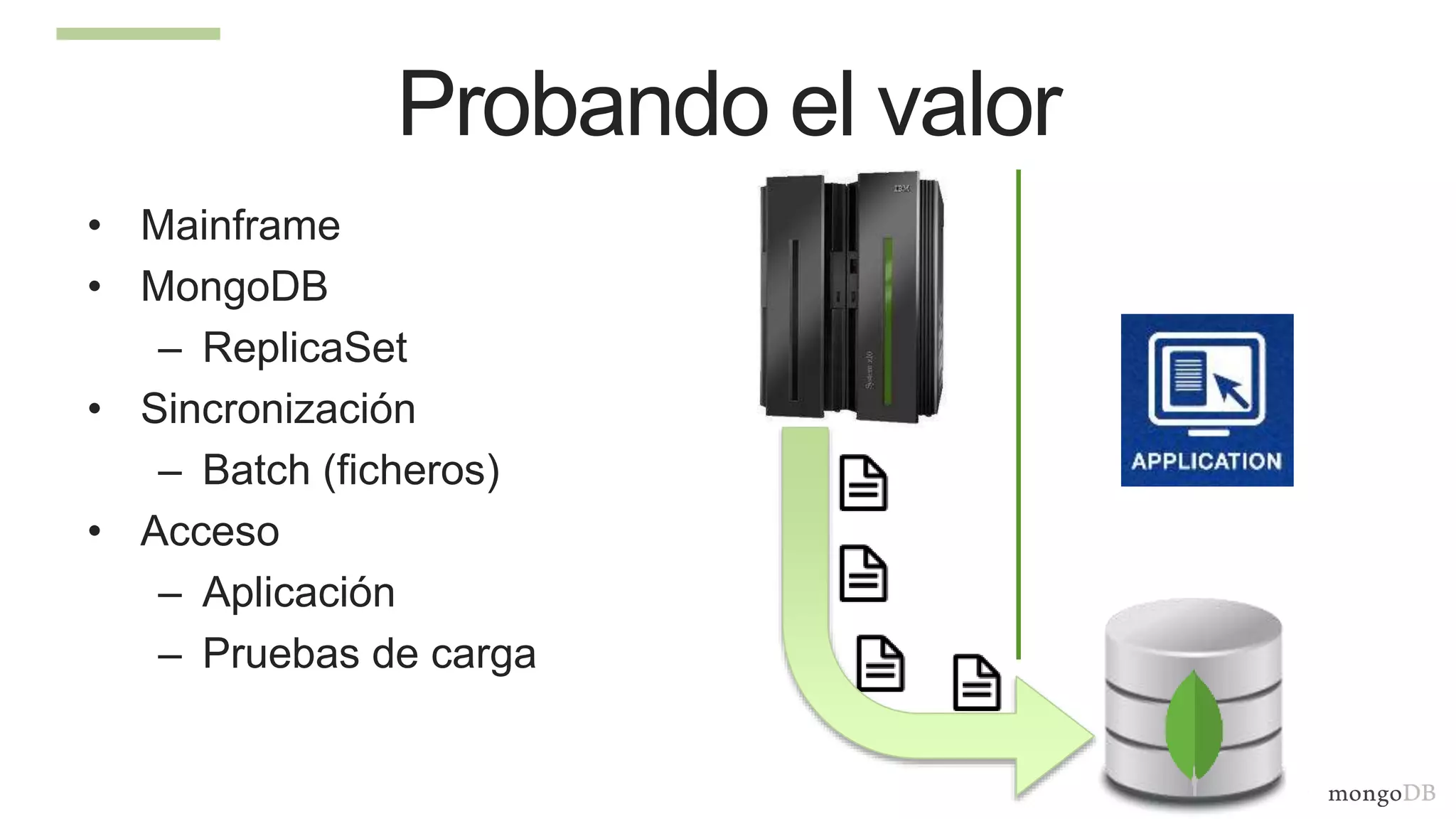
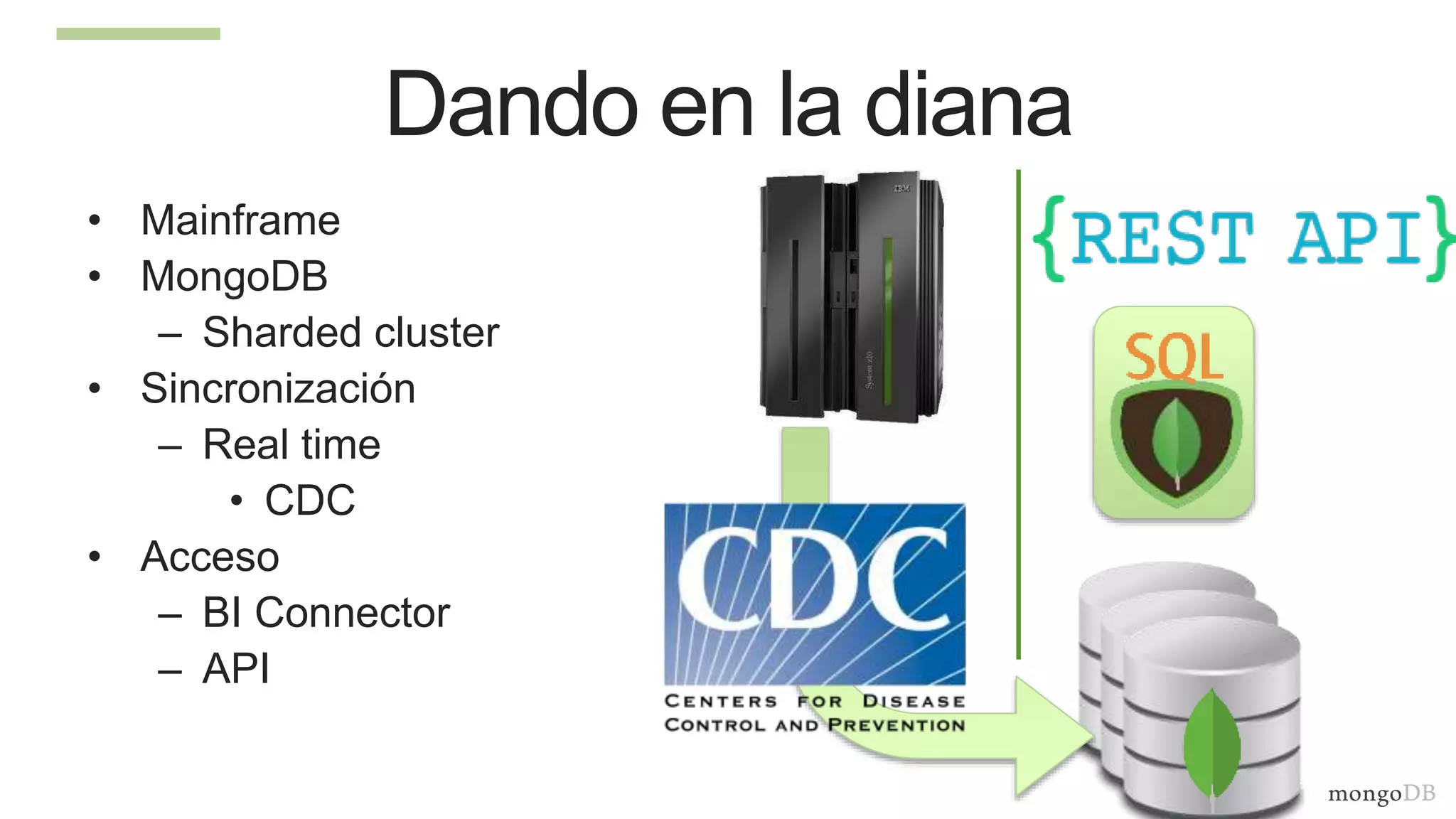
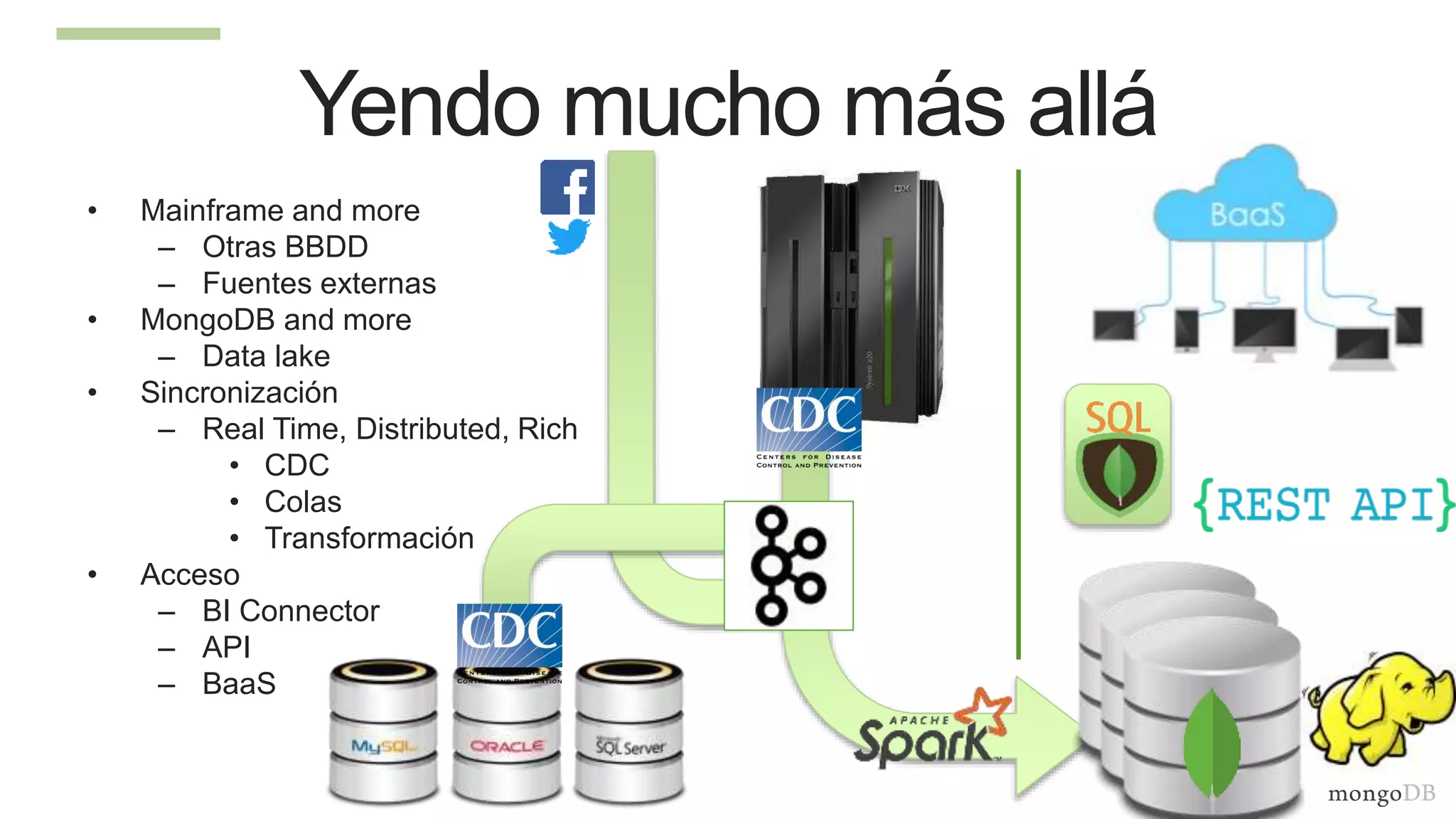
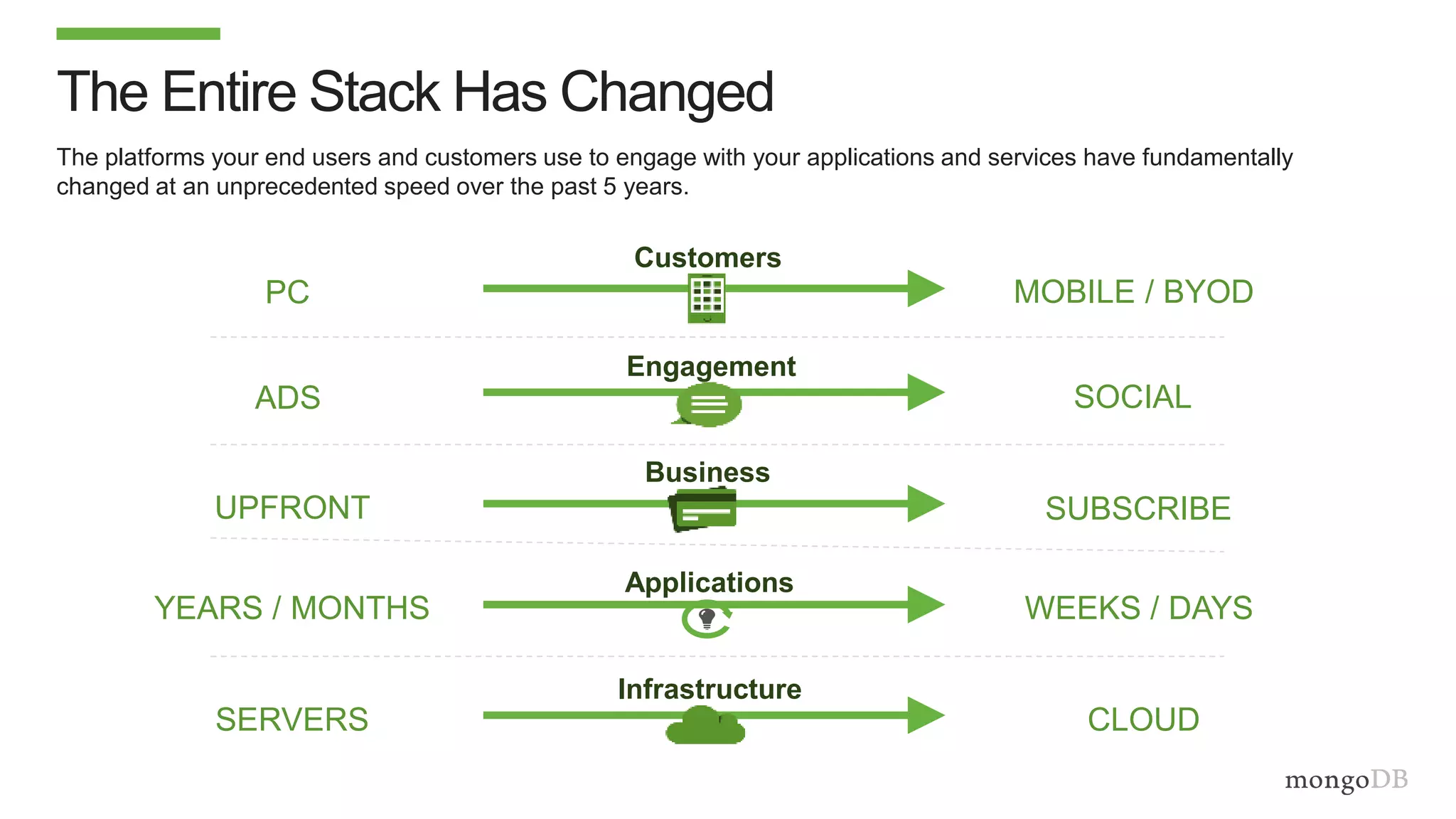
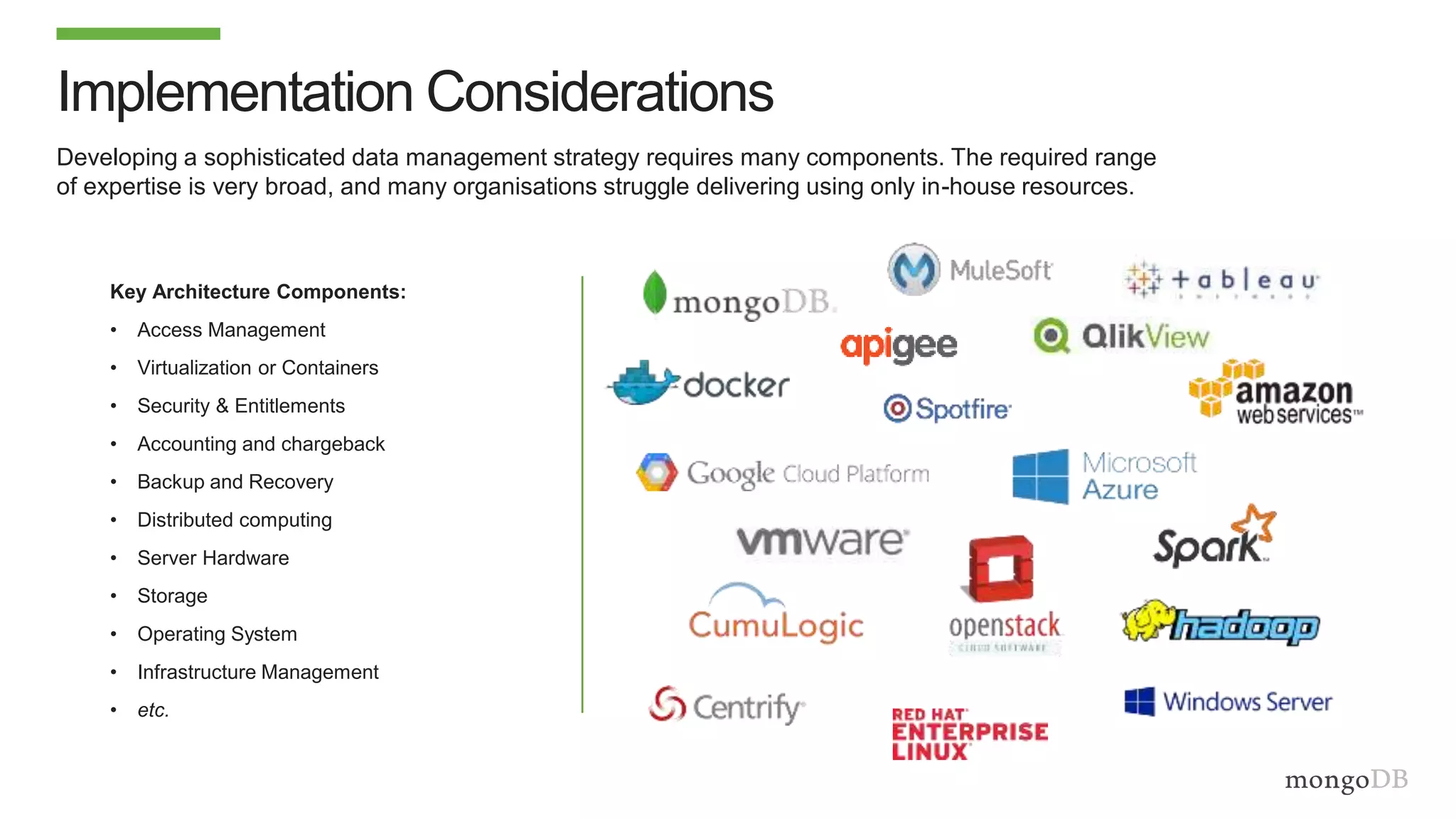
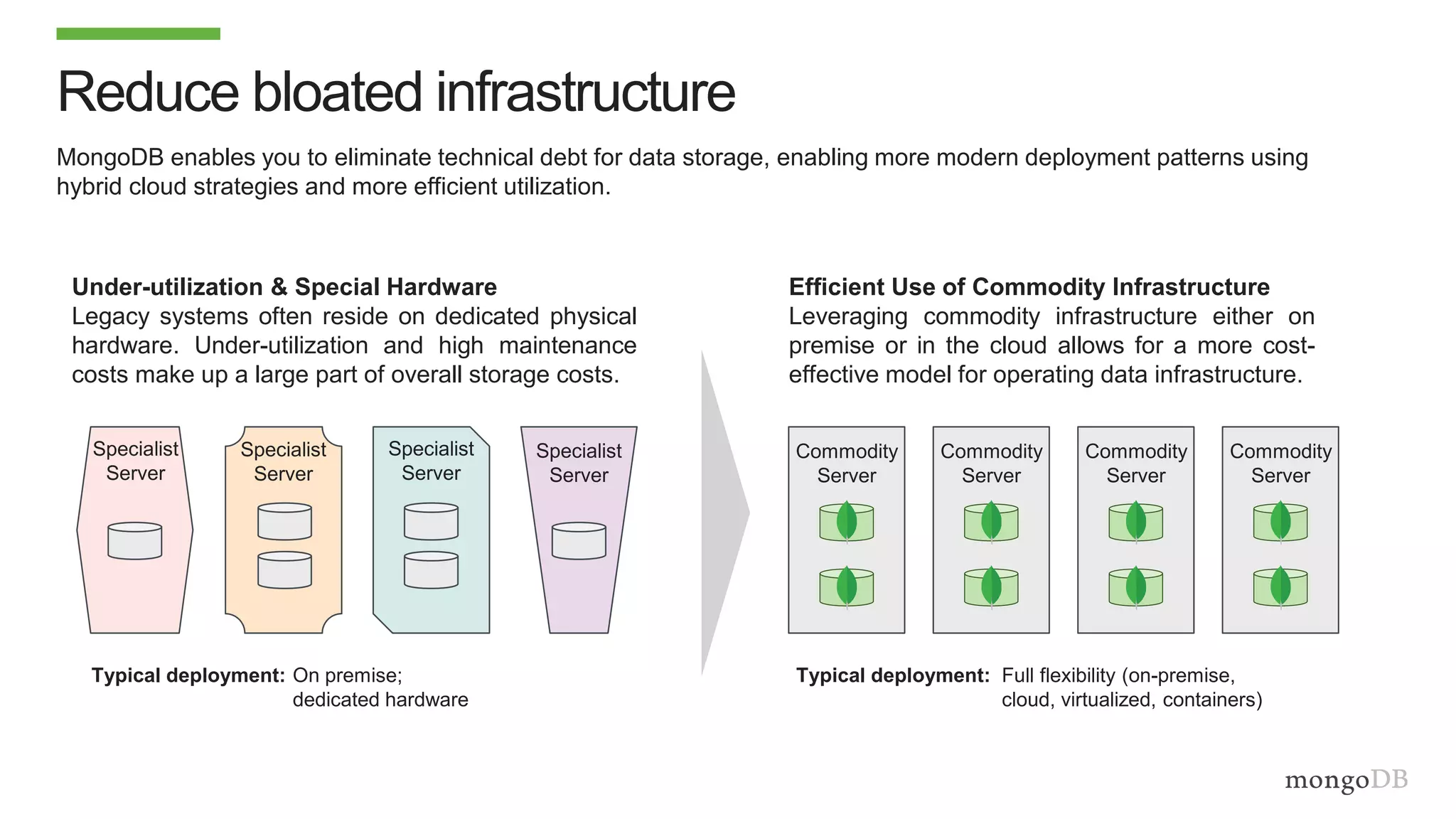
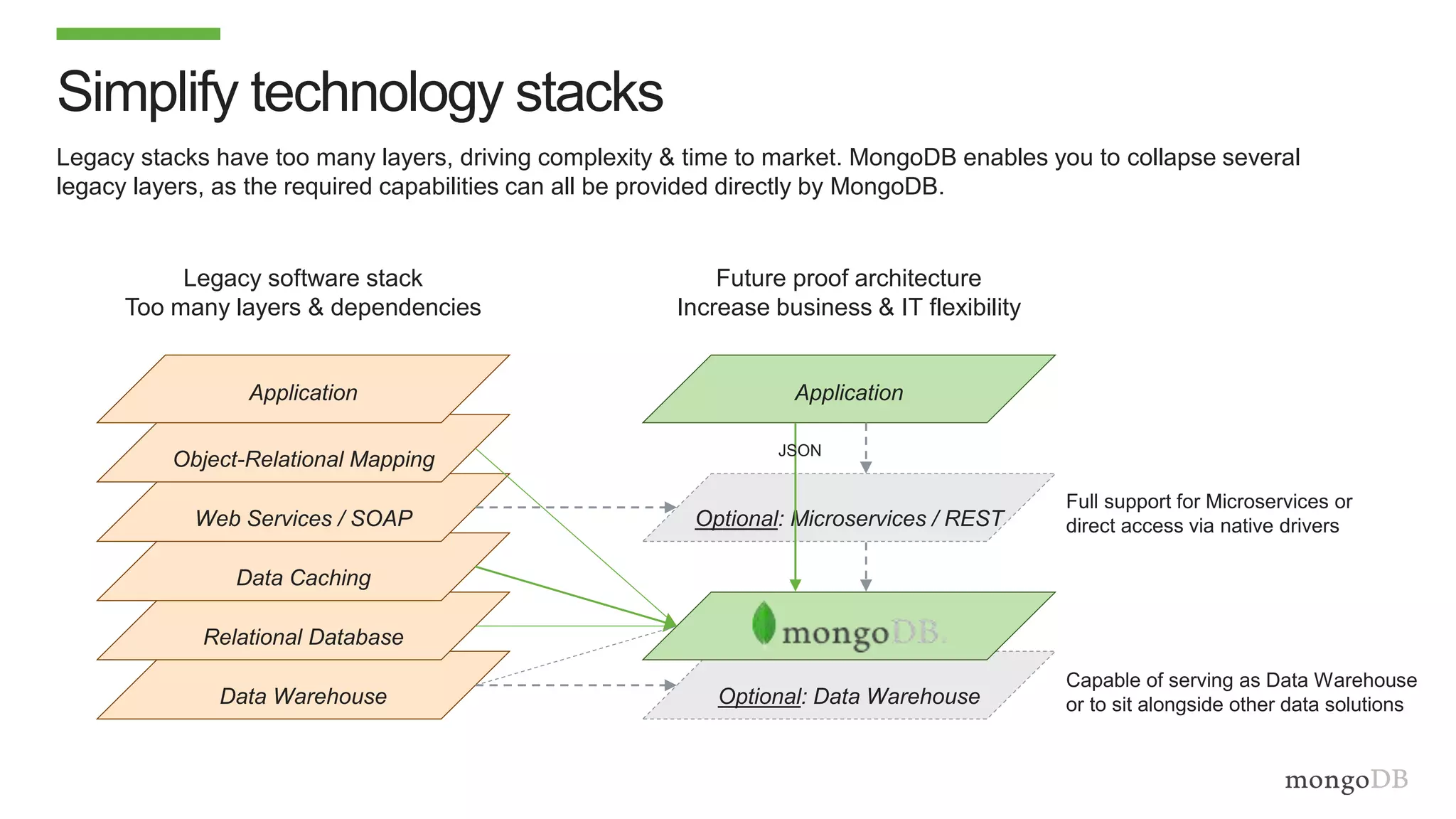
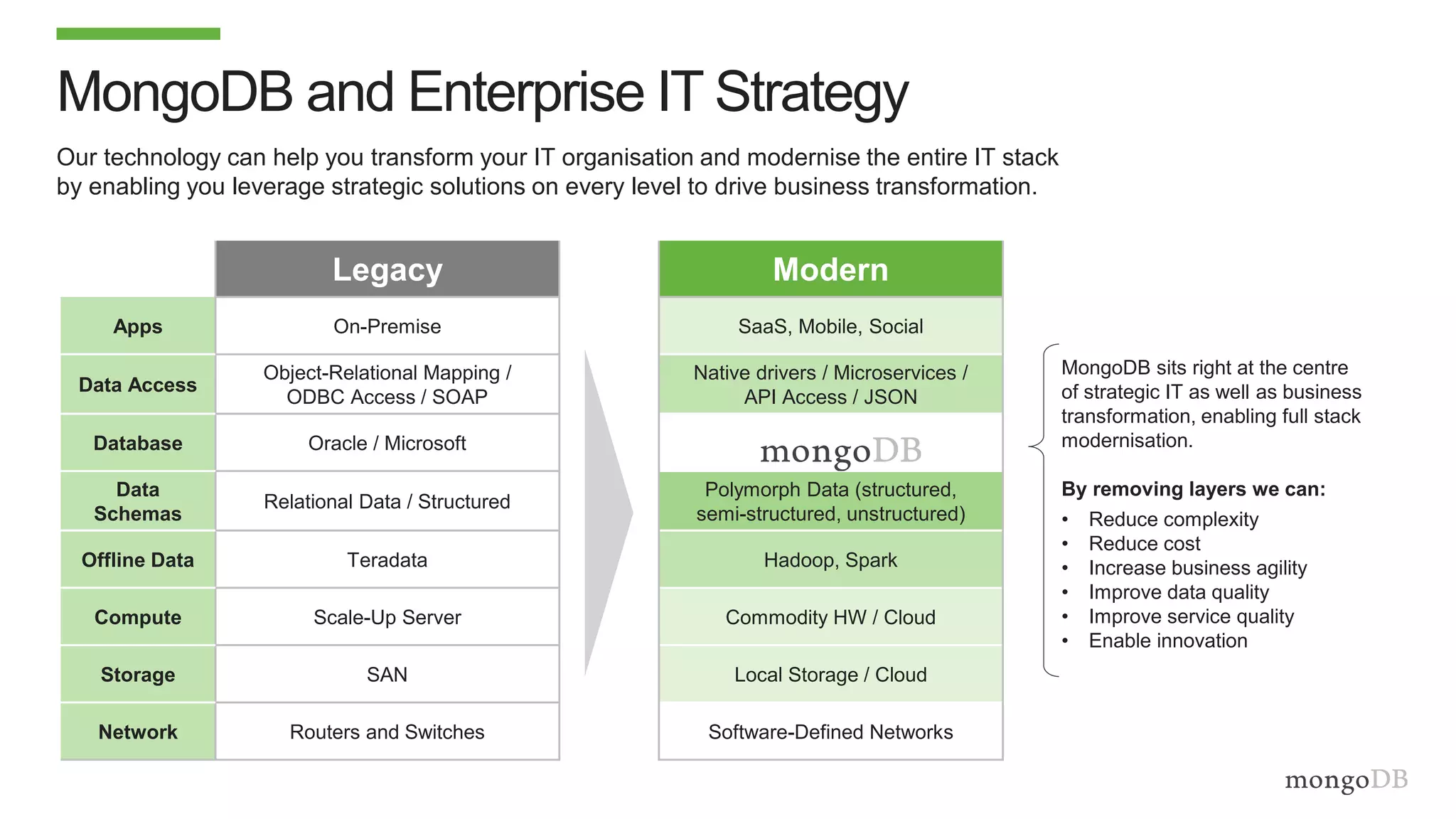
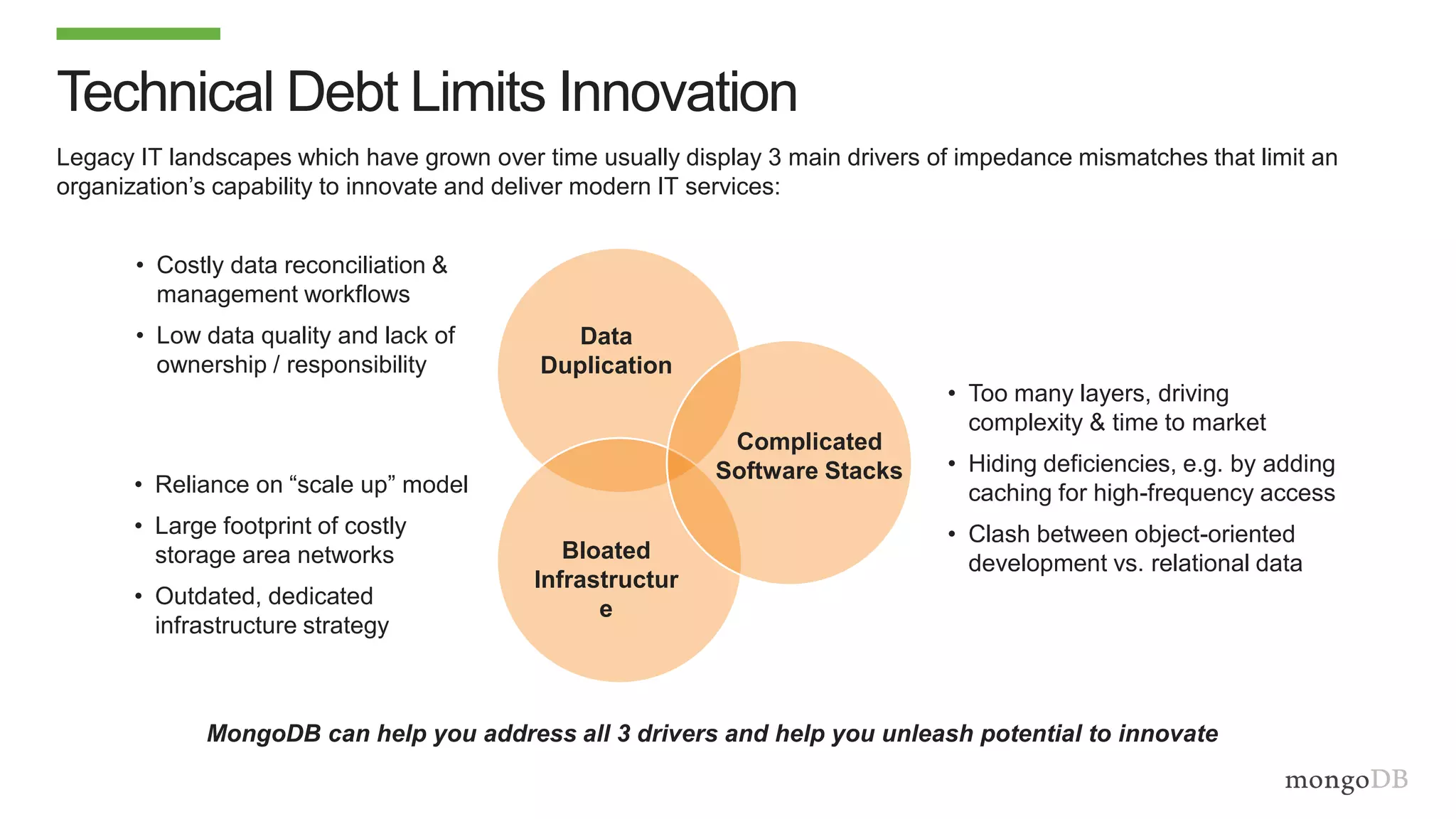
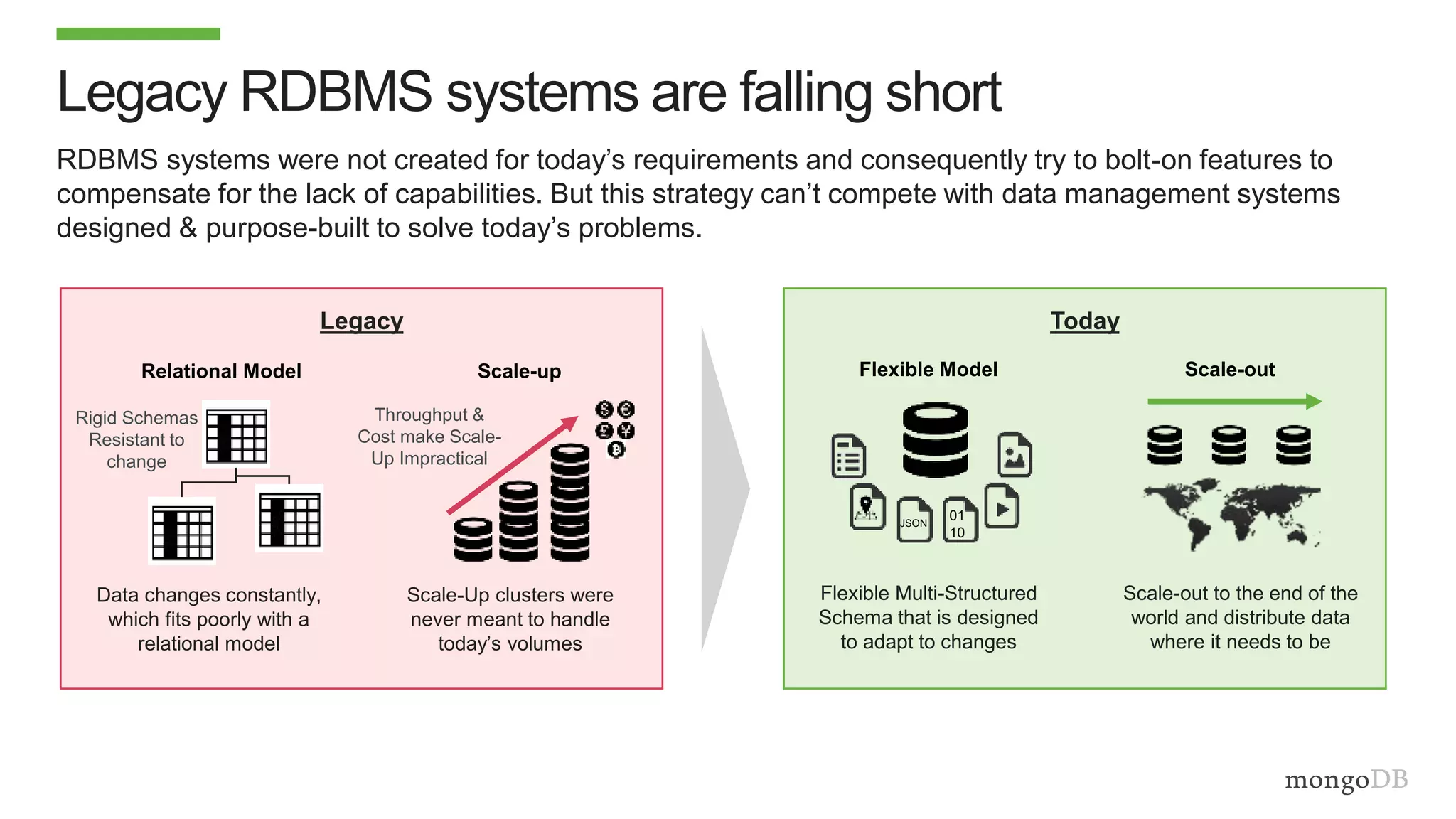
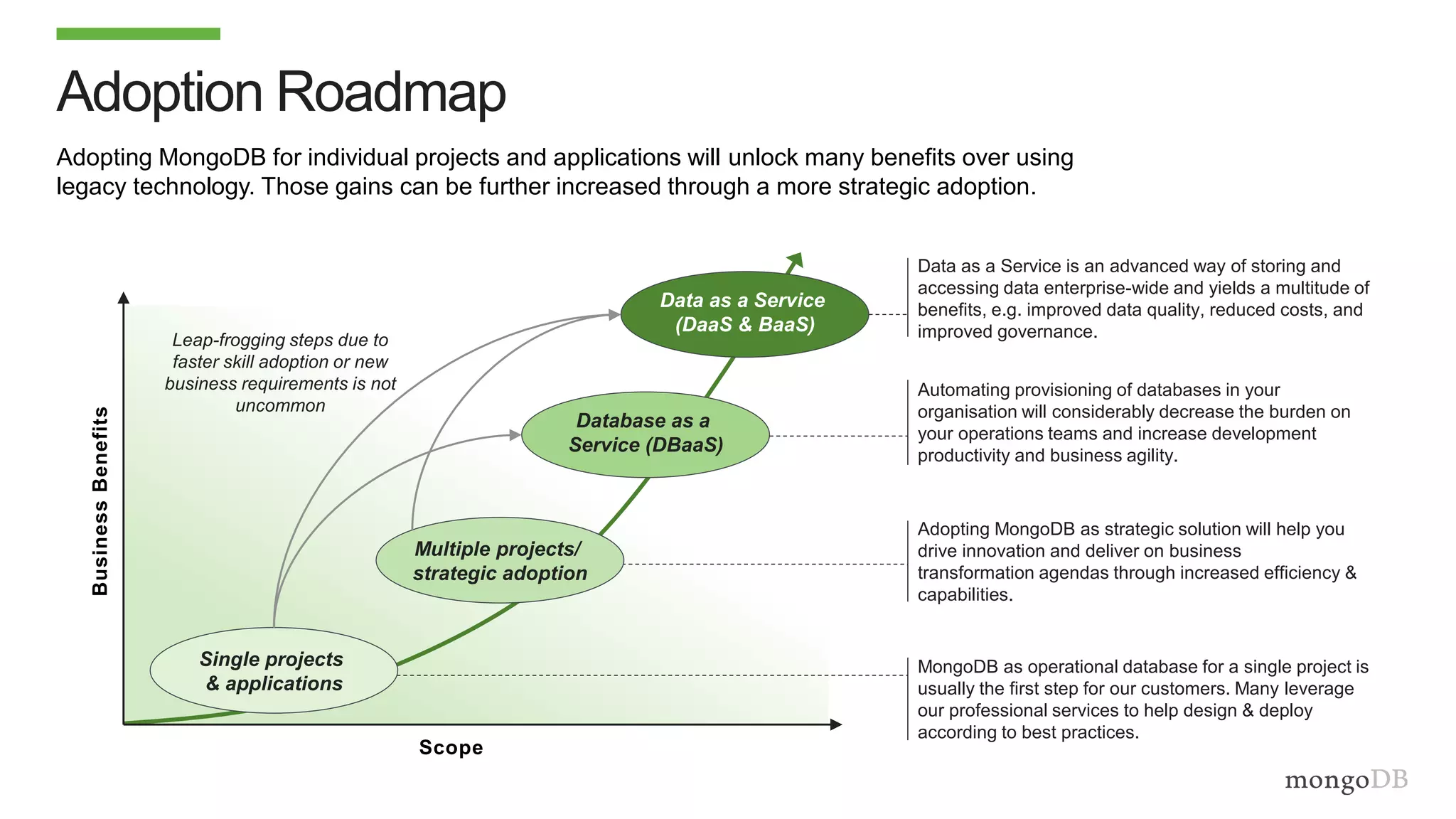
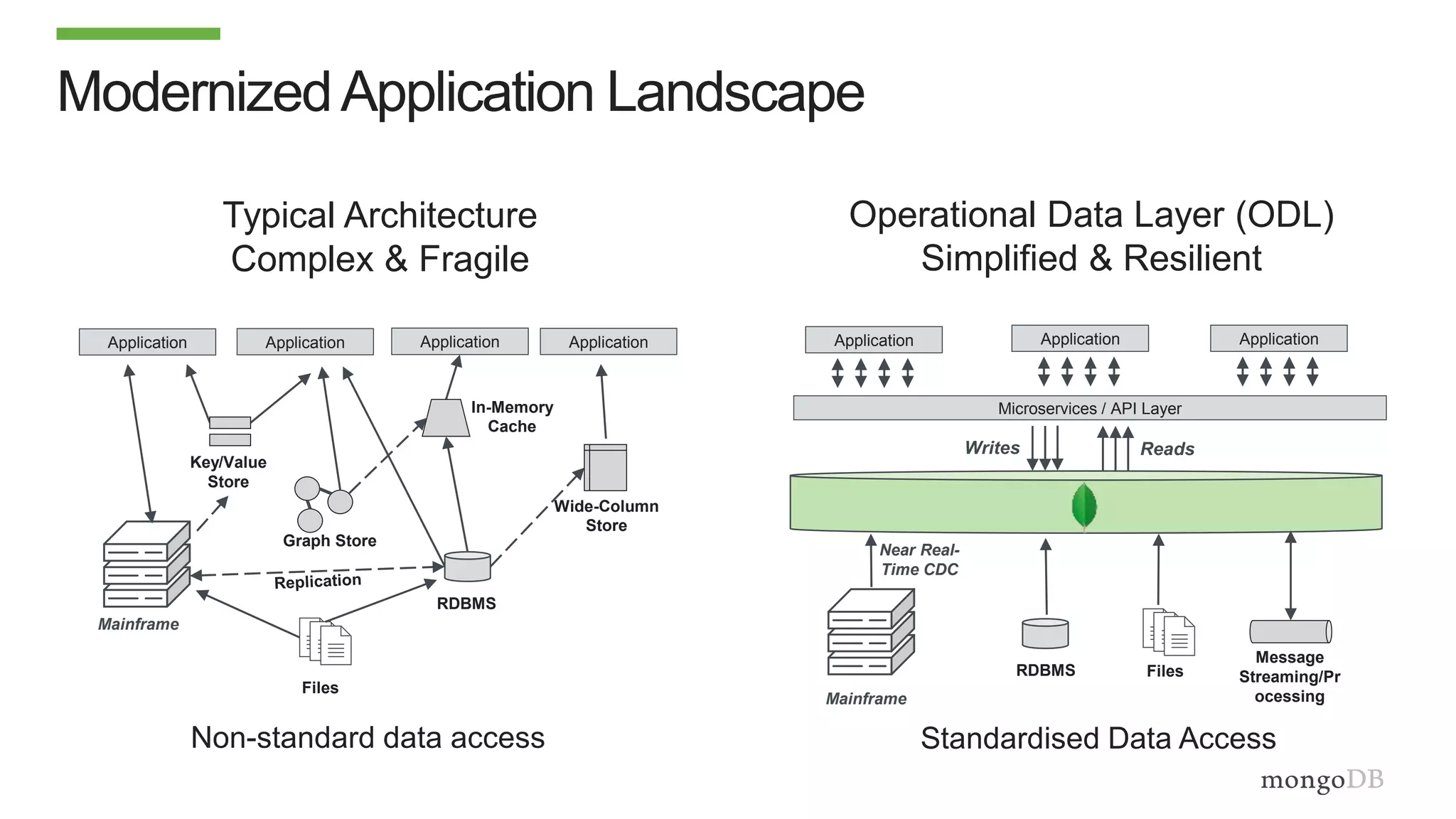
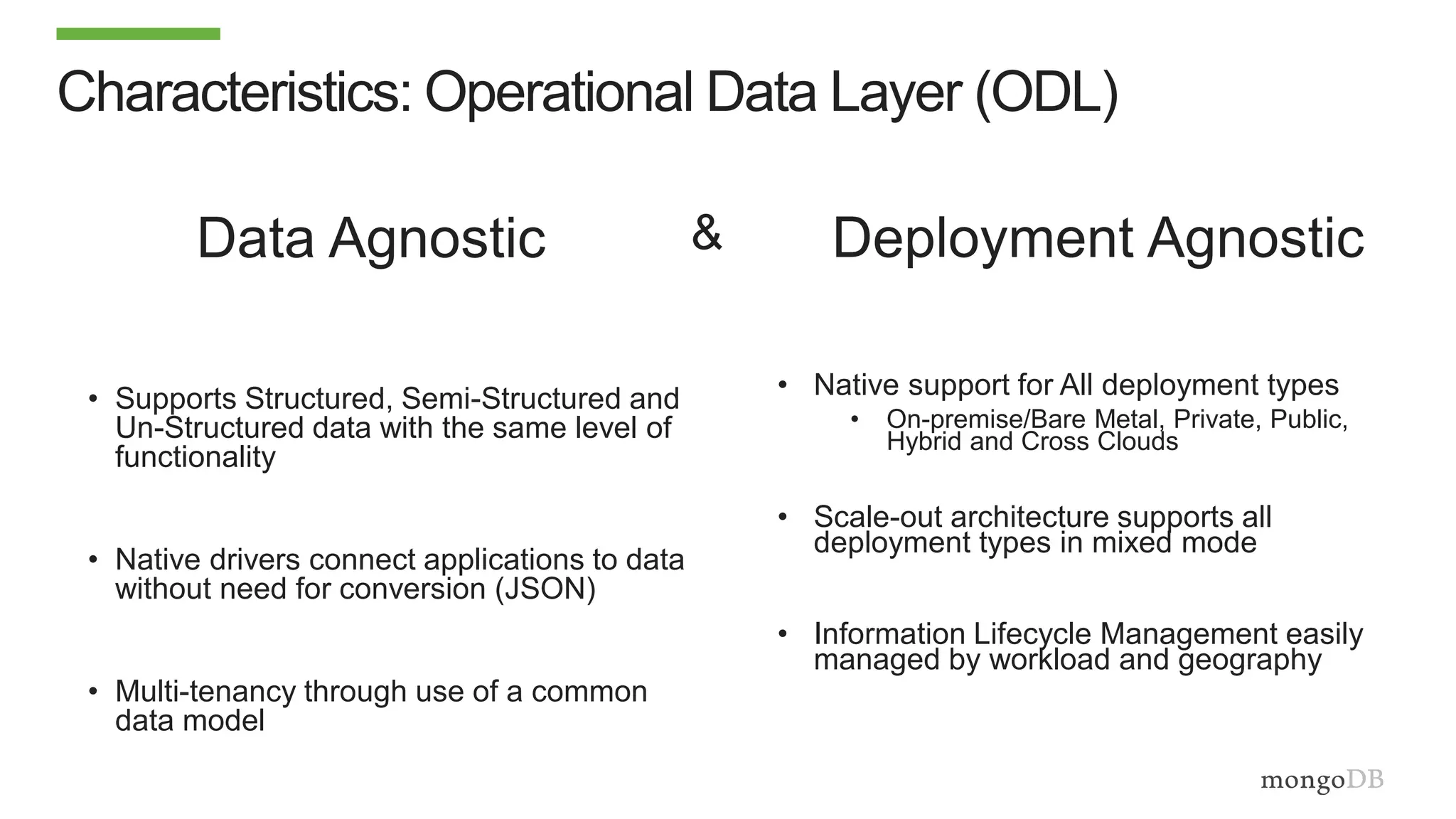
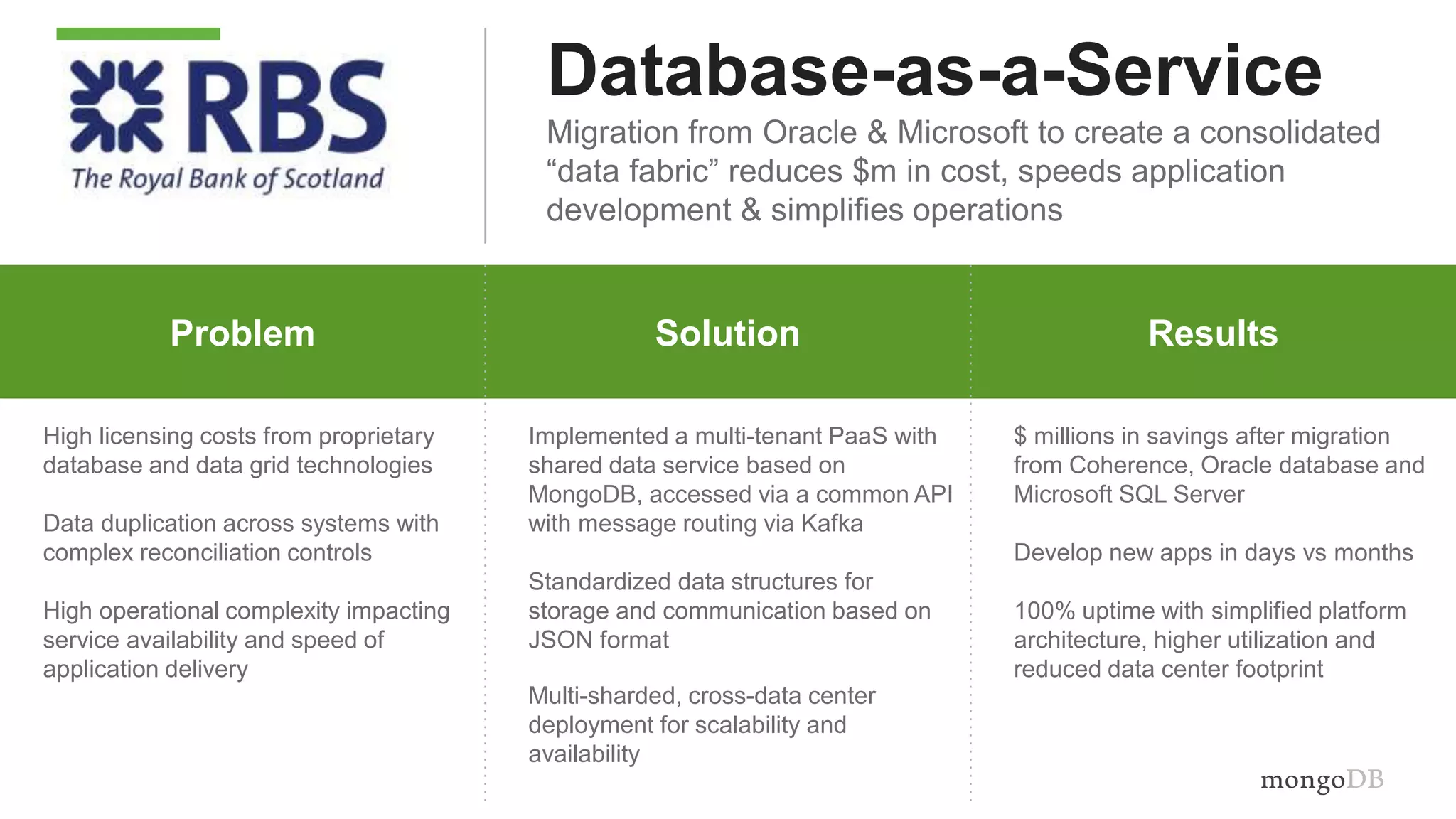
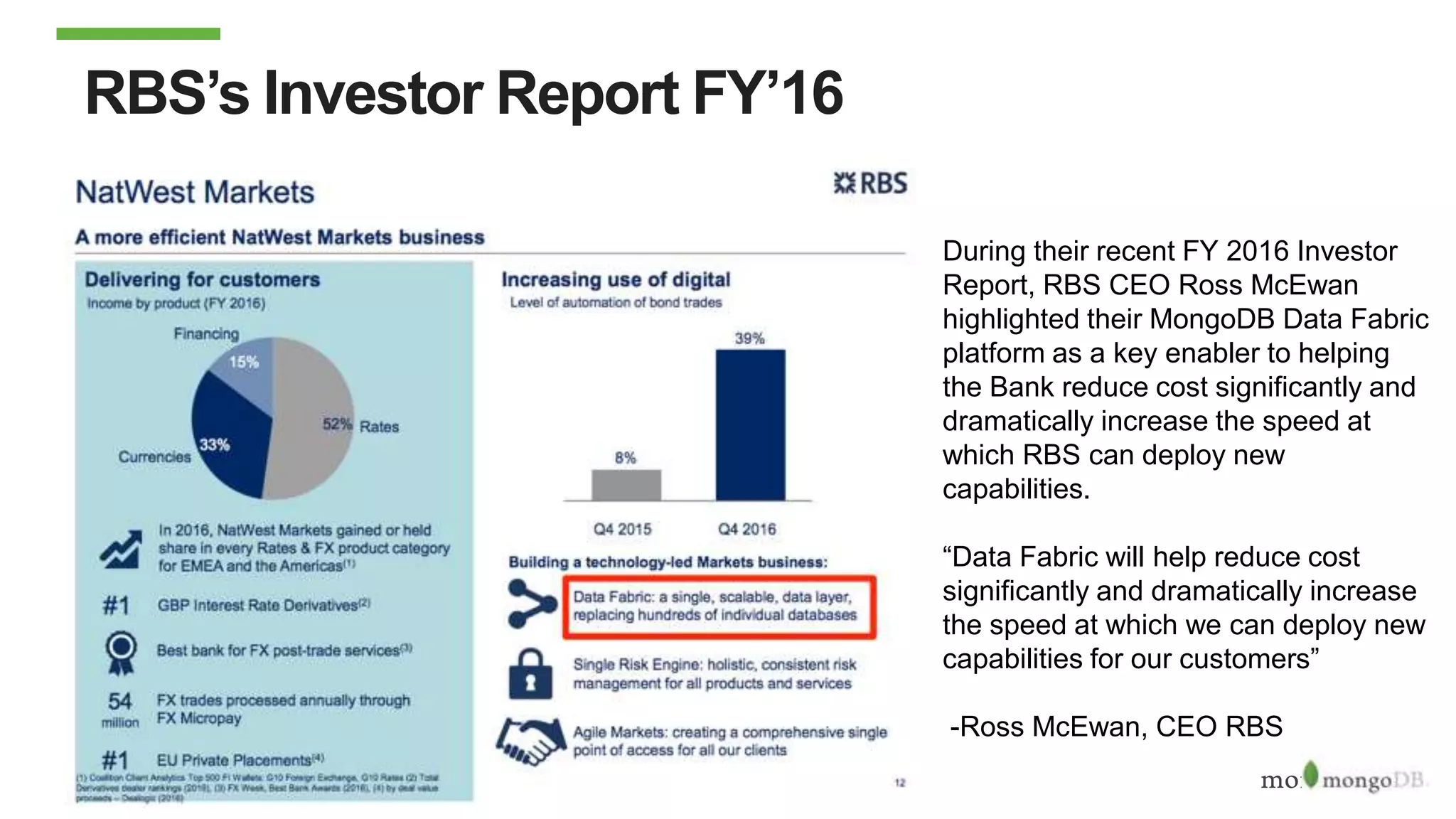
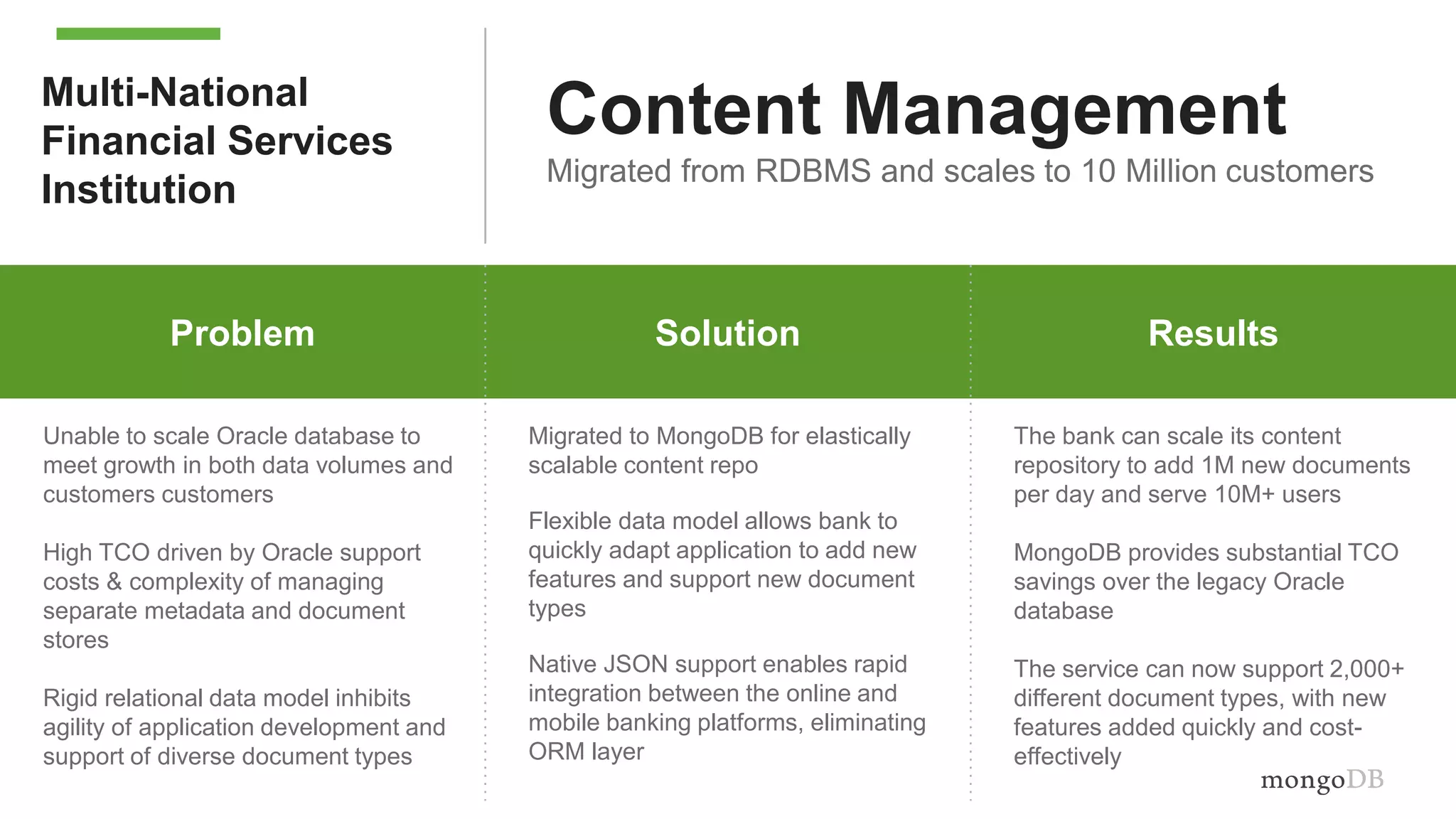
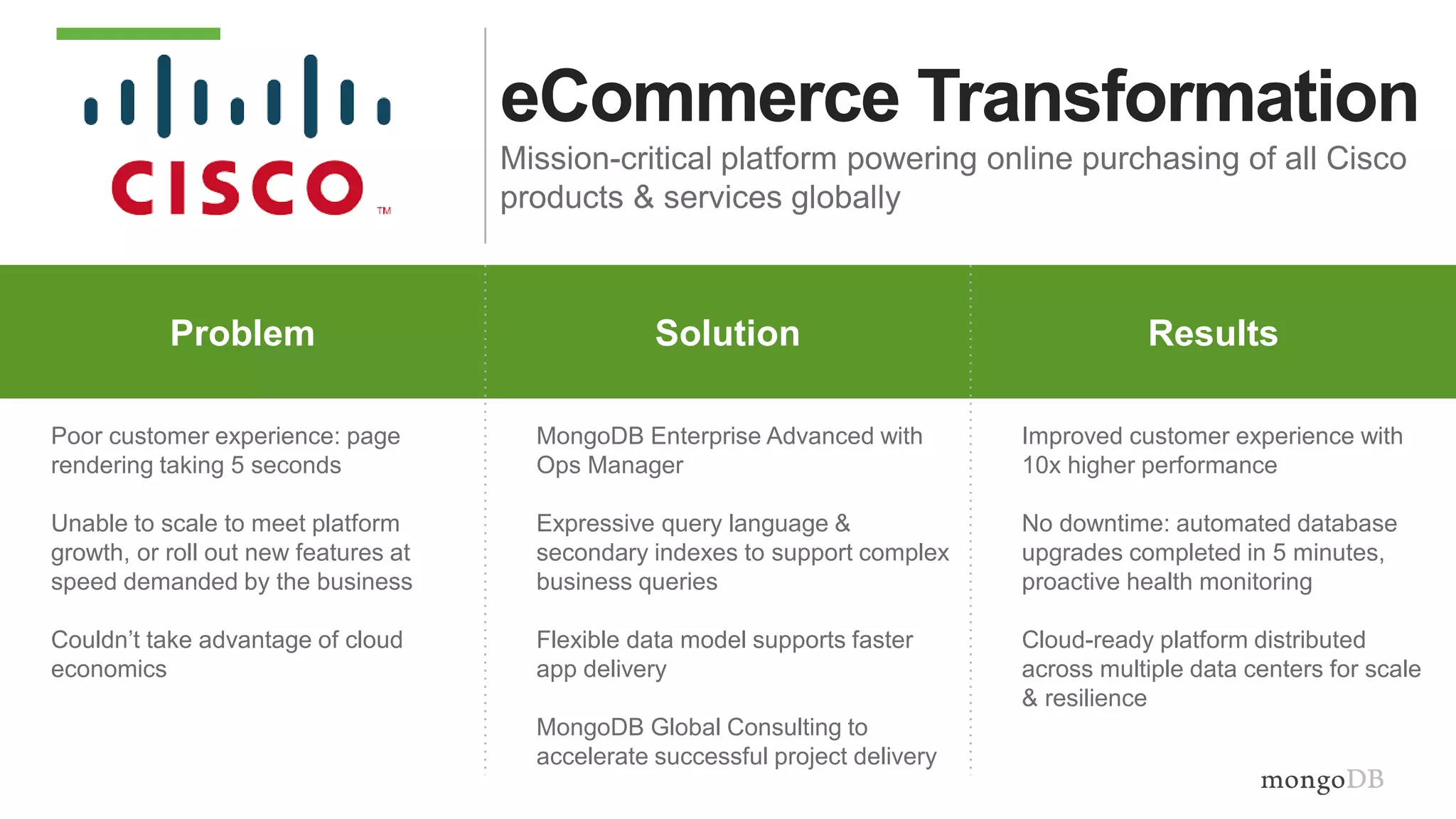
The document discusses using MongoDB to modernize mainframe systems by reducing costs and increasing flexibility. It describes 5 phases of mainframe modernization with MongoDB, from initially offloading reads to using MongoDB as the primary system of record. Case studies are presented where MongoDB helped customers increase developer productivity by 5-10x, lower mainframe costs by 80%, and transform IT strategies by simplifying technology stacks.