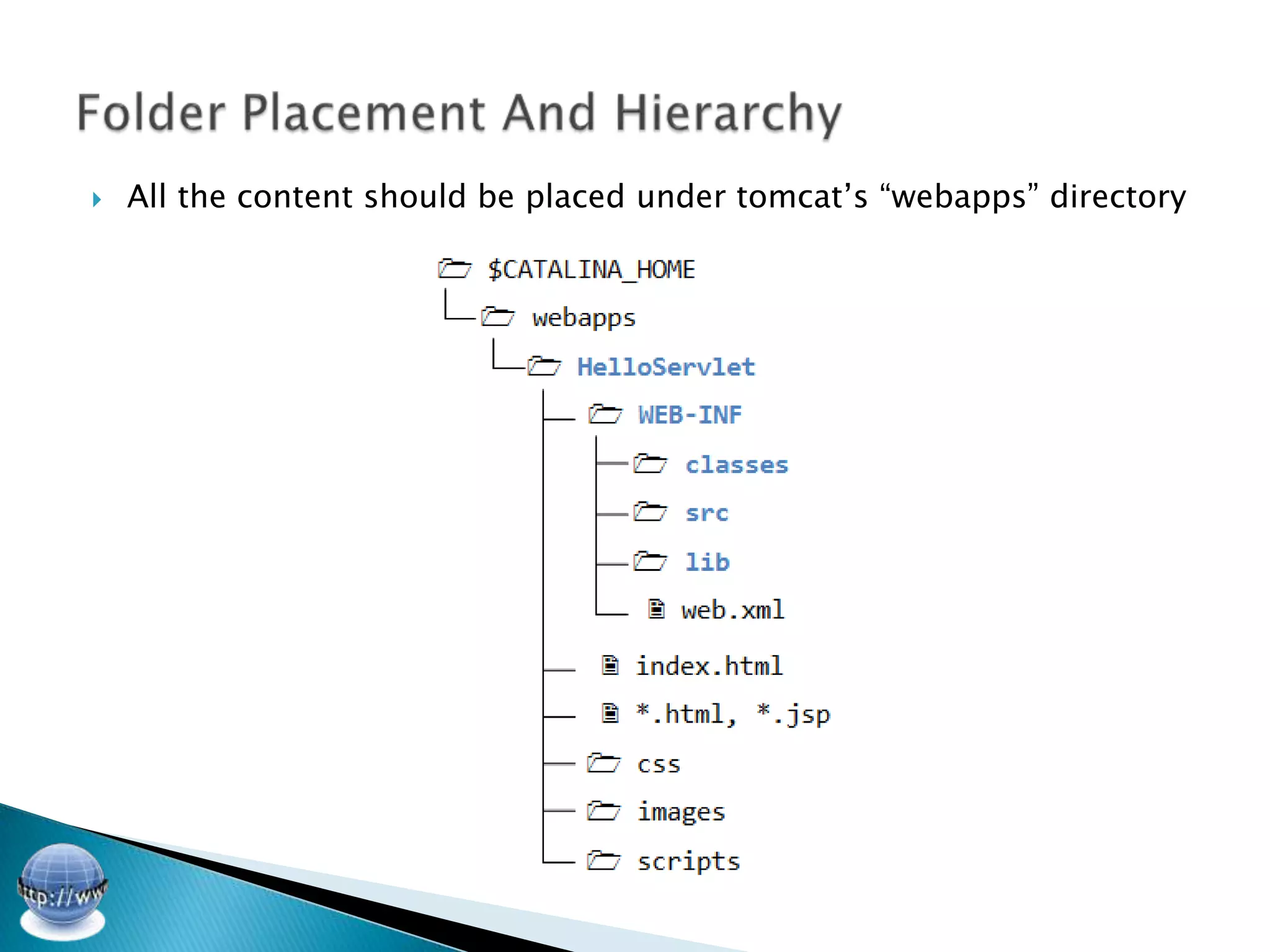
The document discusses various aspects of building a web application using Java including HTML forms, handling form data with servlets and requests/responses, connecting to a database using MySQL and its Java connector library, using the MVC pattern to manage database requests, and implementing user authentication with a login servlet that verifies credentials against a users table.










![private DatabaseManager(String hostName, String databaseName, String userName, String
password) {
super();
try {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(“jdbc:mysql://”);
builder.append(hostName)
.append("/").append(databaseName).append("?").append(PARAM_USER + "=" +
userName).append("&" + PARAM_PASSWORD + "=" + password);
Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”).newInstance();
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(builder.toString());
System.out.println("[DatabaseManager] Connection is created.");
}
catch (SQLException ex) { // handle any errors
System.out.println("SQLException: " + ex.getMessage());
System.out.println("SQLState: " + ex.getSQLState());
System.out.println("VendorError: " + ex.getErrorCode());
}
catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis274-formsandactions-120522160314-phpapp01/75/Web-Technologies-forms-and-actions-12-2048.jpg)
![private Connection conn;
private static DatabaseManager instance = null;
private static final boolean[] LOCK_INSTANCE = new boolean[]{};
public static DatabaseManager getInstance(String hostName, String databaseName,
String userName, String password) {
if (instance != null) { return instance; }
synchronized (LOCK_INSTANCE) { if (instance != null) { return instance; }
instance = new DatabaseManager(hostName, databaseName, userName, password);
return instance;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cis274-formsandactions-120522160314-phpapp01/75/Web-Technologies-forms-and-actions-13-2048.jpg)